Ultrasound measurement of thoracolumbar fascia deformation
Andreas AB Brandl
Disclaimer
DISCLAIMER – FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY; USE AT YOUR OWN RISK
The protocol content here is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, medical, clinical, or safety advice, or otherwise; content added to protocols.io is not peer reviewed and may not have undergone a formal approval of any kind. Information presented in this protocol should not substitute for independent professional judgment, advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Any action you take or refrain from taking using or relying upon the information presented here is strictly at your own risk. You agree that neither the Company nor any of the authors, contributors, administrators, or anyone else associated with protocols.io, can be held responsible for your use of the information contained in or linked to this protocol or any of our Sites/Apps and Services.
Abstract
The authors describe a measurement method for recording the deformation of the thoracolumbar fascia in a clinical setting.
Since physiological (e.g. lack of activity, overload or delayed onset muscle soreness) or pathological (e.g. acute or chronic low back pain) conditions restrict the shear capacity of the thoracolumbar fascia, the method should detect differences between such conditions and other (e.g. healthy, normal weight-bearing) states.
Steps
Trunk extension task
The study participants sit on the treatment table with their feet touching the floor.
Participants are instructed to place their hands lightly on their thighs and keep their elbows close to their body.
A goniometric check of the actual degree of flexion may be carried out in a laboratory test.
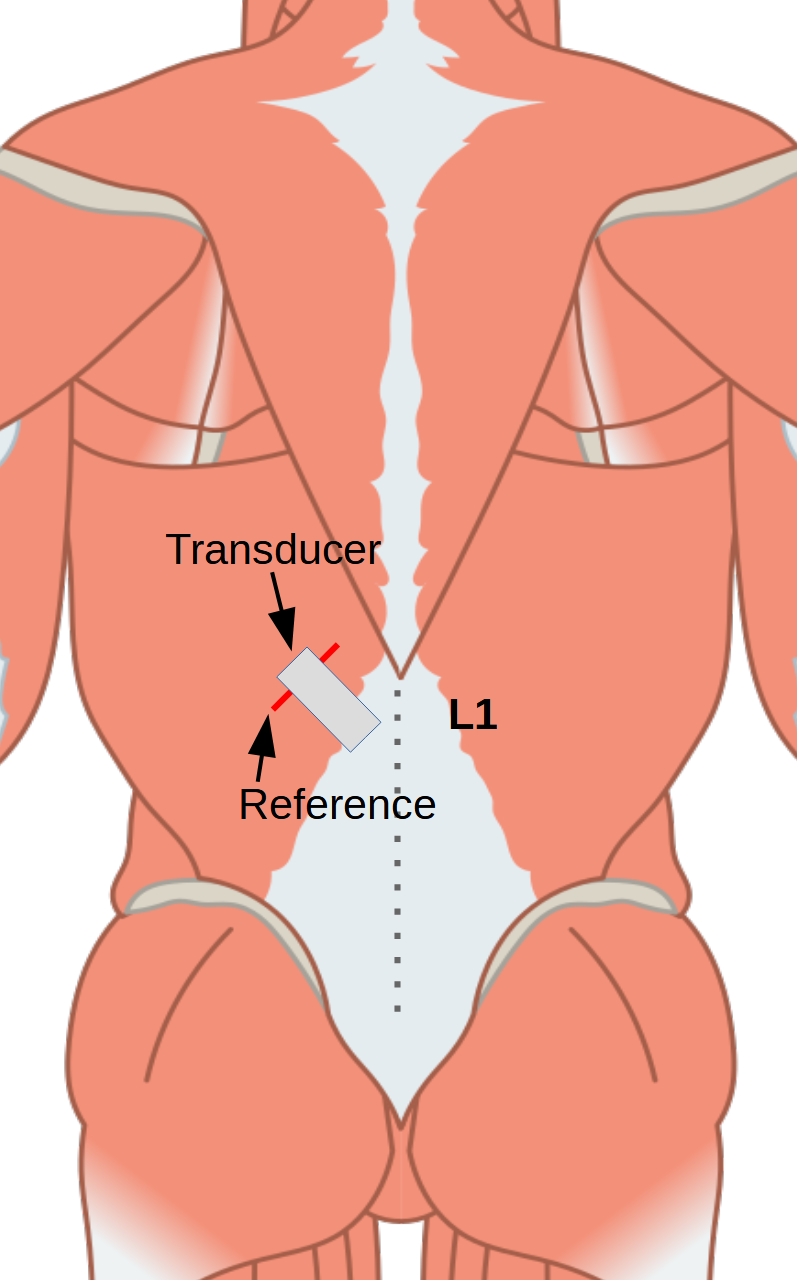
Ultrasound transducer positioning
The transverse process of L1 is recorded sonographically.
The transducer is then moved laterally along a horizontal line from the L1 spinous process in sagittal section until the junction of the latissimus dorsi muscle (LD) into the thoracolumbar fascia (TLF) is visible.
While the junction is still centrally aligned on the image, the transducer is rotated laterally-caudally until the fibers of the LD are aligned in parallel. To make the junction between LD and TLF more visible in the ultrasound image, participants are asked to repeatedly press their arm caudally against the treatment table to activate the LD in isolation.
The junction between the muscle and fascia is then positioned 10 to 20 mm (depending on transducer width) medial to the center of the image section.
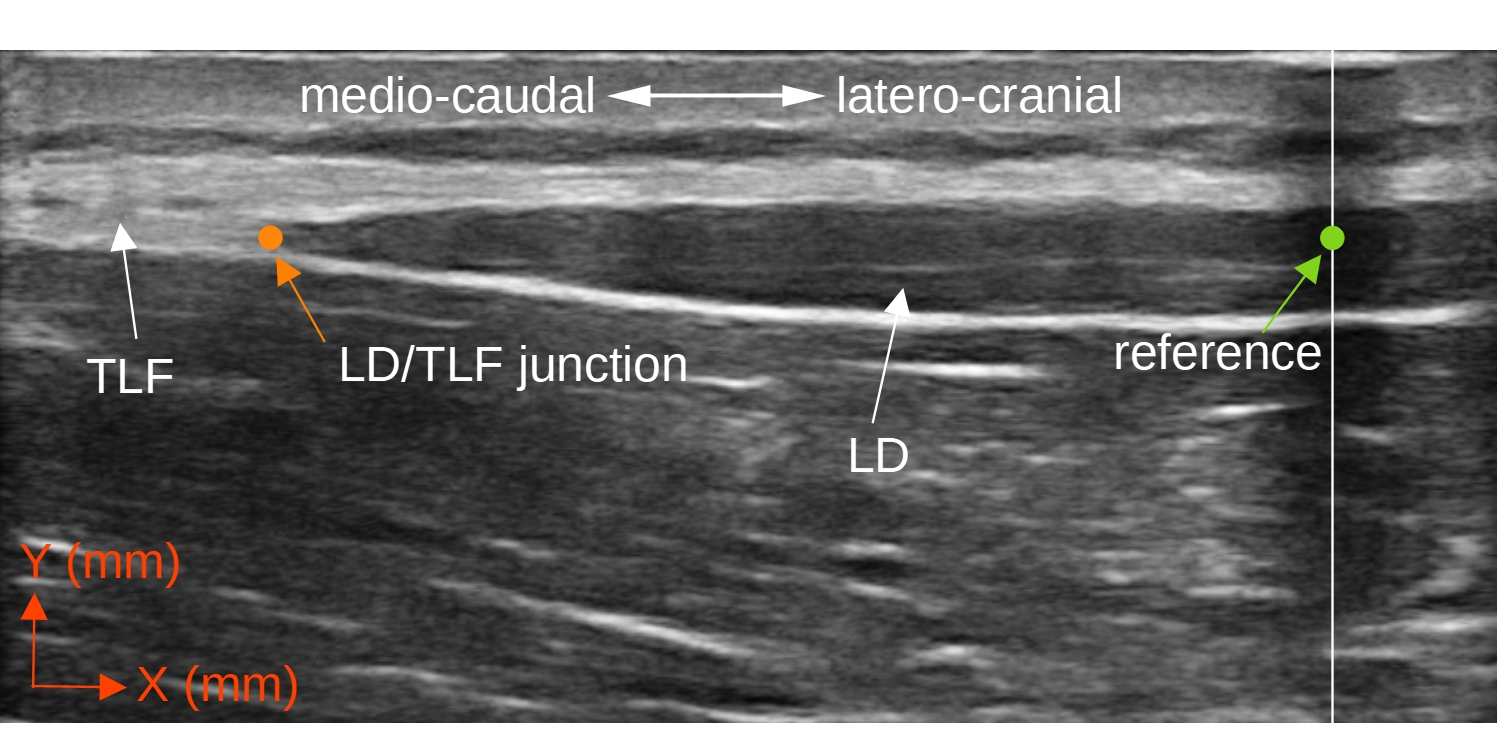
Using a 2 mm wide plastic adhesive tape, which is stuck to the skin 10 to 20 mm lateral to the center of the image section, an artificial shadow is created in the US image, which serves as a reference for the subsequent measurement. This is necessary to compensate for unintended movements between the skin and the transducer during the torso extension (Figure 3 and 4).
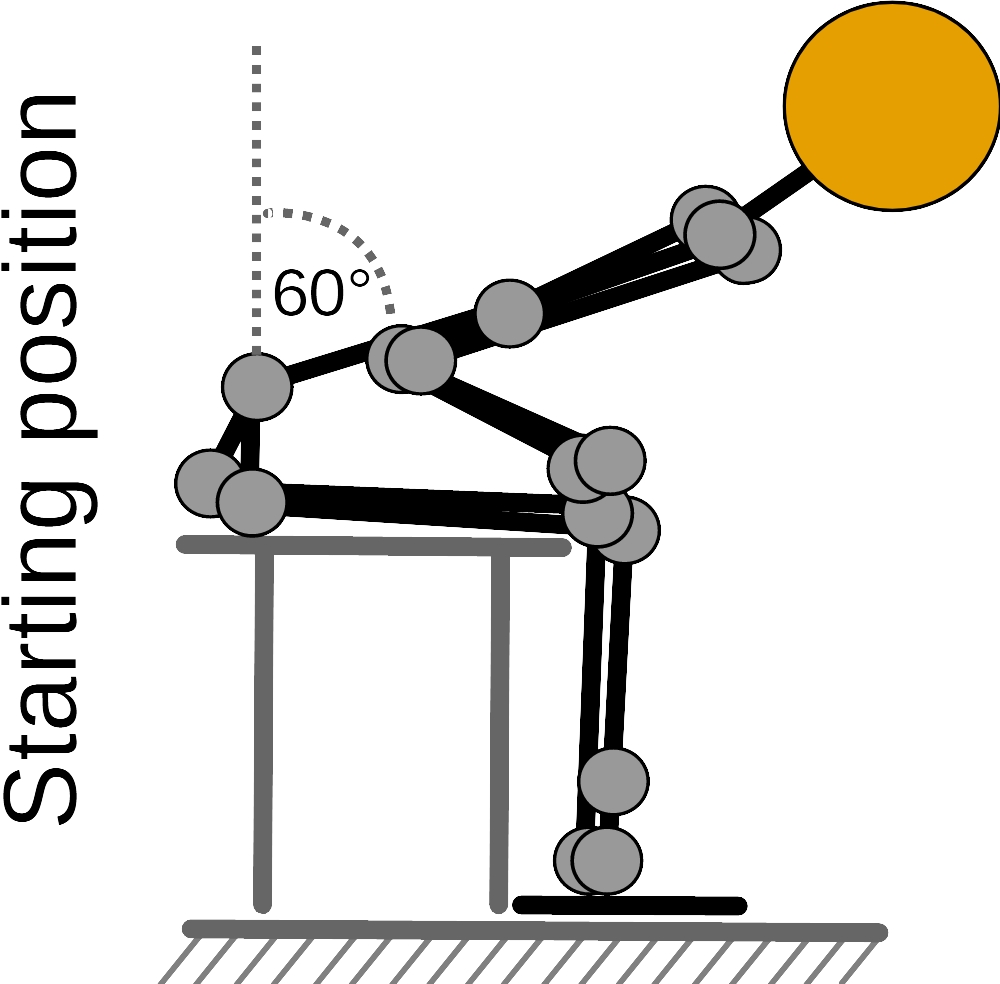
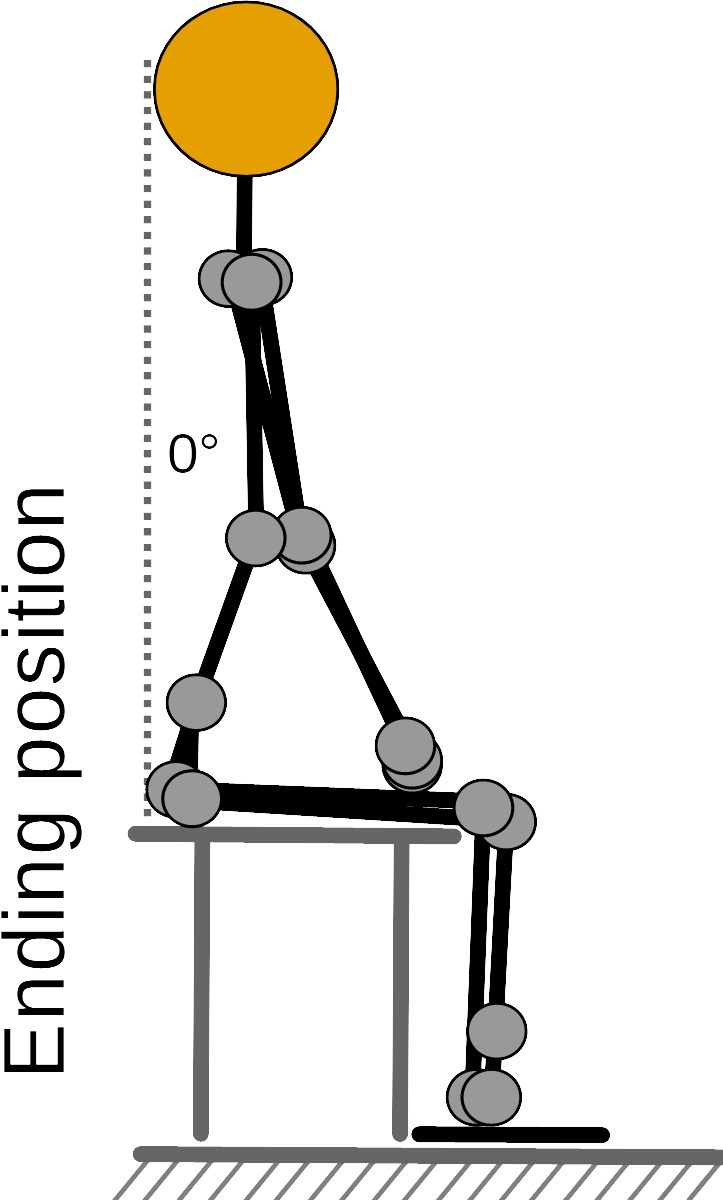
Ultrasound measurement of thoracolumbar fascia deformation
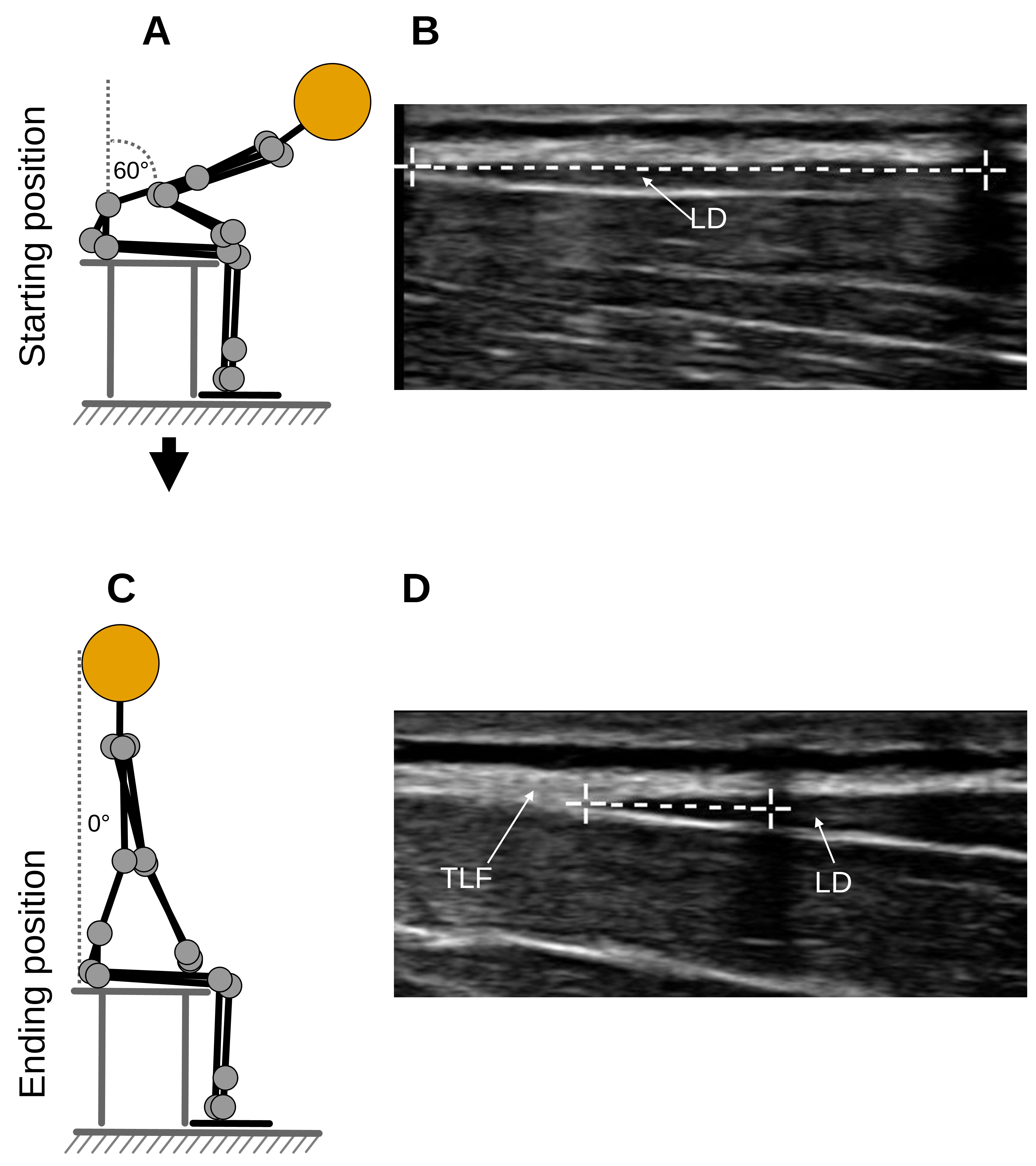
Before the measurement, the participants receive information on how to perform the TET. The experimenter demonstrates a complete cycle of the TET (Figures 1 and 2).
The participants first perform a 60-degree flexion. They then extend the trunk into the neutral position for a period of about 3 s (about 0.1 m/s).
An ultrasonic image is taken at the start position of the TET (t1) and at the end position of the TET (t2) and the respective distances between the LD/TLF transition and the reference are measured using the ultrasonic device's built-in measuring tools (Figure 5).
The TLF deformation (TLFD) is calculated as follows: TLFD = t1 - t2 as an absolute value or as TLFD(%) = (t1 - t2) / t1 * 100 as a relative change in percent.