Microbiome DNA Enrichment for Fecal -seq using the the NEBNext Microbiome DNA Enrichment Kit manual (New England Biolabs cat. #E2612S)
Juliet Bonnevie
Abstract
This protocol is taken from the Scientific Report "Methylation-based enrichment facilitates low-cost, noninvasive genomic scale sequencing of populations from feces"
Chiou, K.L., Bergey, C.M. Methylation-based enrichment facilitates low-cost, noninvasive genomic scale sequencing of populations from feces. Sci Rep 8, 1975 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20427-9
Portions of this protocol are modified from the NEBNext Microbiome DNA Enrichment Kit manual (New England Biolabs cat. #E2612S)
Portions of Auxiliary Protocol A (Step 35) are modified from Pacific Biosciences protocol #001-252-177-03.
This full protocol and other supplementary information can be found here:
Before start
Steps
Before Beginning
Extract and prepare DNA samples
While any fecal DNA (fDNA) extraction method should in principle be compatible with the MBD enrichment, methods that maximize the recovery of host DNA are preferable. Bead-beating methods that increase total DNA yield from feces, for example, should be avoided because the mechanical disruption increases the yield of cell-wall-bound DNA (i.e., from bacteria or plants) while fragmenting host DNA.
It is suggested to aim for a total yield of 1 µg of DNA for all samples in a maximum volume of 30 µl each, although there has been success with as little as 500 ng (the yield of host DNA is likely more important than the yield of total fDNA). If the volume is greater than 30 µl, the DNA can be concentrated via a bead cleanup (Auxiliary protocol A: Step 35 - 45).
Prior to enrichment, DNA should be quantified for the total yield (e.g., by fluorometer or spectrophotometer). Ideally, the host DNA should be quantified by qPCR (Auxiliary protocol B: Step 46 - 49).
Calculate the required volume of MBD2-Fc-bound magnetic beads (hereafter referred to as "MBD beads") for each enrichment reaction, as well as the total volume for a set of reactions as follows.
As an approximate rule, prepare 1µL of MBD beads for every 6.25ng of target host DNA in each enrichment reaction. If samples contain less than 6.25 ng of host DNA or if the amount of host DNA is not quantified, prepare 1 µl of MBD beads.
It is recommend to prepare batches of MBD beads (see Step 5) with a minimum volume of 40µL, as lower volumes preclude adequate mixing. If a smaller volume is needed, leftover unused MBD beads can be stored at 4°C for up to a week.
Resuspend protein A magnetic beads by gently pipetting the mixture up and down until the suspension is homogenous, or by slowly rotating the mixture at 4°C for 0h 15m 0s.
Do not vortex.
Prepare 1X bind/ wash buffer by diluting 1 part 5X bind/ wash buffer with 4 parts DNase-free water. As a general rule, the volume of 2X bind/ wash buffer needed can be calculated as:
2.5 ml +1.2 ml x [number of enrichment reactions]
Then amount of 1X bind/ wash buffer depends on the total volume of MBD beads and the total number of enrichment reactions. MBD beads can be prepared with a maximum volume of 160 µl in a single reaction. As very small volumes (1 - 8 µl) of beads are needed for enrichment method, a single bead preparation reaction is nearly always sufficient. If more beads are needed increase the number of bead preparation reactions and adjust the volume of 1X bind/ wash buffer accordingly. Alternatively, for volumes up to 320 µl, prepare an additional 1 ml of 1X bind/ wash buffer per bead preparation reaction and add an extra wash step (see Step 14).
2.5 ml of 1X bind/ wash buffer are required for a single bead preparation reaction up to 160 µl. Prepare an additional 1.2 ml of 1X bind/ wash buffer per enrichment reaction. This number takes into account the volume needed to prepare 2 M NaCl elution buffer in the following step
Keep 1X bind/ wash buffer on ice throughout the MBD bead preparation. For the wash steps following the capture reaction, 1X bind/ wash buffer can be at room temperature.
Prepare 2 M NaCl elution buffer by diluting 5 M NaCl with 1X bind/ wash buffer. 100µL of 2 M NaCl elution buffer are needed per enrichment reaction.
1X bind/ wash buffer has a NaCl concentration of 150 mM. 1 ML OF 2 M NaCl elution buffer can be prepared by adding 370µL of 5 M NaCl with 630µL of 1X bind/ wash buffer.
Preparing MBD Beads
If preparing 40 µl of MBD beads, add 4µL of MBD2-Fc protein to 40µL of protein A magnetic beads in a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube. For preparing other volumes ( n µl) of MBD beads, add n/ 10 µl MBD2-Fc protein to n µl of protein A magnetic beads.
As a rule, do not prepare less than 40 µl of MBD beads due to diminished efficiency of both rotational mixing and magnetic separation at low volumes
Mix the bead-protein mixture by rotating the tube in a rotating mixer for 0h 10m 0s at room temperature.
Briefly spin the tube and place on the magnetic rack for 0h 2m 0s - 0h 5m 0s or until the beads have collected to the wall of the tube and the solution is clear.
Carefully remove the supernatant with a pipette without disturbing the beads.
Add 1mL of 1X bind/ wash buffer (kept on ice) to the tube to wash the beads. Pipette up and down a few times to mix.
Mix the beads by rotating the tube in a rotating mixer for 0h 3m 0s at room temperature.
Briefly spin the tube and place on the magnetic rack for 0h 2m 0s - 0h 5m 0s or until the beads have collected to the wall of the tube and the solution is clear.
Carefully remove the supernatant with a pipette without disturbing the beads.
Repeat steps 10-13
If preparing between 160 µl and 320 µl of beads, repeat steps 10-13 twice for a total of three washes to ensure the removal of unbound MBD2-Fc protein.
Remove the tube from the rack and add n µl (determined in Step 6) of 1X bind/ wash buffer to resuspend the beads. Mix by pipetting the mixture up and down until the suspension is homogenous.
Capture Methylated Host DNA
Since reaction volumes are well under 100 µl, multiple enrichment reactions can be processed together in a microplate, with pipetting steps conducted using a multichannel pipettor. Compatible rotating mixers and magnetic separators would also be required. Here, the capture procedure using a 1.5 ml tube is described.
The total volume of the capture reaction is an important consideration. A decreased DNA binding efficiency when the concentration of MBD beads or DNA in the capture reaction is low has been observed. It is therefore recommended maintaining a total reaction volume of approximately 40 µl, as a consistent success with this volume even when adding as little as 1 µl of MBD beads has been experienced. Decreasing the reaction volume may result in decreased efficacy of rotational mixing. It is a good idea to keep the volume of all reaction consitent as this facilitates processing of many samples and, if DNA amounts and bead volumes are kept consistent, serves as a control for the effects of bead or DNA concentration on enrichment efficiency. Subsequent procedures assume a reaction volume of 40 µl (not including MDB beads). If using other reaction volumes, pay particular attention to notes following each step in this section.
Aliquot 8µL of 5X bind/ wash buffer to a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube.
For reaction volumes other than 40 µl, tube the volume of 5X bind/ wash buffer to maintain 1X concentration and adjust accordingly the volume of DNase-free water added in Step 18. The volume of MBD beads should be excluded from this calculation as prepared MBD beads are already at 1X concentration.
It is recommend to equilibrate 5X bind/ wash buffer to room temperature prior to aliquoting for more accurate pipetting.
Add up to 30µL of DNA (prepared in Step 1) to the tube. Bring the total volume to 40µL with DNase-free water.
For reaction volumes other than 40 µl, adjust the volume of Dnase-free water added to reach the target volume. Be sure to maintain 1X bind/ wash concentration.
Add MBD beads to the tube using the volume determined in Step 2. Pipette the mixture up and down or swirl a few times to mix.
As an approximate rule and as stated above, add 1µL of MBD beads for every 6.25ng of target host DNA in each enrichment reaction. If samples contain less than 6.25 ng of host DNA or if the amount of host DNA is not quantified, add 1 µl of MBD beads.
Incubate the reaction for 0h 15m 0s at room temperature with rotation.
Following incubation at room temperature, briefly spin the tube and place on the magnetic rack for 0h 5m 0s until the beads have collected to the wall and the solution is clear.
Carefully remove the supernatant with a pipette without disturbing the beads. The supernatant is enriched for microbial DNA and may be saved and purified by bead cleanup (Auxiliary protocol A: Step 35 - 45). Otherwise, discard the supernatant.
Add 1mL of 1 bind/ wash buffer (kept at room temperature) to wash the beads.
If processing in a microplate, decrease the volume of wash buffer to 100 µl.
Carefully remove and discard the wash buffer with a pipette without discarding the beads.
Optional. Add 100µL of 1X bind/ wash buffer (kept at room temperature) to the beads. Pipette the mixture up and down a few times to mix.
It has been found that an individual wash with 100µL of 1X bind/ wash buffer followed by rotation (Steps 25 - 28) substantially improved enrichment. To skip this wash, proceed to step 29.
Mix the beads by rotating the tube in a rotating mixer for 0h 3m 0s at room temperature.
Briefly spin the tube and place on the magnetic rack for 0h 2m 0s - 0h 5m 0s until the beads have collected to the wall of the tube and the solution is clear.
Carefully remove and discard the supernatant with a pipette without disturbing the beads.
Eluting captured Host DNA
The NEBNext Microbiome Enrichment Kit Includes an elution protocol for captured DNA that includes digestion of DNA-bound MBD beads with proteinase K and elution with TE buffer. It has been found that elution with 2 M NaCl is just as effective, is less time consuming, and conserves proteinase K. Most importantly, it has been found that DNA sample eluted with 2 M NaCl and purified by bead cleanup can be further enriched in a repeat enrichment reaction. DNA samples eluted with proteinase K and TE buffer and purified by bead cleanup in contrast produced minuscule yields following a repeat enrichment reaction.
Add 100µL of 2 M NaCl (prepared in Step 5 and kept at room temperature) to the beads. Pipette the mixture up and down a few times to mix.
If large numbers of samples are being processed, considering lowering the elution volume such that the combined volume of DNA and SPRI beads (see Auxiliary protocol A: Step 35 - 45) does not exceed the capacity of microplate wells and thereby preclude the ability to parallelize based cleanups.
Mix the beads by rotating the tube in a rotating mixer for 0h 3m 0s at room temperature.
Breify spin the tube and place on the magnetic rack for 0h 2m 0s - 0h 5m 0s
Carefully remove the supernatant to a fresh microcentrifuge and discard beads.
Proceed to bead cleanup to purify sample (Auxiliary protocol A: Step 35 - 45).
Auxiliary Protocol A: Bead Cleanup
Portions of this protocol are modified from Pacific Biosciences protocol #001-252-177-03.
Add 1.5X - 1.8x volume of pre-washed magnetic beads to DNA in a 1.5 ml tube.
If combined volume of beads and DNA does not exceed the capacity of the tube or well, large numbers of bead cleanups can be conducted in parallel on a microplate.
Mix the bead/ DNA solution thoroughly by pipetting up and down several times.
Vortex the beads for 0h 5m 0s.
Briefly spin the tube and place on the magnetic rack for 0h 5m 0s or until the solution is clear.
Carefully remove and discard the supernatant without disturbing the beads.
Wash beads with freshly prepared 70% ethanol. Wait 0h 1m 0s, then pipette and discard the ethanol.
Use a sufficient volume of 70% ethanol to completely cover the bead pellet (e.g., 100 µl for microplates and 400 µl for 1.5 ml tubes). Slowly dispense the 70% ethanol against the side of the tube opposite the beads. Do not disturb the bead pellet.
Repeat Step 40 above.
Remove residual 70% ethanol and air-dry the bead pellet for 0h 1m 0s.
Spin at full speed for 0h 2m 0s in order to collect residual 70% ethanol. Then place on the magnetic rack for 0h 0m 30s before pipetting the residual 70% ethanol and air-drying for 0h 1m 0s.
Resuspend the beads in 30µL - 40µL of 1X TE buffer or another suitable DNA stabilization buffer.
Vortex for 0h 1m 0s, then incubate for 0h 2m 0s. Spin the sample at full speed to pellet beads. Return to the magnet and collect the supernatant in a new 1.5 ml microcenrifuge tube.
Following bead cleanup, quantify with a fluorometer or spectrometer. Validate enrichment by qPCR (Auxiliary protocol B: Step 46 - 49). Enriched DNA can be sequentially enriched by repeating the enrichment protocol adding 30µL of the enriched product to the FecalSeq enrichment protocol: Step 18.
Auxiliary Protocol B: qPCR Estimation of Enrichment
Run samples and standards at least in duplicate. It is recommended to run a positive and negative control with each set of quantifications.
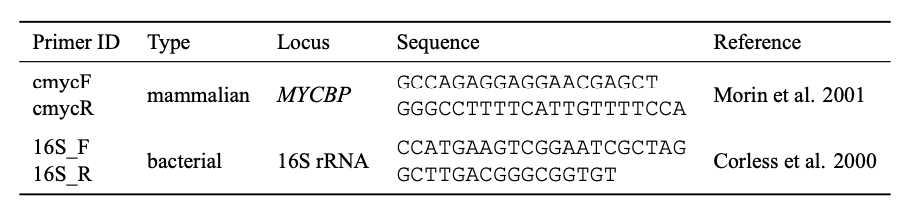
Use primers specific to the analysis.
a. The proportion of host DNA can be quantified by comparing qPCR results using host-specific primers to the absolute quantification estimated by some independent means (e.g., fluorometer or spectrophotometer). For the baboon DNA quantifications used here, a universal mammal primers for the MYCBP (c-myc) gene (Morin et al. 2001) was used.
b. Enrichment of DNA captured with MBD beads can be quantified as above using host-specific primers with enriched methylated host DNA. Alternatively, enrichment can be estimated by observing the n -fold decrease in quantified levels from unenriched to enriched samples using the universal 16S rRNA primer (Corless et al. 2000). 1 µl of unenriched DNA can be diluted to the concentration of the enriched sample prior to qPCR to standardize concentrations. Because MBD enrichment can in principle be biased towards densely methylated areas of the host genome, the latter method for estimating enrichment success is preferred.
Set up qPCR reactions in a 20µL total volume containing 1X of SYBR Green master mix, 0.5mM of each primer, and 1µL of DNA.
Run samples in the qPCR instrument at 95°C for 0h 15m 0s, followed by 50 cycles of 94°C for 0h 0m 15s, 59°C (for all primers specified above; adjust for other primers) for 0h 0m 25s, and 72°C for 0h 0m 20s.

