Genetic Characterization of Schistosomes
Isaac Owusu-Frimpong, Yvonne A. Ashong, Naa A. Kuma, Frank Twum Aboagye, Samuel .K. Armoo, Mike Y. Osei-Atweneboana
Abstract
Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease transmitted through water by blood-fluke trematodes of the genus Schistosoma. After malaria and soil-transmitted helminthiasis, it is the third most important parasitic tropical disease. An estimated 236 million people are infected, with another 700 million at risk of infection. It is estimated that 90% of all schistosomiasis cases occur in Africa. The disease is regarded as a public health threat, with numerous debilitating effects on growth, well-being, and overall health. The importance of snail-intermediate hosts in schistosomiasis transmission cannot be overstated, and thus monitoring the prevalence and distribution of Schistosoma cercariae is critical for indirect estimation of schistosomiasis in human or animal populations. As a result, developing sensitive tools to aid in the characterization of specific schistosomes is critical, and this protocol outlines procedures ranging from DNA isolation to PCR and the expected outcomes from newly developed oligonucleotides.
Before start
Aliquot the required volume of reagents for extraction into a sterile tube for the assay.
Allow the frozen reagents to thaw completely at 4°C before use and avoid centrifuging to thaw.
Reagent Preparation for Nucleic Acid Isolation
Genomic Lysis Buffer
Add 500µL of β-mercaptoethanol to 100 mL of Genomic Lysis Buffer. Shake slightly to mix
2% PVPP in 1 X TE Buffer
Dissolve 2 g of PVPP powder in 100 mL of 1X TE Buffer
Steps
Cercariae Suspension Pre-Treatment
Centrifuge the cercariae suspension at 1600rpm,0h 0m 0s for 0h 5m 0s to concentrate the cercaria
Pipette off the supernatant leaving 200µL of cercariae suspension for nucleic acid isolation.
Schistosome Vector (Snail) Pre-Treatment
Crush each snail in 200µL of 1XTE Buffer using a pestle in a 1.5mL microcentrifuge tube. Ensure the end mixture is as fine as possible.
Nucleic Acid Isolation
Transfer 200µL of the pre-treated sample (cercariae suspension or snail) into a sterile 1.5mL microcentrifuge tube.
Add 200µL of 2Mass / % volume PVPP in 1XPBS and vortex the sample with glass beads at 3000rpm for 0h 1m 0s
Add 400µL of Genomic Lysis Buffer and 10µL of Proteinase K (20ng/mL) to the sample.
Vortex briefly and incubate the sample at 56°C for 3 - 5 hours or 0h 20m 0s
Vortex the sample at 3000rpm for 0h 0m 30s and centrifuge at 10000rpm,0h 0m 0s for 0h 1m 0s
Transfer the supernatant into a Zymo-Spin IIC column in a new collection tube.
Centrifuge at 10000rpm,0h 0m 0s for 0h 1m 0s. Discard the flow-through liquid.
Transfer the Zymo-Spin IIC column into a new collection tube
Add 200µL of DNA Pre-Wash Buffer to the spin column and centrifuge at 10000rpm,0h 0m 0s for 0h 1m 0s.
Add 500µL of gDNA Wash Buffer to the spin column and centrifuge at 10000rpm,0h 0m 0s for 0h 1m 0s
Transfer the Zymo-Spin IIC column into the sterile 1.5mL microcentrifuge tube.
Add 100µL of DNA Elution Buffer to the spin column and incubate for 0h 30m 0s
Centrifuge at 13000rpm,0h 0m 0s for 0h 0m 30s to elute the DNA.
Store the DNA at -20°C pending further analysis.
Preparation of PCR Master Mix and Reaction
Prepare the master mix for each schistosome species separately following the protocol:
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | Reagent | 1X Volume (µL) |
| 2X | One Taq Mastermix | 5.0 |
| 10 µM | Forward Primer | 2.0 |
| 10 µM | Reverse Primer | 2.0 |
| NA | Nuclease-Free Water | 1.6 |
| Template DNA | 3.0 | |
| Total Reaction Volume | 10.0 |
| A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schistosome species | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Fragment Size | Primer Tm |
| ITS - Schistosome sp. | TCT TGA CCG GGG TAC CTA | ATT AAG CCA CGA CTC GAG CAC | 691 bp | 60.1°C |
| S. mansoni | GAG GGG TCT GGT TTT GGT GT | GCA GAT AAA GCC ACC CCT GT | 659 bp | 58.7°C |
| S. haematobium | TTG AGC CTAT GGG TGG TGG T | ACC AGT AAC ACC ACC TAT CGT | 410 bp | 58.7°C |
| S. bovis | TGG GCA TCC TGA GGT GTA T | CAC AGG ATC AGA CAA ACG AGT ACC | 301 bp | 55.6°C |
| S. haematobium/S. bovis hybrid | CCT CCA TTA TCT ATA TCT GAG AAT TCT | CGA AGT CTT AAA ATC CAC ACA ACT | 141 bp | 55.6°C |
Thermal Cycling Conditions
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step | Temperature | Time | Cycles |
| Initial Denaturation | 95°C | NA | |
| Denaturation | 95°C | 45 seconds | 40 |
| Annealing | Tm | 45 seconds | |
| Extension | 72°C | 45 seconds | |
| Final Extension | 72°C | 5 minutes | NA |
Tm: Refer to the primer list for the individual annealing temperatures of the primer pairsNA: Not applicable
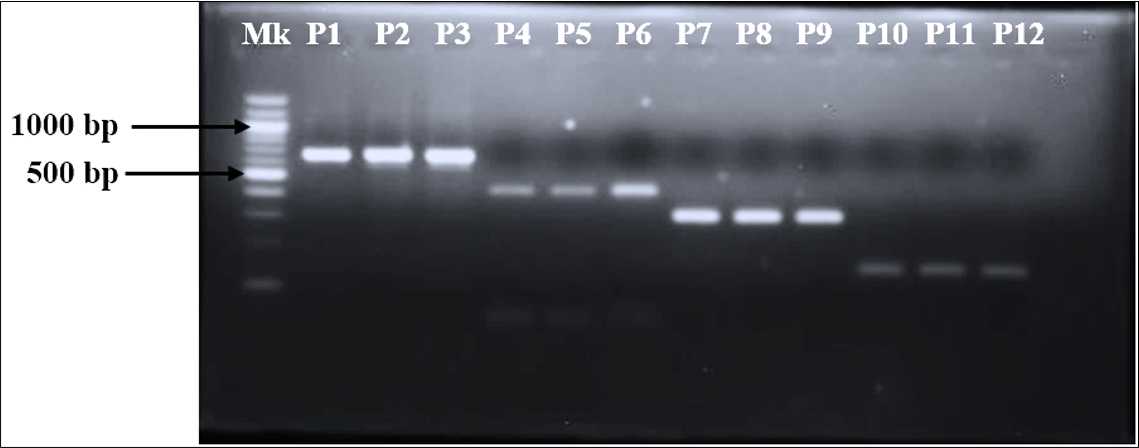
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
To prepare 1.5Mass / % volume agarose solution, weigh 1.5g of agarose into a glass beaker containing 100mL 1XTBE Buffer
Microwave the solution until the agarose completely dissolves and forms a clear solution.
Allow the solution to cool at Room temperature to about 50°C.
Add 5µL of 10mg/mL Ethidium Bromide to the agarose solution. Swirl to ensure complete mixing of the stain with the agarose solution.
Pour the stained agarose molten solution into a casting tray (5mm deep) fitted with combs of the desired size for a well. Allow the molten solution to solidify for about 0h 20m 0s at Room temperature
Gently remove the combs from the solidified agarose gel and move the casting tray into the electrophoresis tank.
Load 5µL to 12µL the Sample into each well (mix 1µL of 6X Loading with 5µL of amplicon).
Load 3µL of 100 or 50 bp (depending on the fragment size of the amplicon of interest) Molecular Weight Marker into the first well which will serve as a reference.
Electrophorese the amplicons at 100 volts until the molecular weight marker has travelled two-thirds of the length of the agarose gel.
Visualize the agarose gel under UV light using the transilluminator.