Open thoracic surgical implantation of cardiac pacemakers in rats
John A. Rogers, Helen S. Knight, Rose T. Yin, Sheena W. Chen, K. Benjamin Lee, Yeon Sik Choi, Jahyun Koo, Quansan Yang, Michael A. Napolitano, Jokubas Ausra, Timothy J. Holleran, Jessica B. Lapiano, E. Alex Waters, Anlil Brikha, Grant Kowalik, Alana N. Miniovich, Bender A. Russo, Alexi Kiss, Alejandro Murillo-Berlioz, Tatiana Efimova, Chad R. Haney, Philipp Gutruf, Gregory D. Trachiotis, Igor R. Efimov















Extended
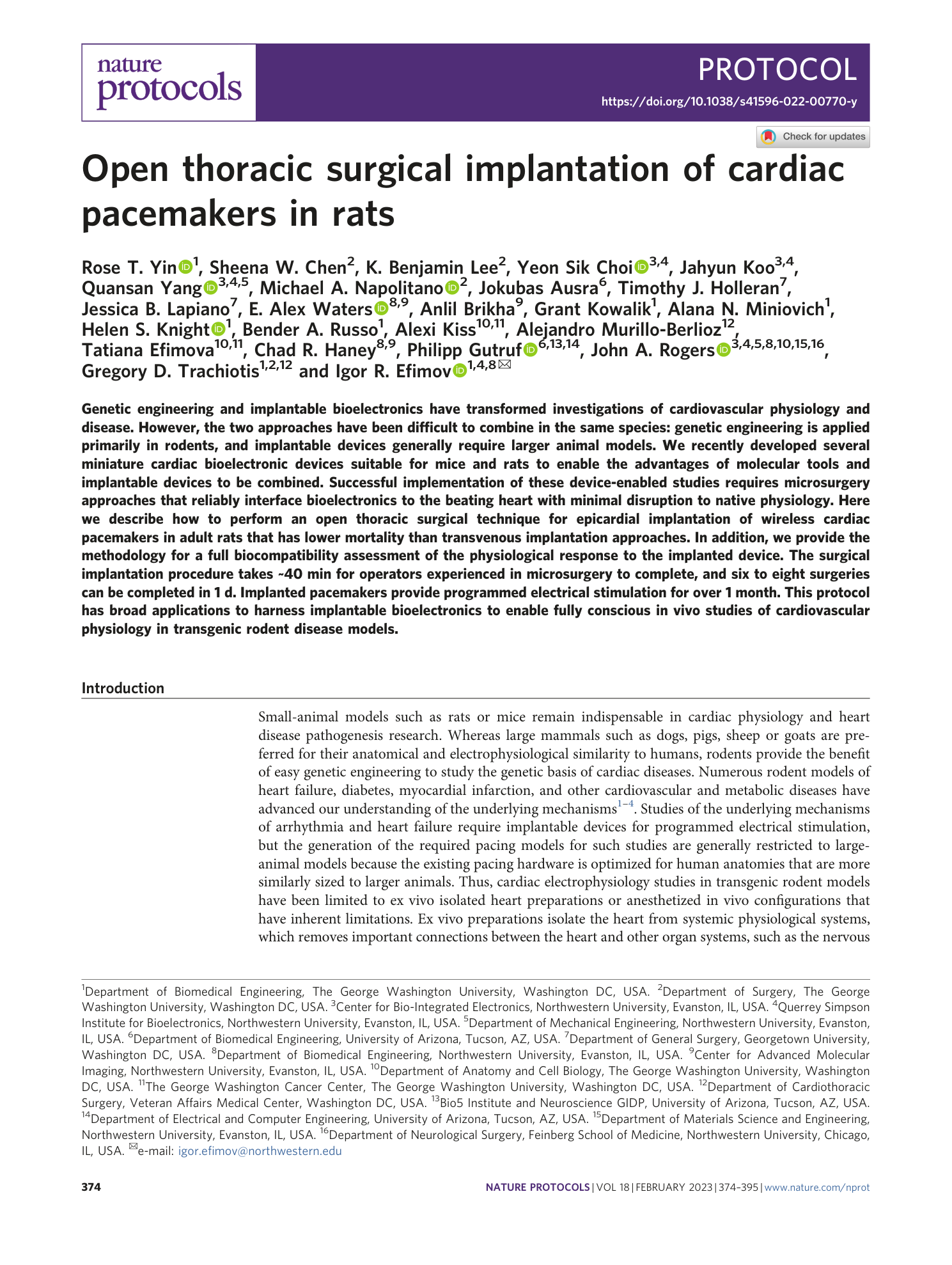
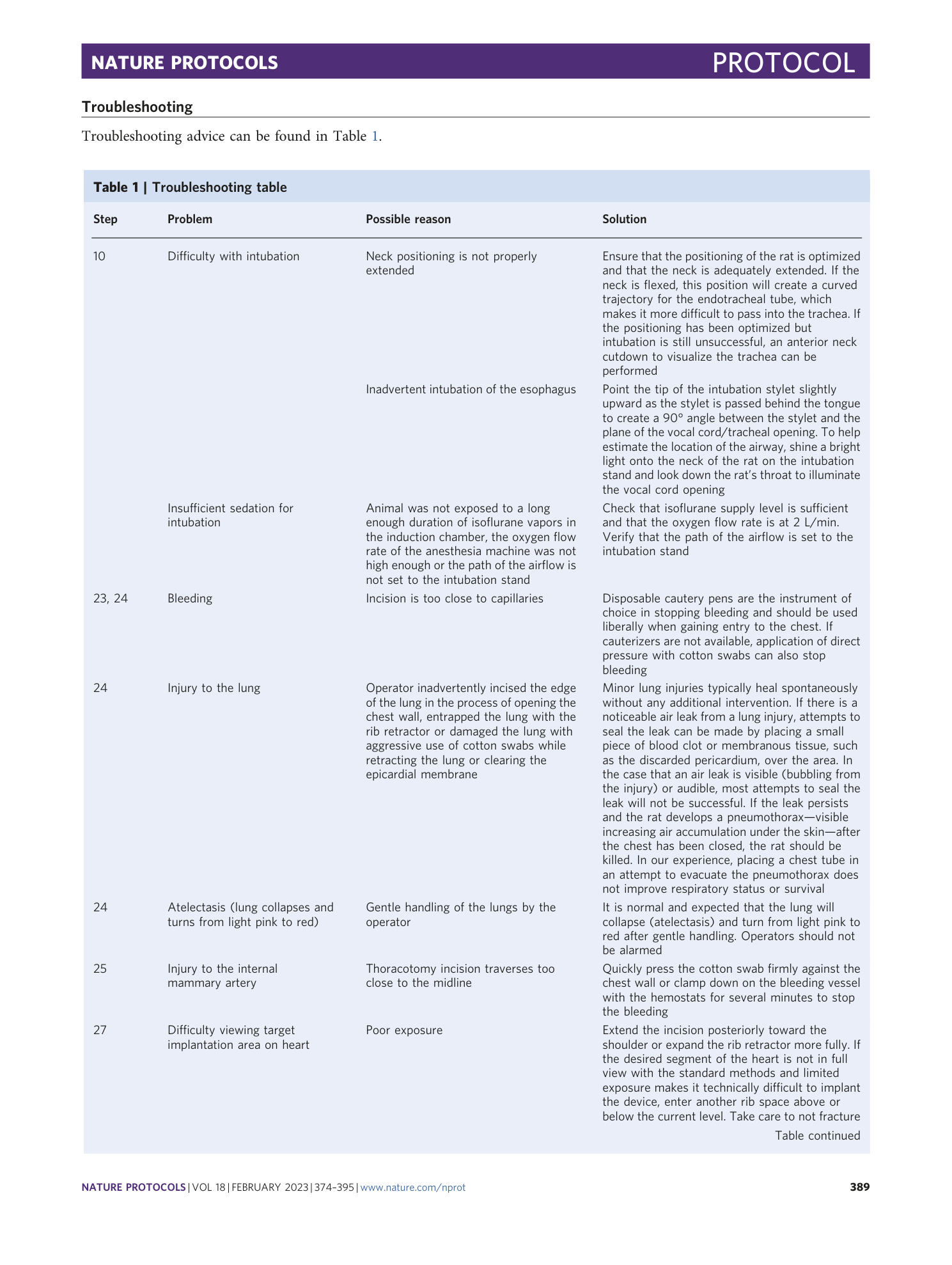
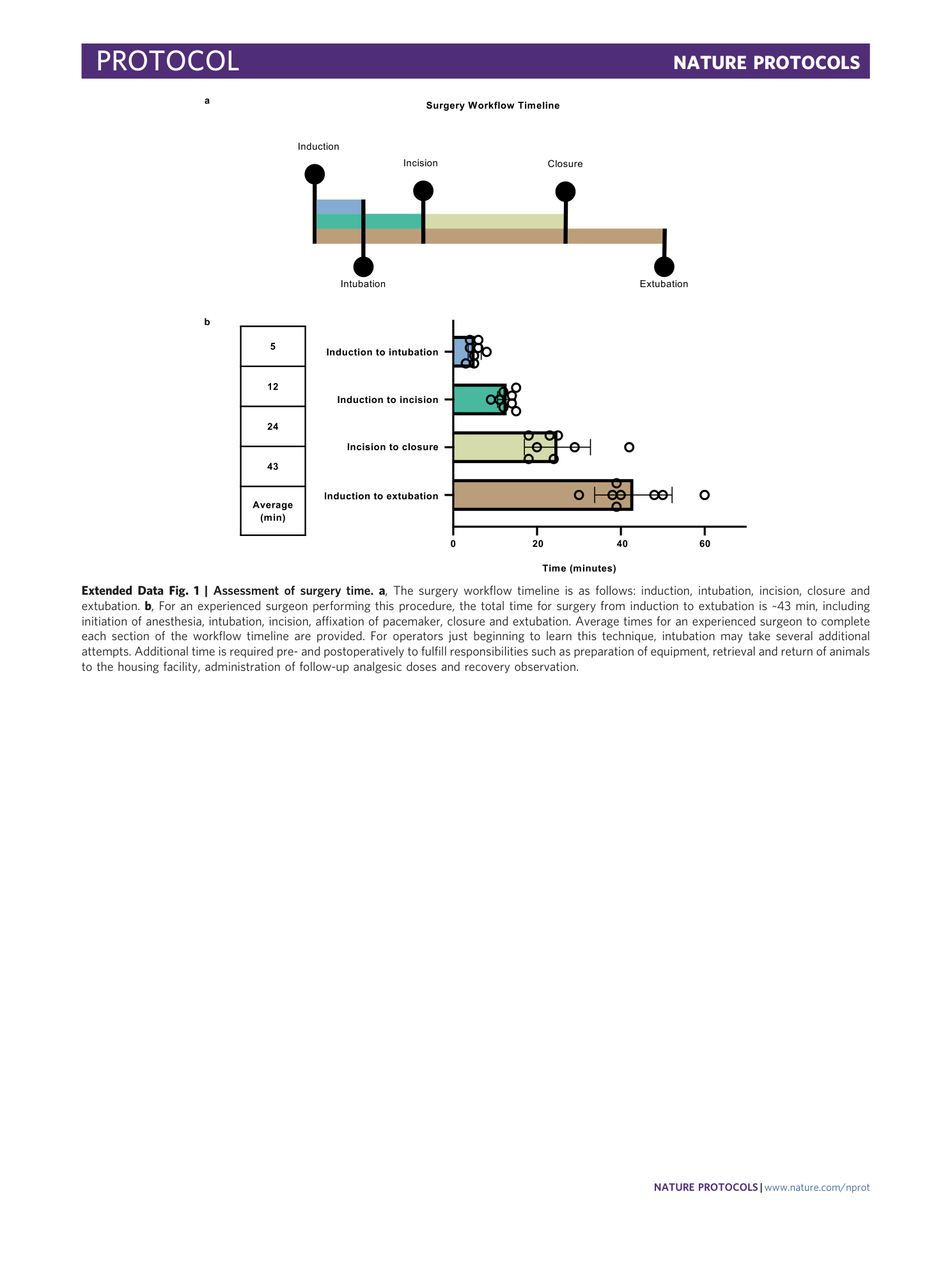
Extended Data Fig. 1 Assessment of surgery time.
a , The surgery workflow timeline is as follows: induction, intubation, incision, closure and extubation. b , For an experienced surgeon performing this procedure, the total time for surgery from induction to extubation is ~43 min, including initiation of anesthesia, intubation, incision, affixation of pacemaker, closure and extubation. Average times for an experienced surgeon to complete each section of the workflow timeline are provided. For operators just beginning to learn this technique, intubation may take several additional attempts. Additional time is required pre- and postoperatively to fulfill responsibilities such as preparation of equipment, retrieval and return of animals to the housing facility, administration of follow-up analgesic doses and recovery observation.
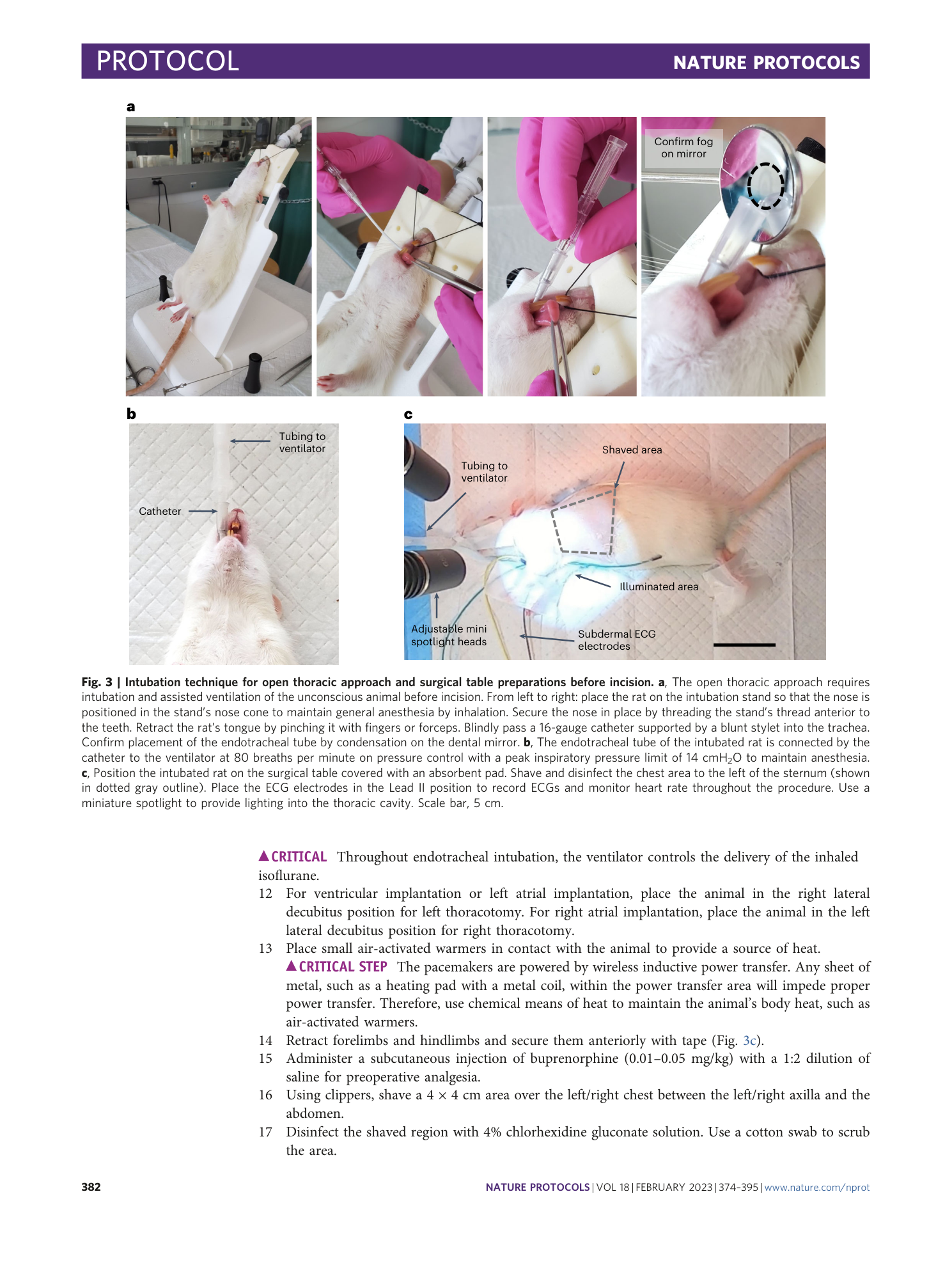
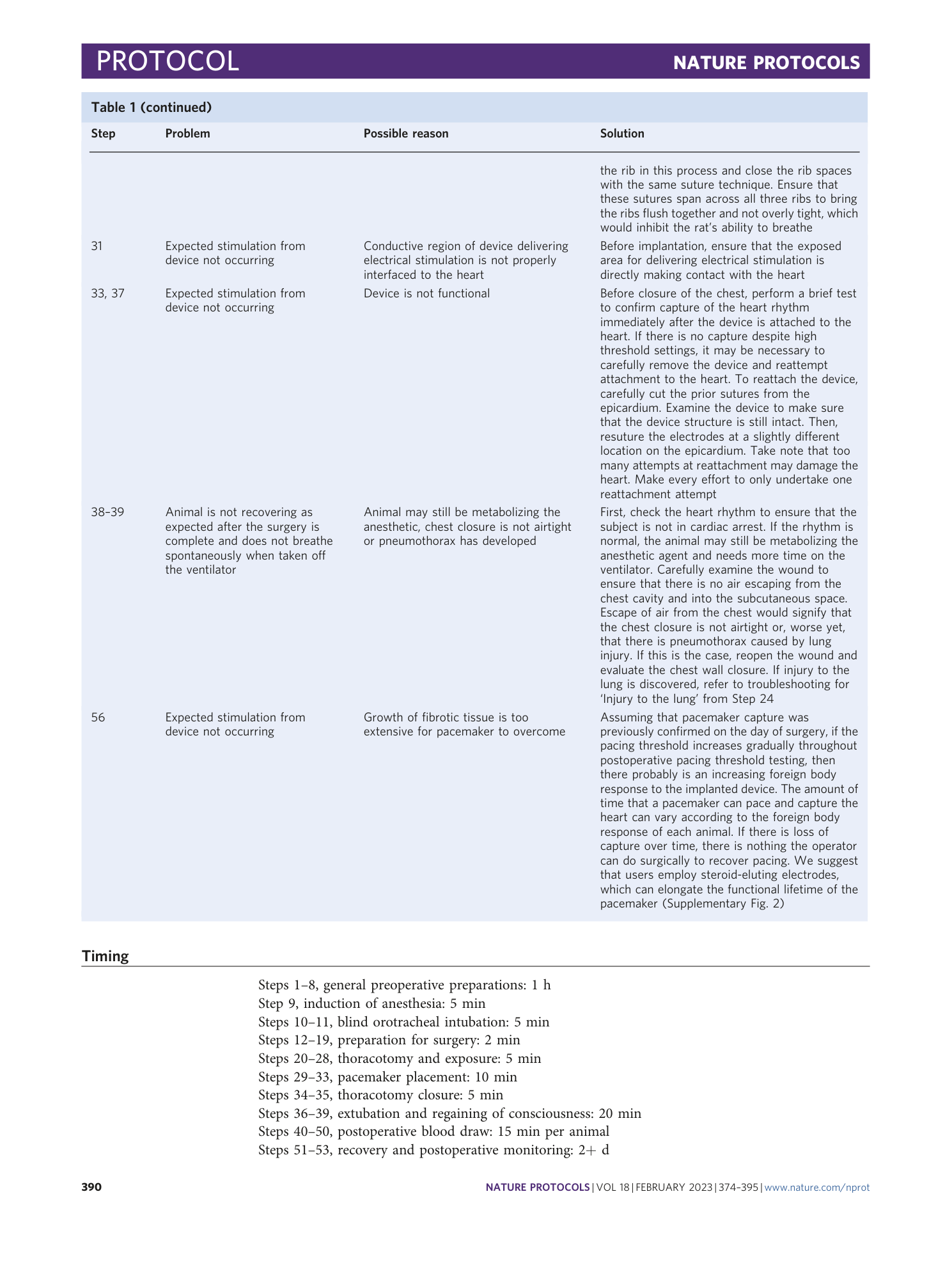
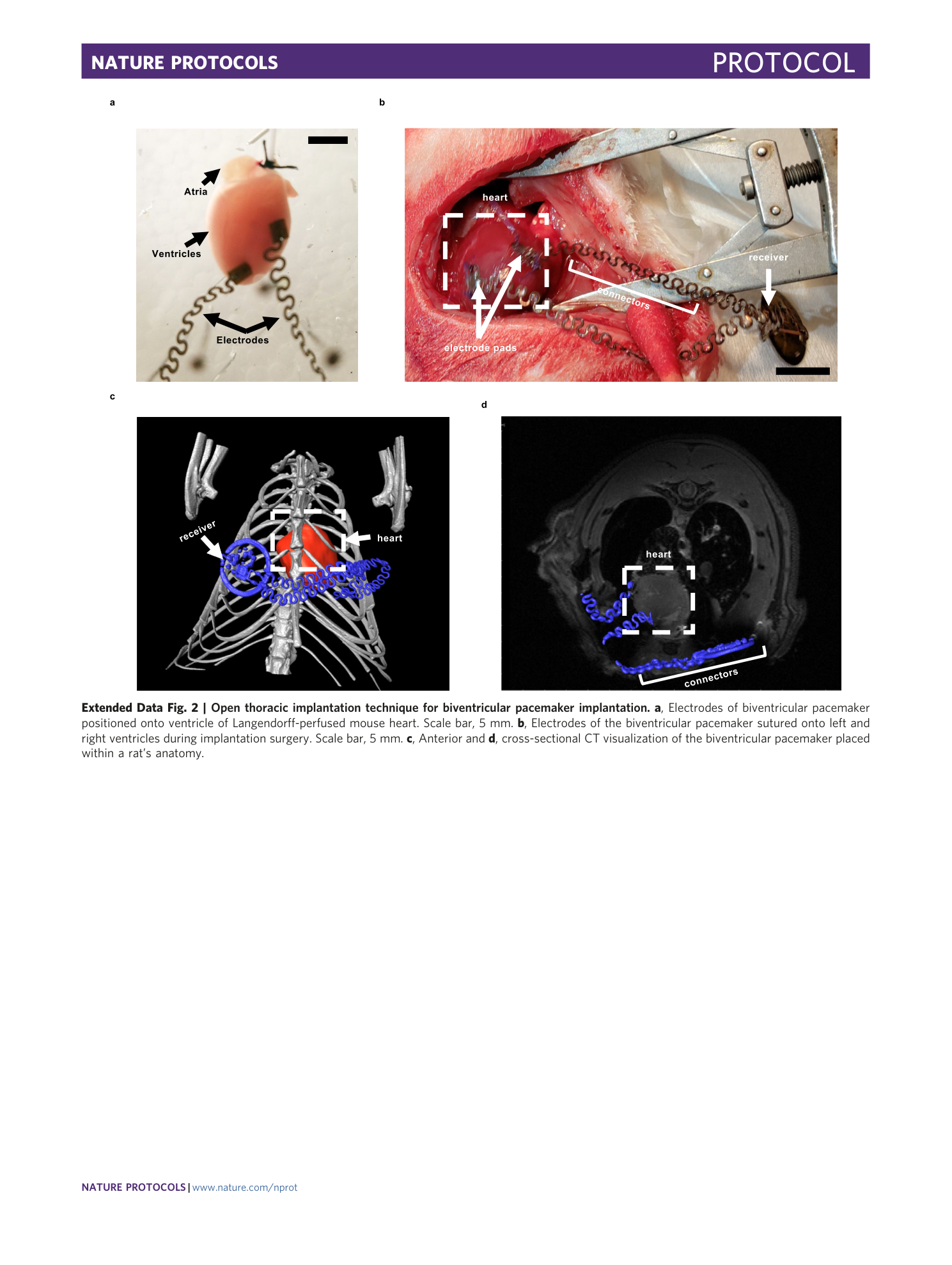
Extended Data Fig. 2 Open thoracic implantation technique for biventricular pacemaker implantation.
a , Electrodes of biventricular pacemaker positioned onto ventricle of Langendorff-perfused mouse heart. Scale bar, 5 mm. b , Electrodes of the biventricular pacemaker sutured onto left and right ventricles during implantation surgery. Scale bar, 5 mm. c , Anterior and d , cross-sectional CT visualization of the biventricular pacemaker placed within a rat’s anatomy.
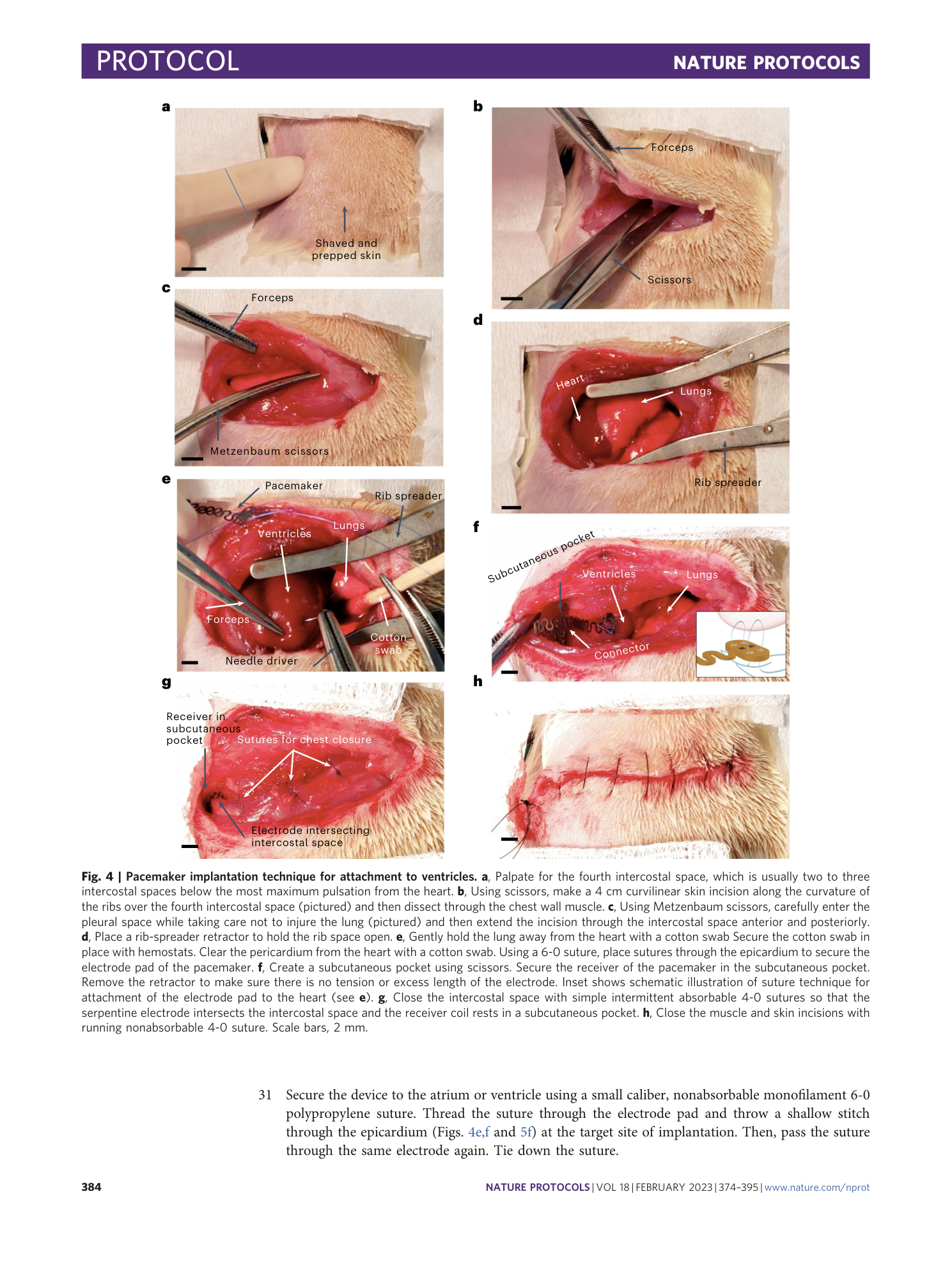
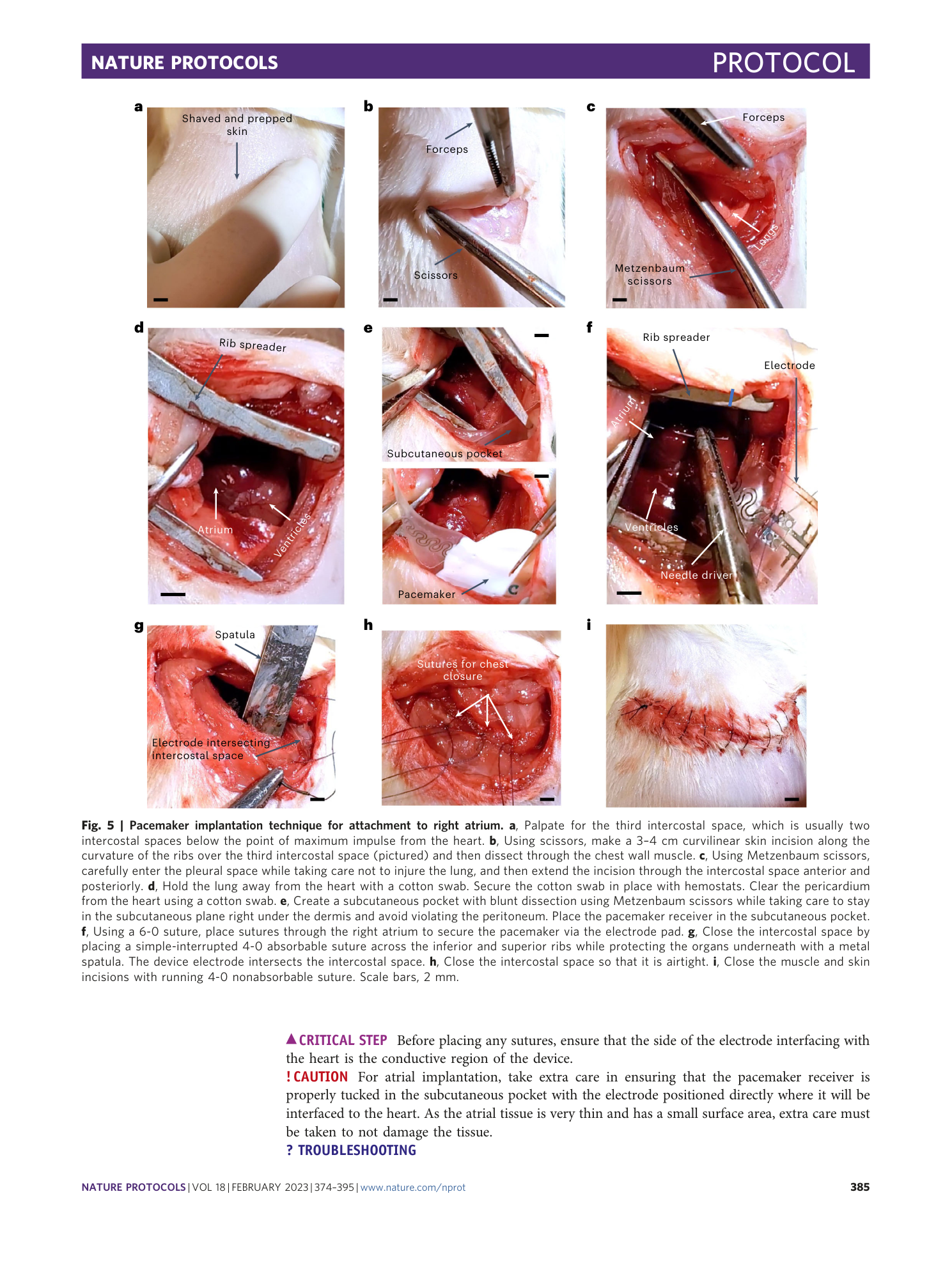
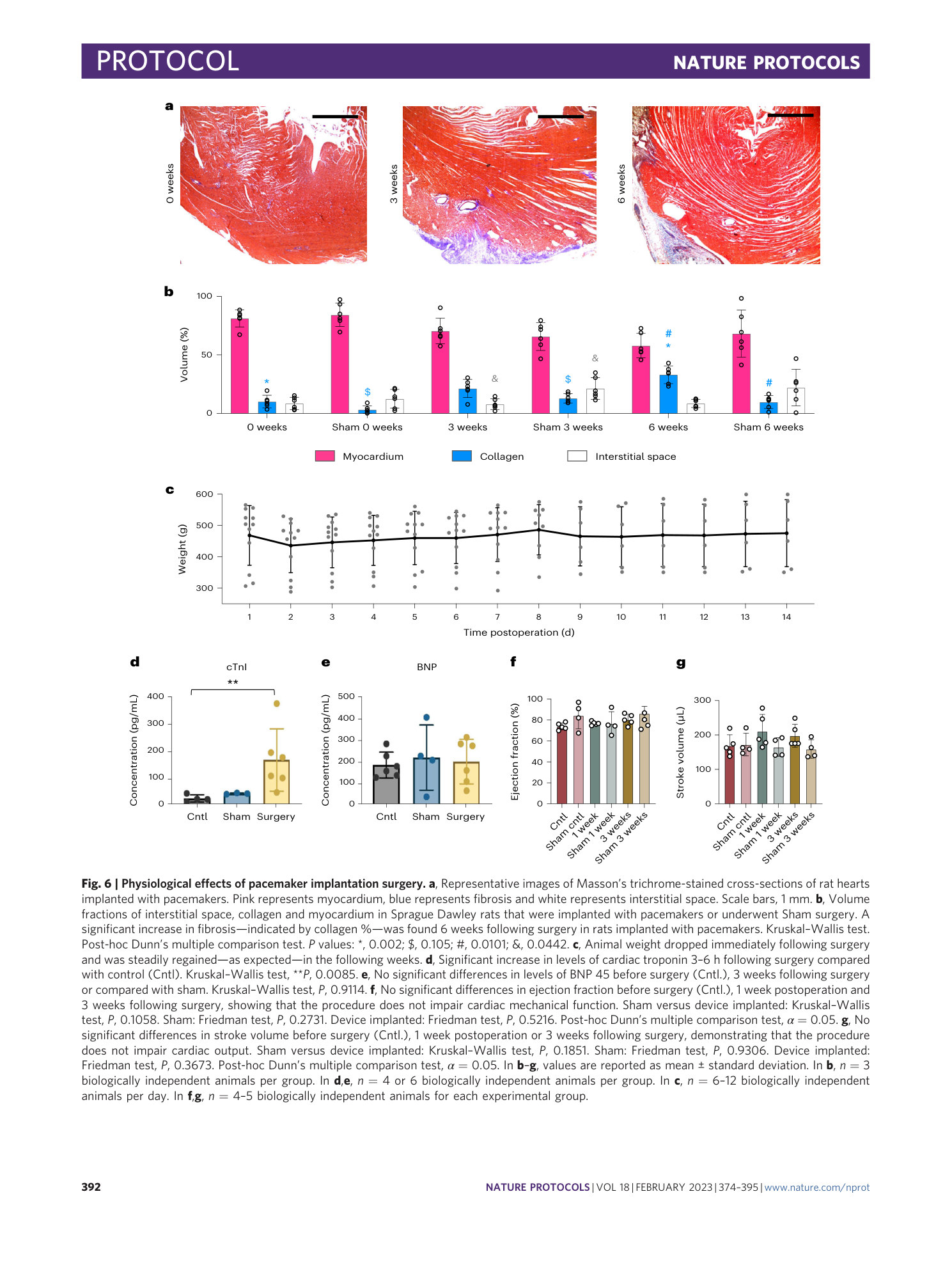
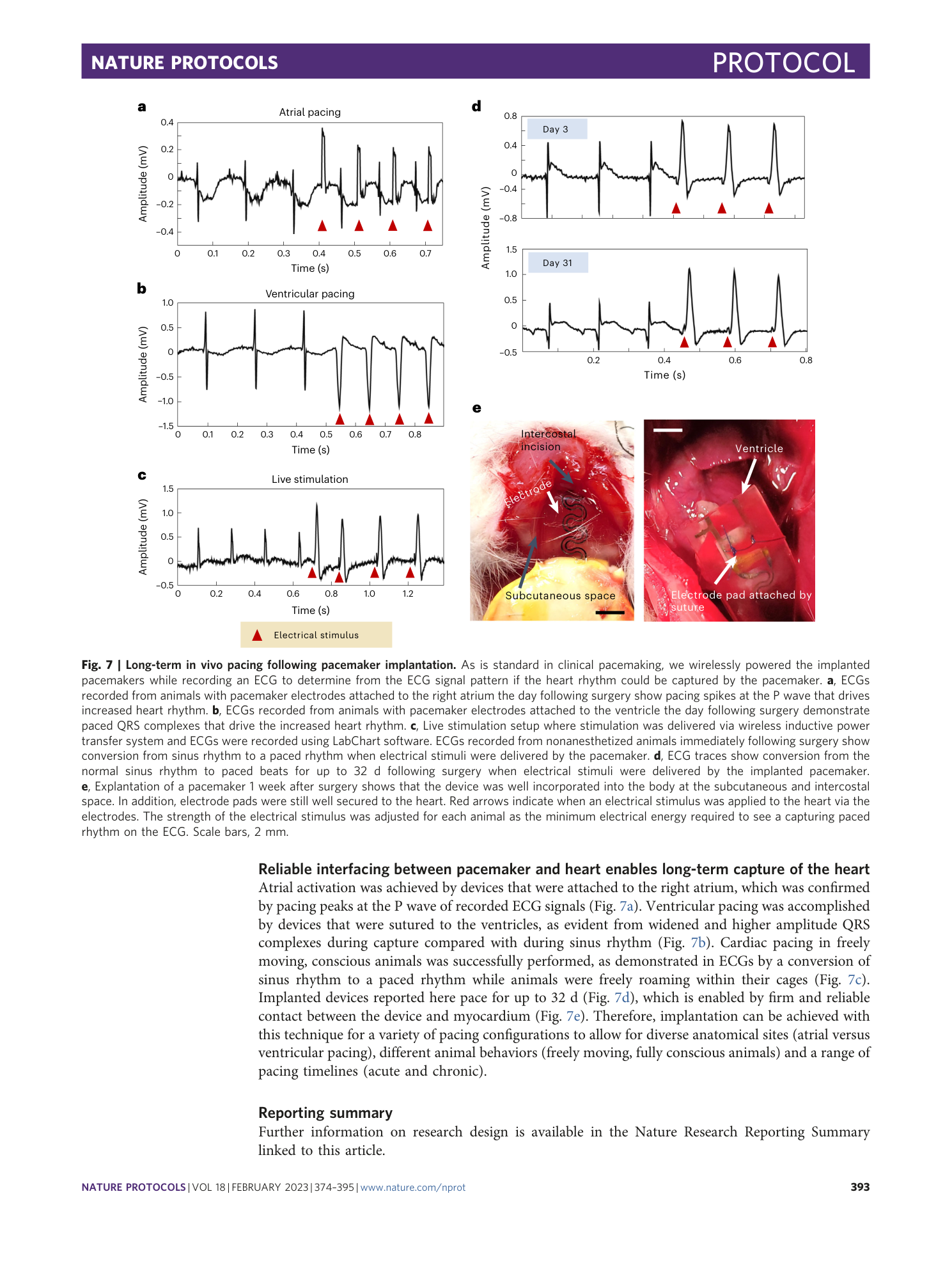
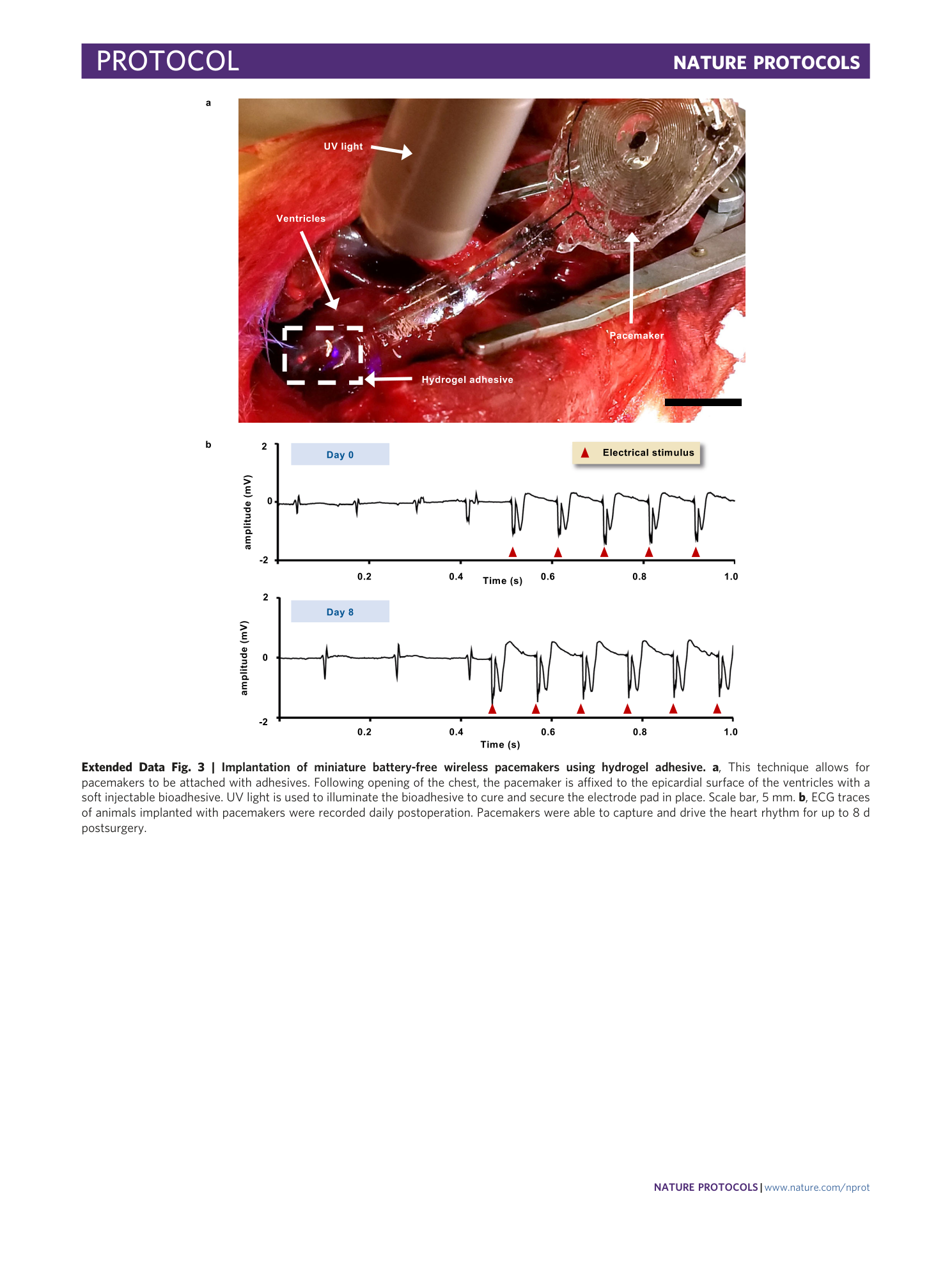
Extended Data Fig. 3 Implantation of miniature battery-free wireless pacemakers using hydrogel adhesive.
a , This technique allows for pacemakers to be attached with adhesives. Following opening of the chest, the pacemaker is affixed to the epicardial surface of the ventricles with a soft injectable bioadhesive. UV light is used to illuminate the bioadhesive to cure and secure the electrode pad in place. Scale bar, 5 mm. b , ECG traces of animals implanted with pacemakers were recorded daily postoperation. Pacemakers were able to capture and drive the heart rhythm for up to 8 d postsurgery.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–6.
Reporting Summary
Supplementary Data 1
Raw data of surgery mortality rate relating to operator experience
Supplementary Data 2
Raw data on functional lifetime of pacemakers in all rat subjects
Supplementary Data 3
Raw data of systemic assessment of animal behavior, appearance, and reactivity to handling
Supplementary Data 4
Raw data of ELISA assessment of BNP 45 for rats with pacemakers attached to the atrium
Supplementary Data 5
Raw data of ELISA assessment of CK-MB for rats with pacemakers attached to the ventricles
Supplementary Data 6
Raw data of echocardiography parameters (fractional shortening, cardiac output, diastolic volume, diastolic diameter, systolic volume, and systolic diameter)

