Static Incubation of Pancreatic Islets
Islet and Pancreas Analysis Core
Abstract
This SOP defines the methods used by the Vanderbilt Diabetes Center Islet and Pancreas Analysis (IPA) Core for static incubation of pancreatic islets isolated from mouse or human tissue. See also our islet isolation protocol.
Steps
Reagent preparation
RPMI with 5.6 mM glucose (cell culture media):
- Remove 5 mL from a 500 mL bottle of RPMI, and add 5 mL penicillin/streptomycin. Close bottle and invert to mix.
- Add 0.505 g glucose to RPMI, invert to mix, and incubate at room temperature for
1h 0m 0sto allow glucose to go into solution. - In a BSL-2 culture hood, vacuum filter 450 mL RPMI.
- Add 50 mL FBS.
Note
Once made, media can be stored at 4°C for up to 1 month.
DMEM (static incubation media):
Add the following ingredients into a 1 L Erlenmeyer flask.
- 8.28 g DMEM
- 3.2 g sodium bicarbonate
- 0.58 g L-gutamine
- 1.11 g HEPES
- 0.11 g sodium pyruvate
- 1 g bovine serum albumin
- 70 mg ascorbate
- 1 L deionized water
Place a stir bar into the flask and situate on top of a magnetic stir plate. Stir at medium-high speed for 0h 15m 0s to allow all ingredients to go into solution.
Aliquot 500 mL of DMEM media into each of 2 plastic storage bottles to make 5.6 mM glucose and 16.7 mM glucose solutions.
DMEM with 5.6 mM glucose:
- Add 0.505 g glucose to 500 mL prepared DMEM media.
- Incubate for
1h 0m 0sto allow glucose to go into solution. - Vacuum-filter media.
DMEM with 16.7 mM glucose:
- Add 1.504 g glucose to 500 mL prepared DMEM media.
- Incubate for
1h 0m 0sto allow glucose to go into solution. - Vacuum-filter media.
Acid ethanol (for hormone extraction):
- Pipet 5.5 mL 95% ethanol into a 15 mL conical tube.
- Add 50µL hydrochloric acid.
- Invert to mix.
Static incubation
Pipet 5 mL RPMI with 5.6 mM glucose into each of two 6-cm cell culture dishes.
Using an electronic pipette and an inverted microscope, pass islets into the first plate, and then into the second.
Place islets into a 37°C cell culture incubator with 5% CO2 and leave overnight for a minimum of 18h 0m 0s.
Pipet 5 mL of DMEM with 5.6 mM glucose into a 6-cm cell culture dish.
Using an electronic pipette and an inverted microscope, transfer islets from overnight incubation plate (step 6) into the 6-cm plate with DMEM media. Islets will be picked from this plate and placed into the 12-well static incubation plate described in steps 9-10.
Label a 12-well plate for static incubation according to your experimental design. In the example below, two conditions are shown, low glucose (5.6 mM) and high glucose (16.7 mM). These conditions can be repeated in subsequent rows and/or plates for biological replicates as desired.
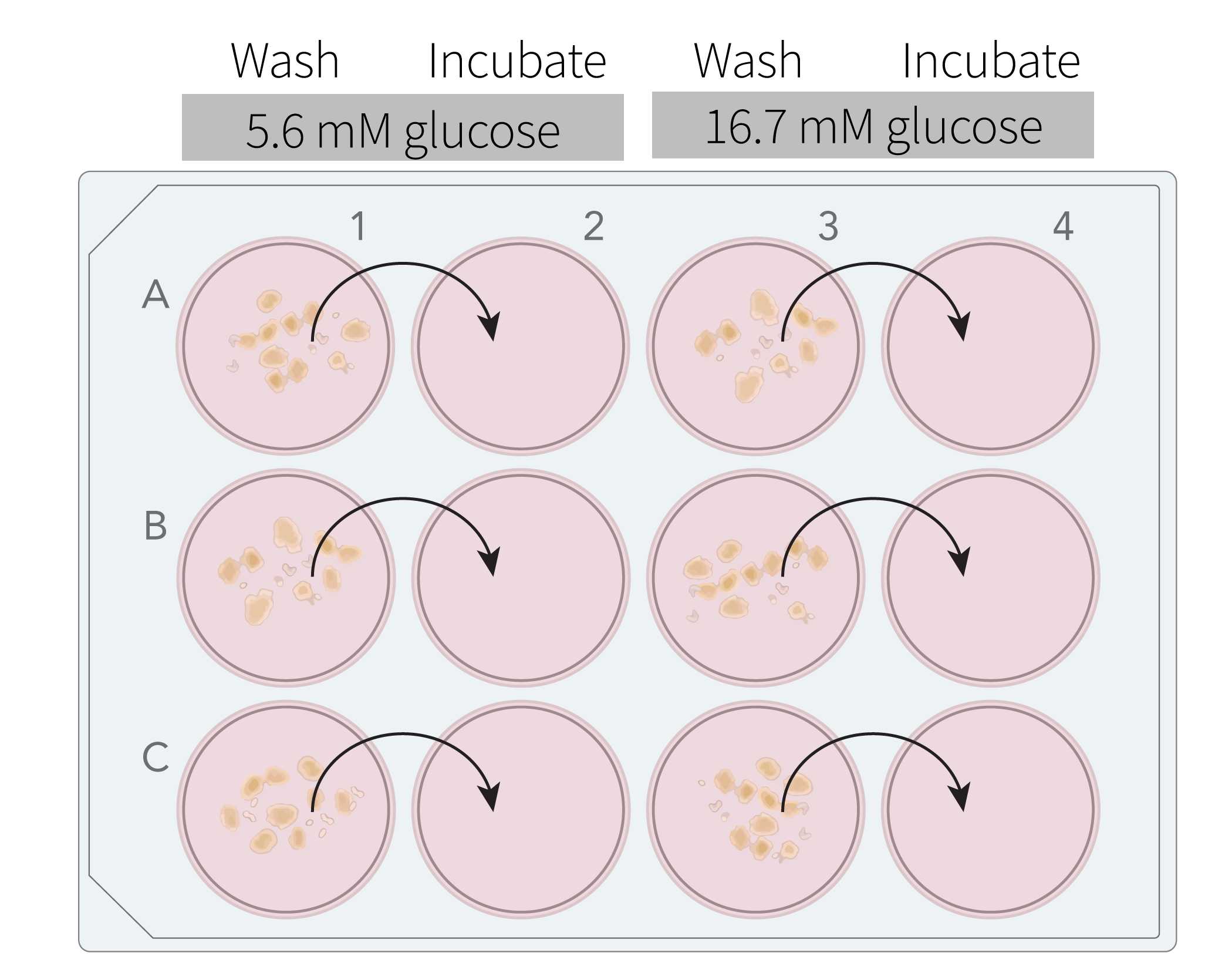
Pipet 2 mL of the appropriate media into each well. Note that each condition requires two wells , a "wash" well and an "incubation" well.
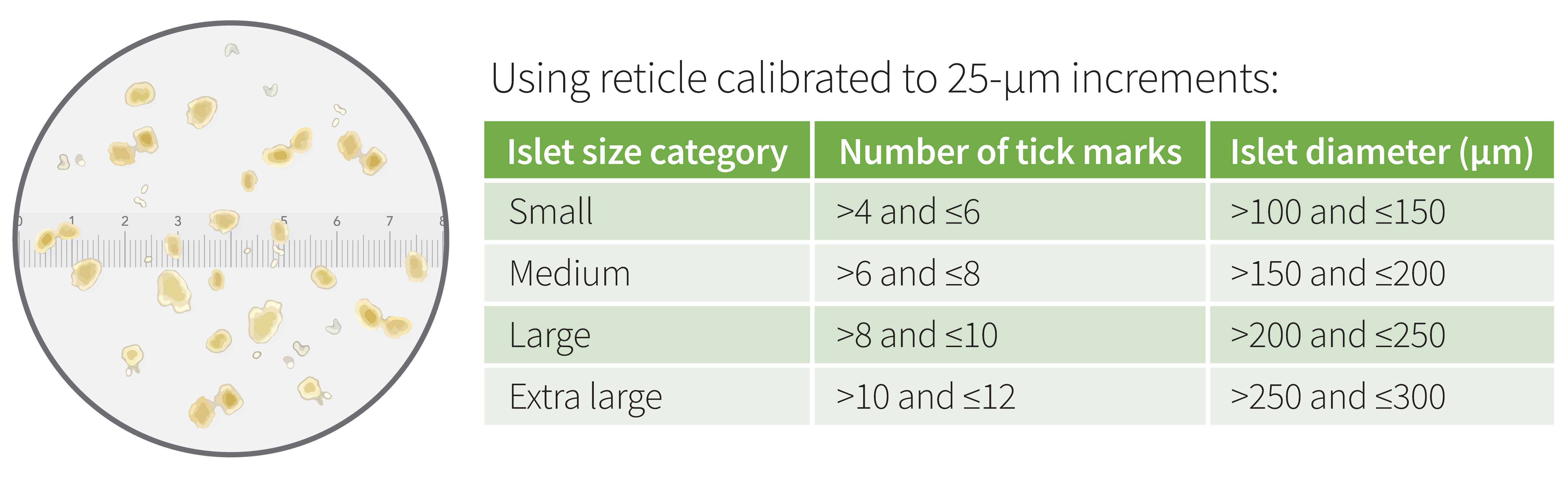
Under microscope guidance, place around 20 islet equivalents (IEQs) into each wash well. This is typically a combination of 12 small, 5 medium, and 2 large islets. Use the chart below to measure islet sizes.
Once islet aliquots have been distributed to wash wells, place the 12-well plate onto the stereomicroscope stage, swirl the plate to move islets to center of each well, and transfer the islets into the subsequent incubation wells. Use no more than 20 µL media for the transfer to avoid dilution of culture media.
Cover the 12-well plate and place in 37°C incubator with 5% CO2 for 1h 10m 0s.
Media collection and hormone extraction
Remove plate from incubator and place on ice to cool down for 0h 10m 0s. During this time, label two 2-mL microcentrifuge tubes for each incubation well (islet aliquot): the first for islet extract and the second for media.
Return plate to the stereomicroscope stage, swirl the plate to move islets to center of each well, and pipet the islets in each incubation well into the first of each pair of labeled microcentrifuge tubes.
Centrifuge the islet tubes for 0h 3m 0s at 200rcf,0h 0m 0s.
Remove supernatant from islet pellets, and add 200 µL acid ethanol to each tube.
Transfer islet extract tubes to 4°C to begin incubation for 24h 0m 0s. Meanwhile, proceed to step 18.
After islets are removed, transfer 1.5 mL media from each incubation well into the second of each pair of labeled microcentrifuge tubes. Store at -20°C.
Following the 24h 0m 0s incubation in step 17, spin down islet extract tubes for 0h 5m 0s at 3000rcf,0h 0m 0s.
Transfer three 50-µL supernatant aliquots from each islet extract tube into prelabeled 2-mL screwcap tubes and store at -80°C.
Perform hormone assay of your choice.

