A computational pipeline to quantify primary cilia in mouse embryonic fibroblasts with CellProfiler
Suzanne R Pfeffer, Herschel Dhekne, Ebsy Jaimon, Chloe A Hecht, Sreeja V Nair
Abstract
We present here an automated CellProfiler (Stirling et al., 2021) software pipeline to quantify the number of primary cilia in cultured cells. The primary cilia were labeled using anti-Arl13b antibodies and nuclei were labeled using DAPI. This protocol works with .czi format images which are acquired using a Zeiss laser scanning confocal microscope and are maximum intensity projected.
Steps
Import data into CellProfiler and extract metadata from file names
Select the Images module, drag and drop the maximum intensity projected .TIF files as indicated
Select the Metadata module
In the Metadata module:
Extract metadata? Yes.
Metadata extraction method: Extract from file/folder names
Metadata source: File name
Regular expression to extract file name :
“regular expression” will have the form:
^(?P
Here,
^ indicates the beginning of the file name
(?P
(?P
Extract metadata from: All images
Add another extraction method
Metadata extraction method: Extract from image file headers
Extract metadata from: All images
Hit “Extract metadata”
Metadata data type: Text
Hit “update” to populate the metadata field
Group individual channels and create image subsets
Go to Names and types module
Assign a name to : “Images matching rules”
Process as 3D : No
Select the rule criteria
Match “All” of the following rules
“Metadata/Does/Have C matching 0”
Name to assign these images: Arl13b
Select the image type: Grayscale image
Set intensity range from : Image metadata
Add another image
Match “All” of the following rules
“Metadata/Does/Have C matching 1”
Name to assign these images: dapi
Select the image type: Grayscale image
Set intensity range from : Image metadata
Hit “update” to populate the names and types field
Select Groups module
Do you want to group your images? Yes
Metadata category: celltype
Add another metadata item
Metadata category: imagenumber
This groups images based on cell type and image number as identified in the metadata module.
Identification of nuclei
Click on the “+” sign at the bottom next to Adjust Modules. One can choose different modules by double-clicking from the list or by typing in the search box. Under module category, object processing, add Identifyprimaryobjects module.
Use advanced settings? Yes
Select the input image: dapi
Name the primary objects to be identified: nuclei
Typical diameter of objects, in pixel units: 60-200
Note :
This has to be optimized for each image set.
Discard objects outside the diameter range? Yes
Discard objects touching the border of the image? No
Note:
Check by clicking “Start Test Mode” and hitting the green triangle next to the IdentifyPrimaryObjects module.
Threshold strategy? Global
Thresholding method? Minimum Cross-Entropy
Threshold smoothing scale 1.3488
Threshold correction factor 1.0
Lower and upper bounds on threshold 0.05 and 0.8
Log transform before thresholding? No
Method to distinguish clumped objects? Intensity
Method to draw dividing lines between clumped objects? Intensity
Automatically calculate size of smoothing filter for declumping? No
Size of smoothing filter 30
Automatically calculate minimum allowed distance between local maxima? Yes
Speed up by using lower-resolution image to find local maxima? Yes
Display accepted local maxima? No
Fill holes in identified objects? After both thresholding and declumping
Handling of objects if excessive number of objects identified? Continue
Note
These parameters will need to be optimized for each image set. Check by clicking “Start Test Mode” and hitting the green triangle next to the IdentifyPrimaryObjects module each time a parameter is changed to find the best parameters for each image set. Green outlines represent valid objects whereas magenta/orange outlines represent invalid objects, as they are either touching the border or outside the diameter range set.
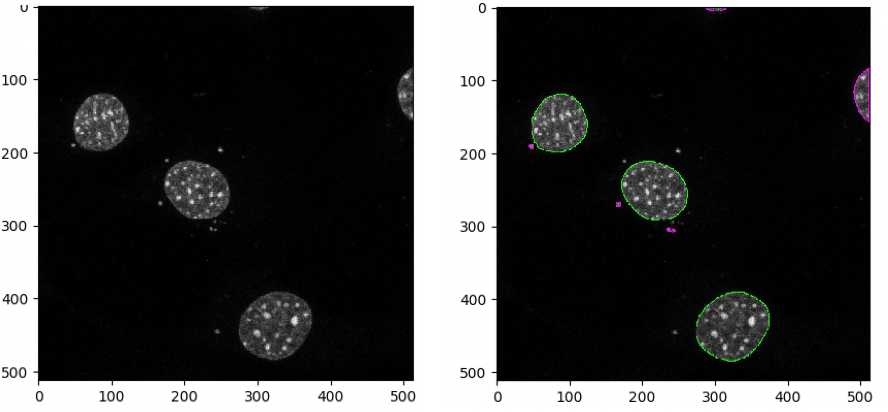
Identification of primary cilia objects
Add Identifyprimaryobjects module
Use advanced settings? Yes
Select the input image: Arl13b
Name the primary objects to be identified: cilia
Typical diameter of objects, in pixel units: 5-15
Discard objects outside the diameter range? Yes
Discard objects touching the border of the image? Yes
Threshold strategy? Global
Thresholding method? Otsu
Two-class or three-class thresholding? Two classes
Threshold smoothing scale 1.0
Threshold correction factor 0.5
Lower and upper bounds on threshold 0.0 and 1.0
Log transform before thresholding? No
Method to distinguish clumped objects? None
Fill holes in identified objects? After both thresholding and declumping
Handling of objects if excessive number of objects identified? Continue
Note
Check by clicking “Start Test Mode” and hitting the green triangle next to the IdentifyPrimaryObjects module each time a parameter is changed to find the best parameters for each image set.
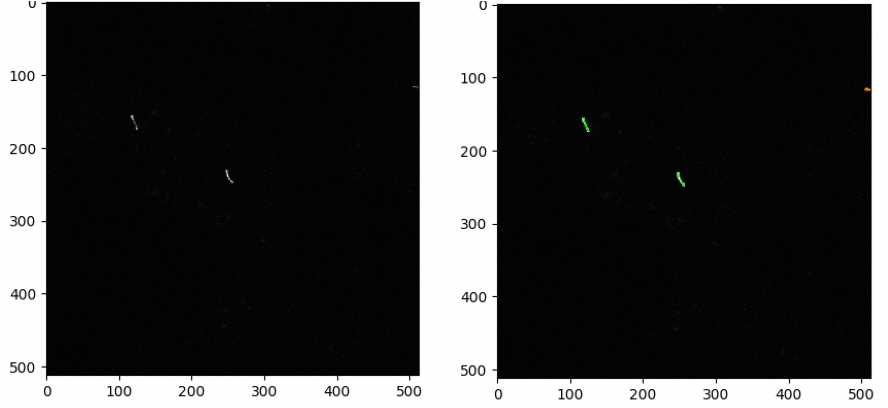
Measuring the number of cilia and nuclei in each image
Add MeasureObjectSizeShape module
Select object sets to measure : cilia, nuclei
Calculate Zernike features?No
Calculate the advanced features? No
Exporting data
Add the ExportToSpreadsheet module from the + at the bottom
Select the column delimiter: Tab
Output file location: choose a folder where you want the images to be saved.
Add a prefix to file names? Yes.
File name prefix: Add experiment identifier
Overwrite existing files without warning? No
Note: While the pipeline is run for optimizing the parameters, choose Yes to avoid being asked to rewrite each file.
Add image metadata columns to your object data file? Yes
Add image file and folder names to your object data file? No
Representation of Nan/Inf: NaN
Select measurements to export? Yes
Press button to select measurements:
Select measurements: Choose number under cilia and nuclei
Calculate the per-image mean values for object measurements? No
Calculate the per-image median values for object measurements? No
Calculate the per-image standard deviation values for object measurements? No
Create GenePattern GCT file? No
Export all measurement types? No
Data to export: nuclei
Use the object name for the file name? Yes
Add another data set
Data to export: cilia
Combine these object measurements with those of the previous object? Yes
Save the pipeline from File-Save Project and hit Analyze Images on bottom left.
The pipeline will run and export the data to the folder previously specified. The output file can be opened in Excel software. Distinct columns will indicate number of nuclei and number of cilia in each image.

