Tools for experimental and computational analyses of off-target editing by programmable nucleases
X. Robert Bao, Yidan Pan, Ciaran M. Lee, Timothy H. Davis, Gang Bao
off-target editing
programmable nucleases
amplicon-based NGS
in silico tools
therapeutic genome editing


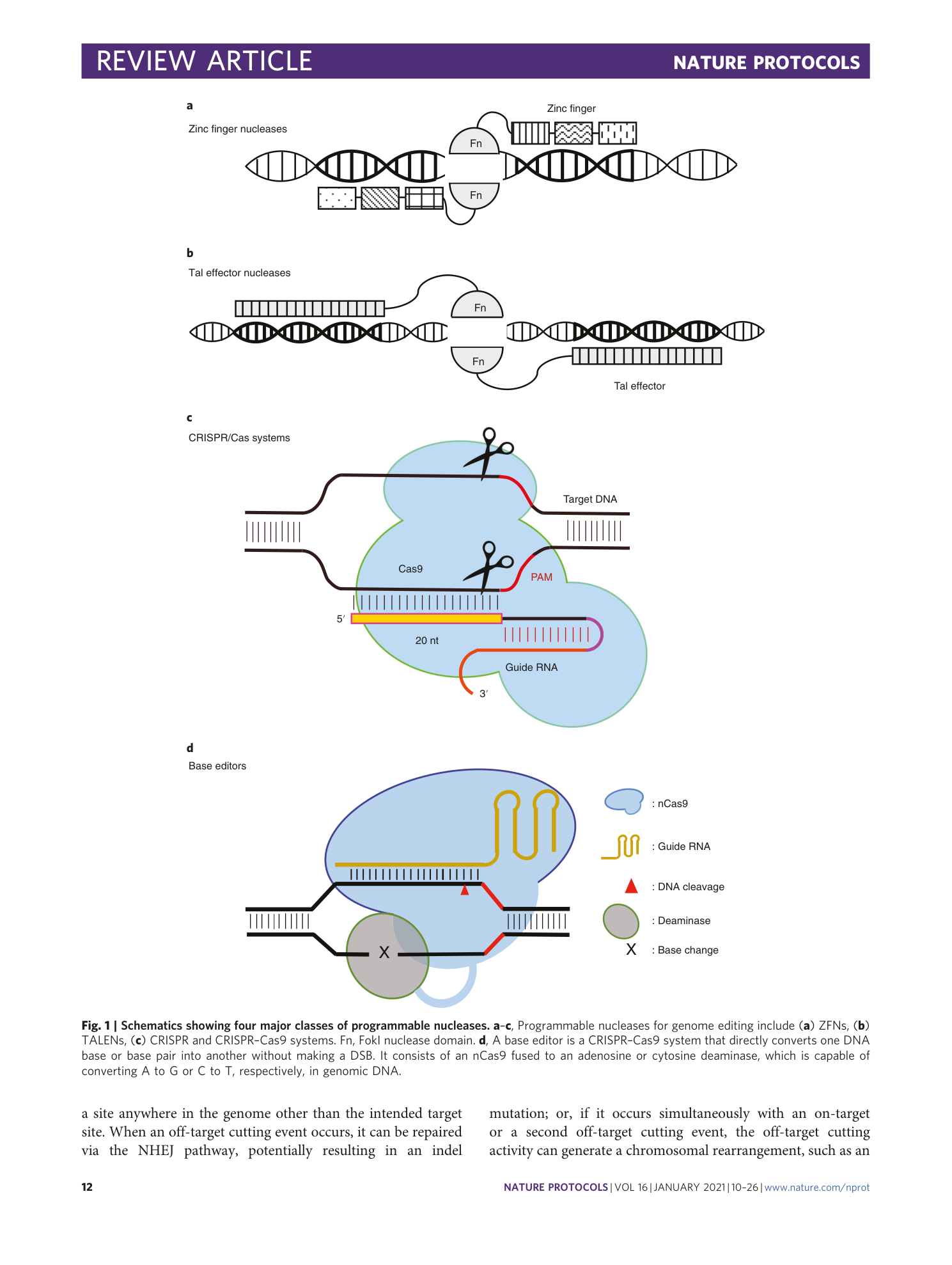
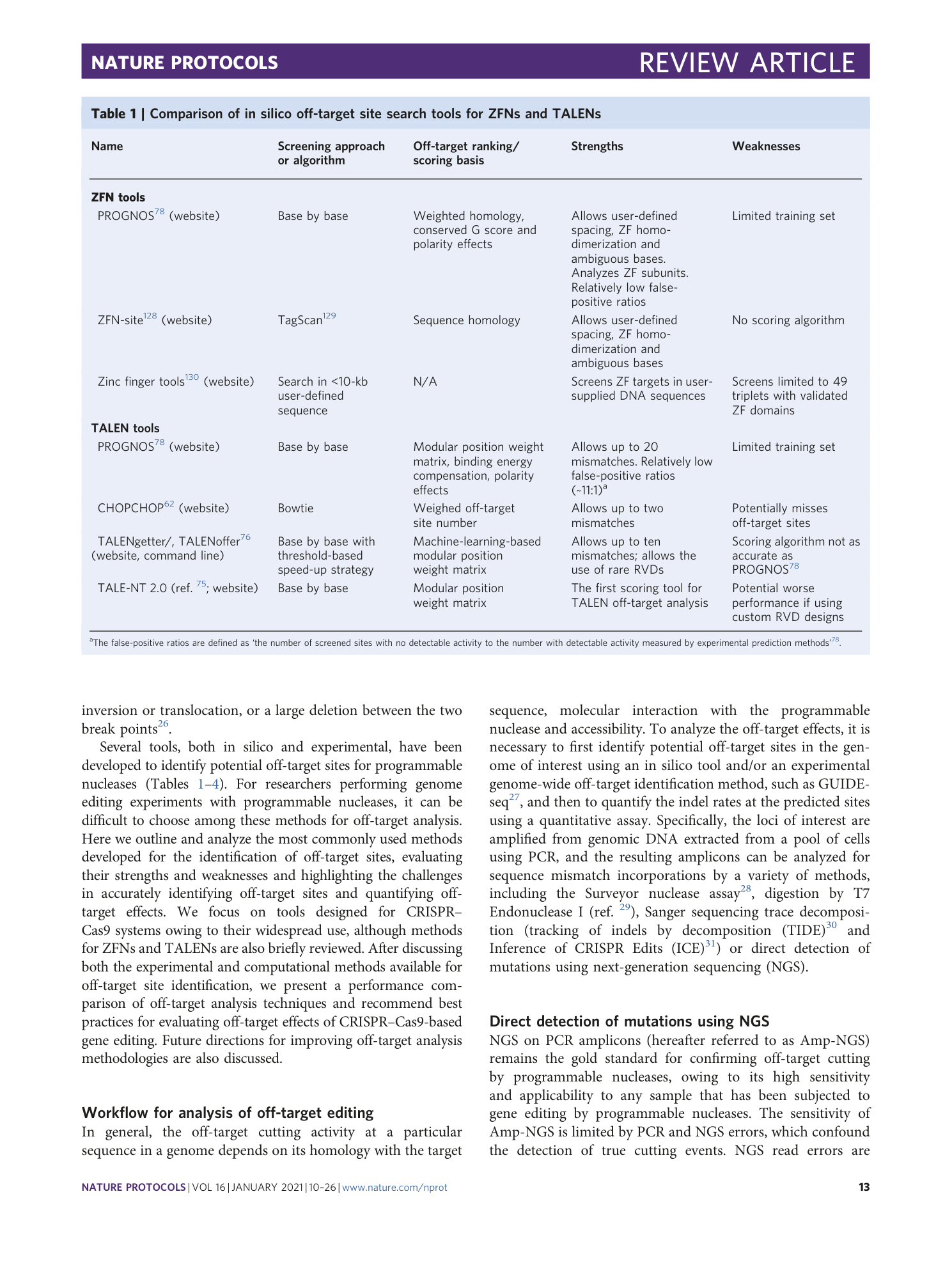
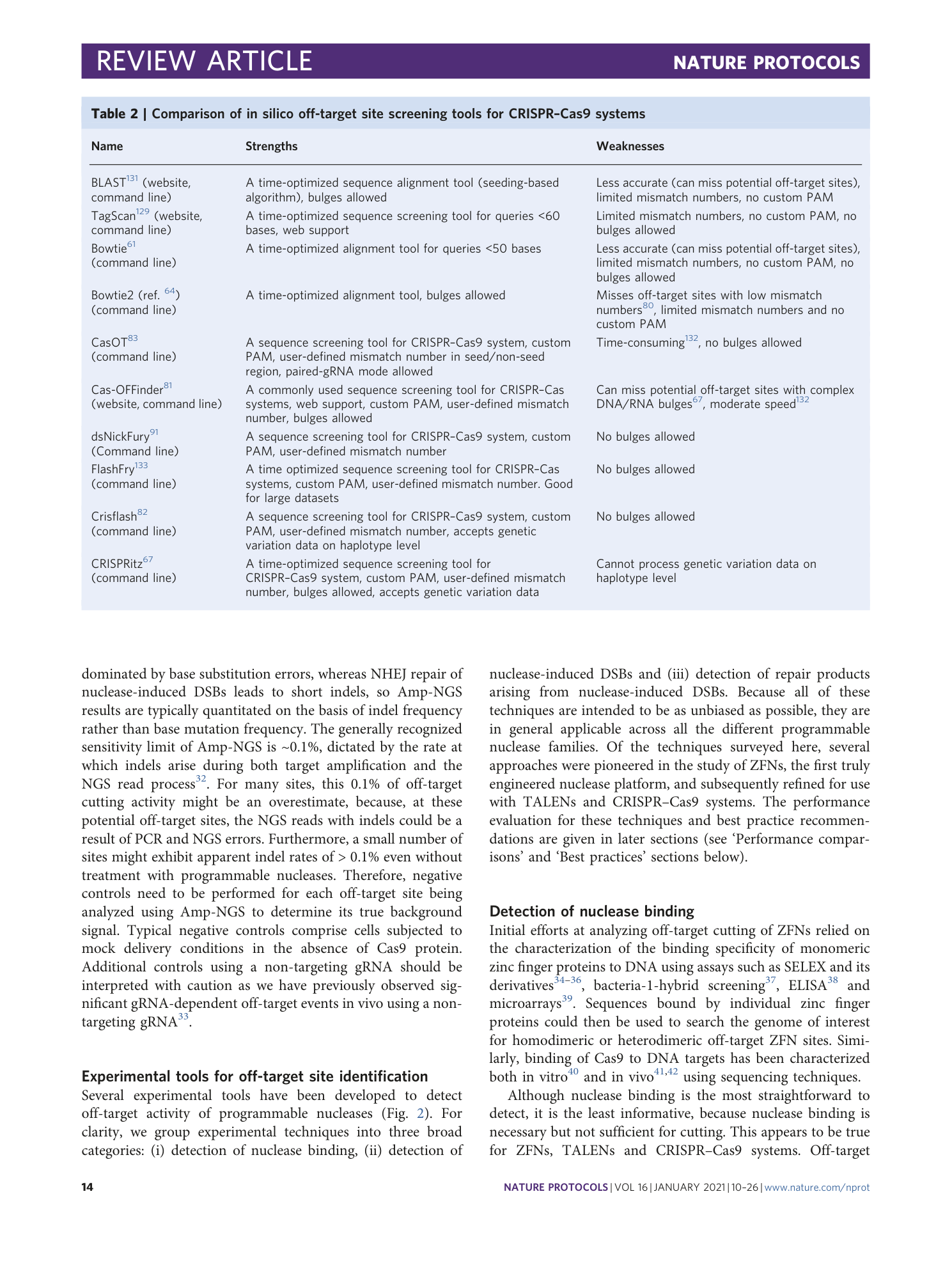
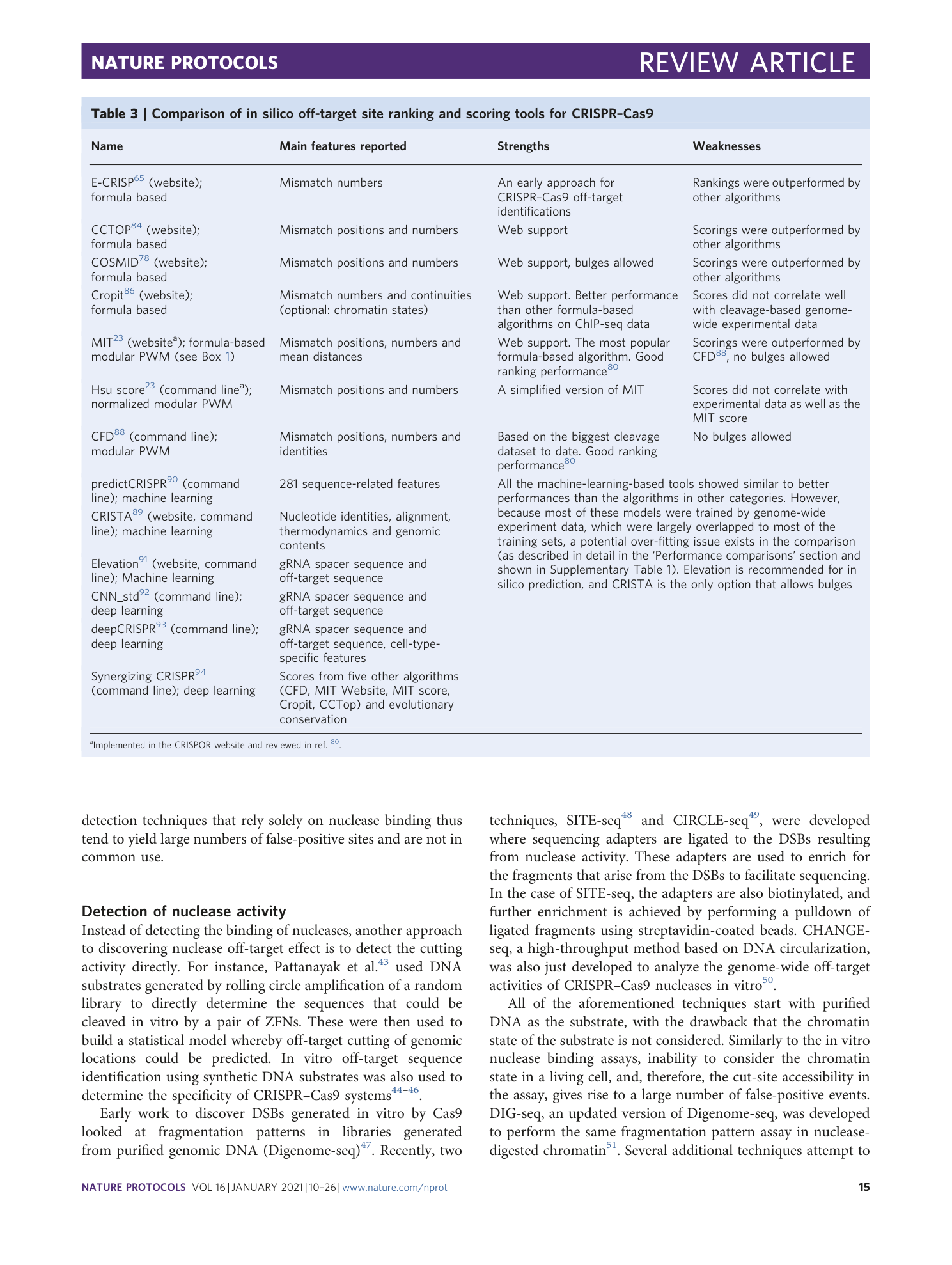







Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1 and 2.
Supplementary Table 1
Structures and training sets of machine learning-based algorithms for off-target prediction.
Supplementary Table 2
List of datasets from the Sequence Read Archive used to calculate on-target enrichment for performance comparison of experimental techniques. All genomic coordinates reference the hg38 human genome assembly.
Supplementary Table 3
Components of the true-positive list used in the analysis for performance comparison of computational techniques, taken from nine studies that used amplicon-specific experimental techniques to detect off-target editing rates. ‘OT’ in this table stands for off-target.
Supplementary Table 4
The full off-target dataset used in the performance assessment of computational techniques. Potential off-target sites of 27 gRNAs from nine studies shown in Supplementary Table 3 were screened by Cas-OFFinder, allowing up to four mismatches and one base DNA/RNA bulge and scored by each of the algorithms. ‘noind’: DNA/RNA sequences before alignments. Note that, after introducing bulges, one locus might be called by Cas-OFFinder multiple times with different alignment patterns, leading to different scores. These sites were treated the same as other off-target sites without manipulation. Source data for Supplementary Figure 1 and Fig. 3a.
Supplementary Table 5
The off-target dataset of novel gRNAs used in the performance assessment of computational techniques. Potential off-target sites and scores of four gRNAs that were not in the CRISPOR dataset 1 . These were screened by Cas-OFFinder, allowing up to four mismatches and one base DNA/RNA bulge and scored by each of the algorithms. Note that, after introducing bulges, one locus might be called by Cas-OFFinder multiple times with different alignment patterns, leading to different scores. These sites were treated the same as other off-target sites without manipulation. ‘noind’: DNA/RNA sequences before alignments. Source data for Supplementary Fig. 2 and Fig. 3b.

