An LC-MS/MS assay and complementary web-based tool to quantify and predict compound accumulation inE. coli
Emily J. Geddes, Zhong Li, Paul J. Hergenrother


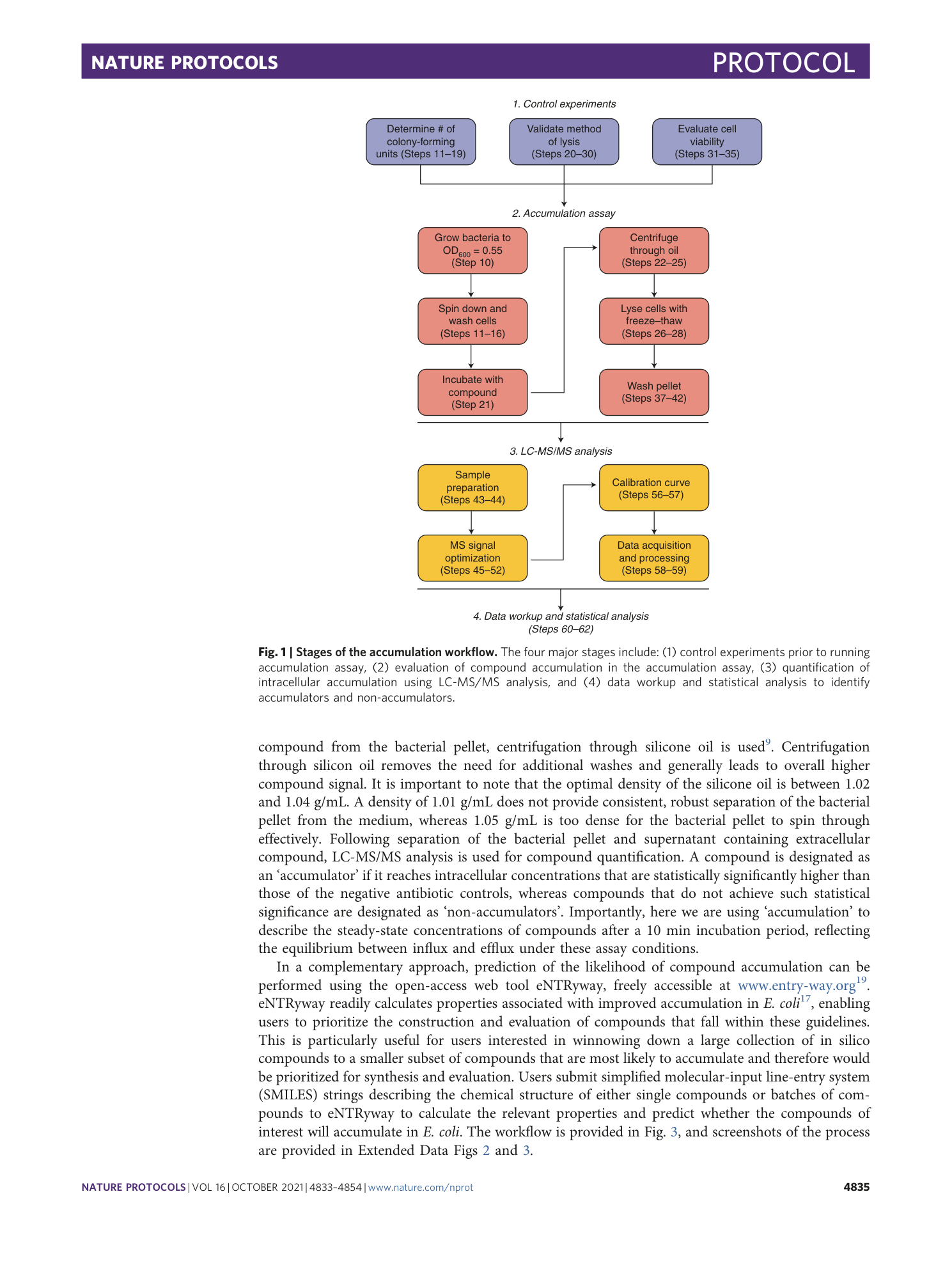

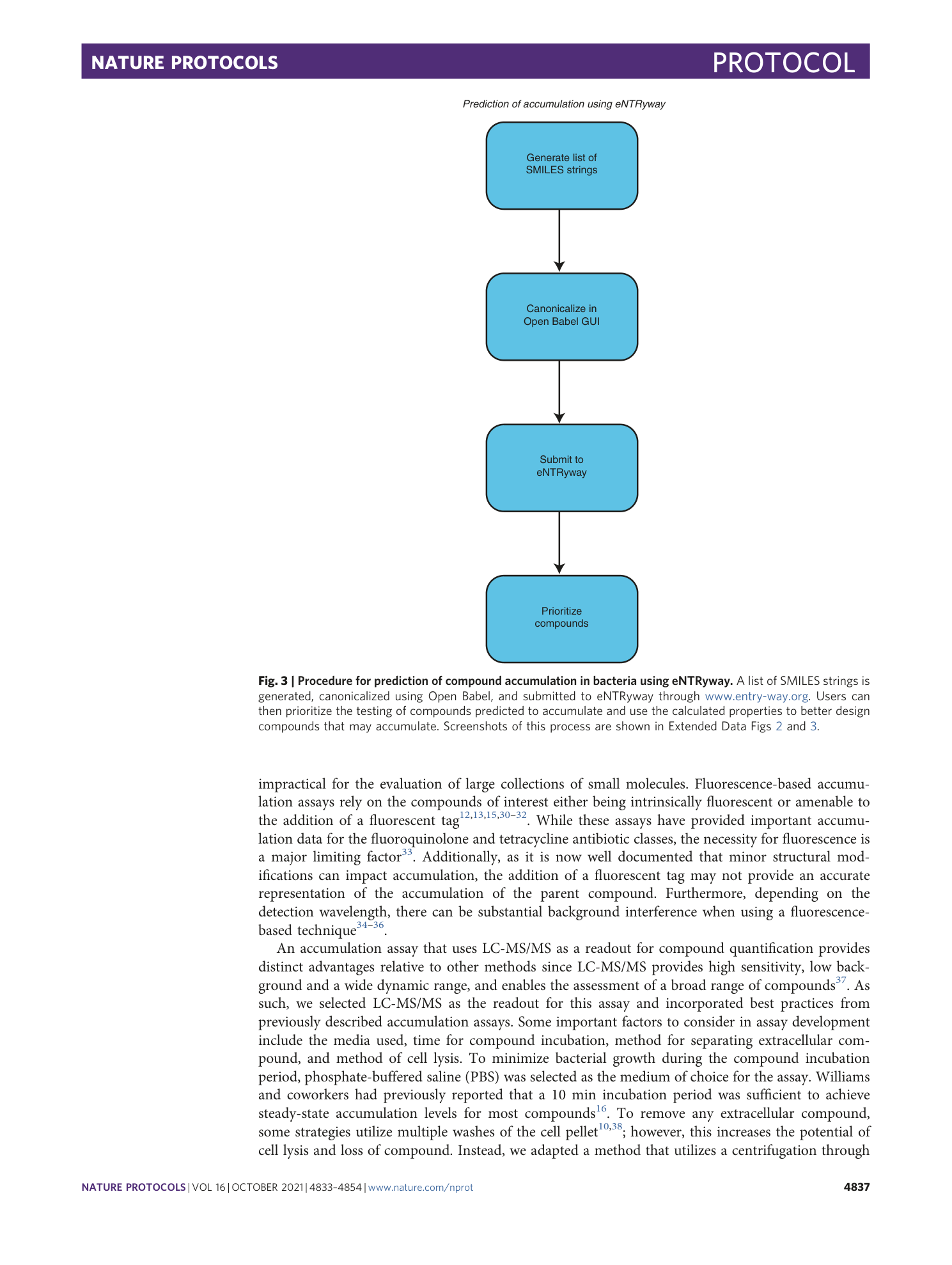


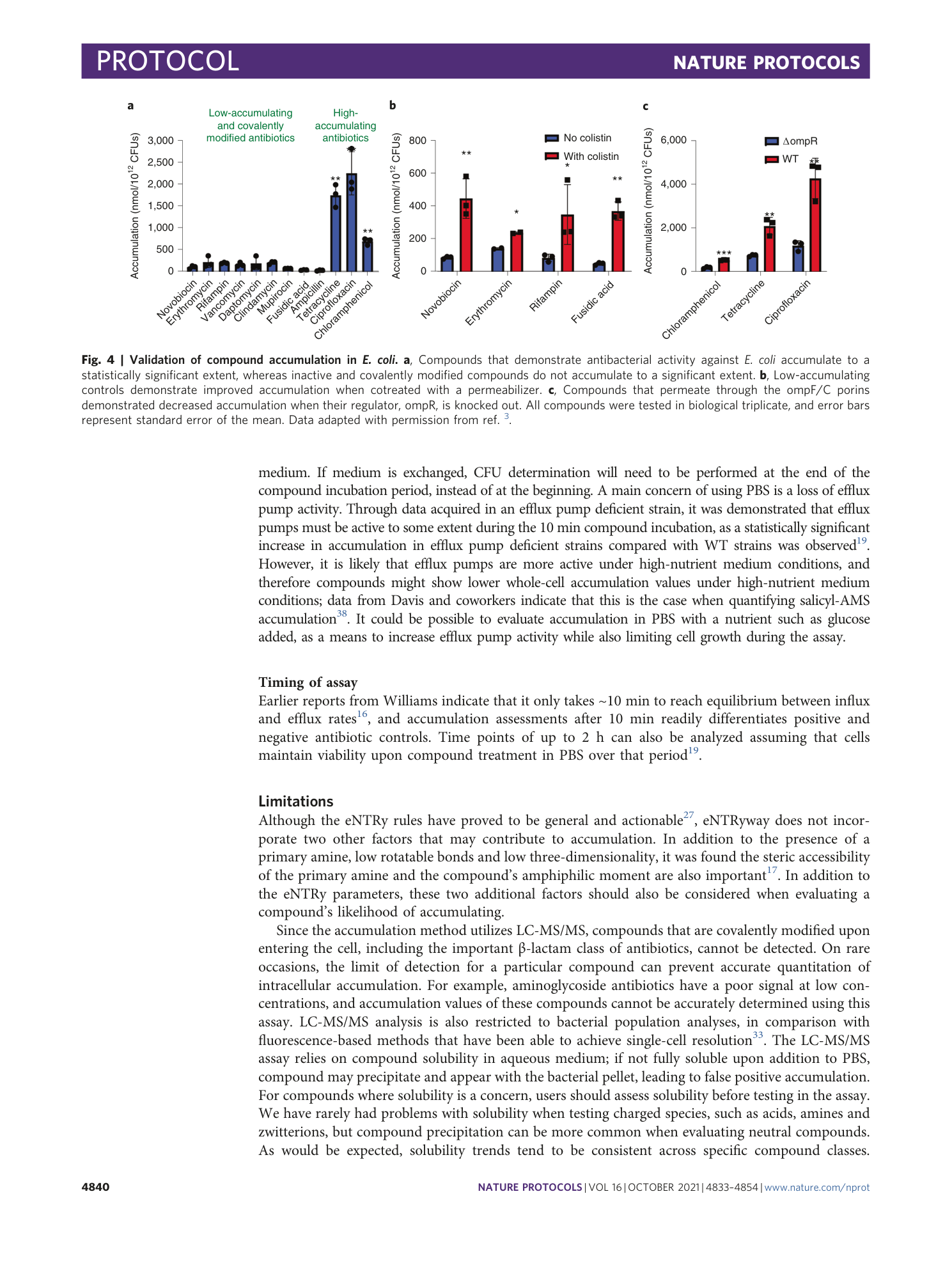







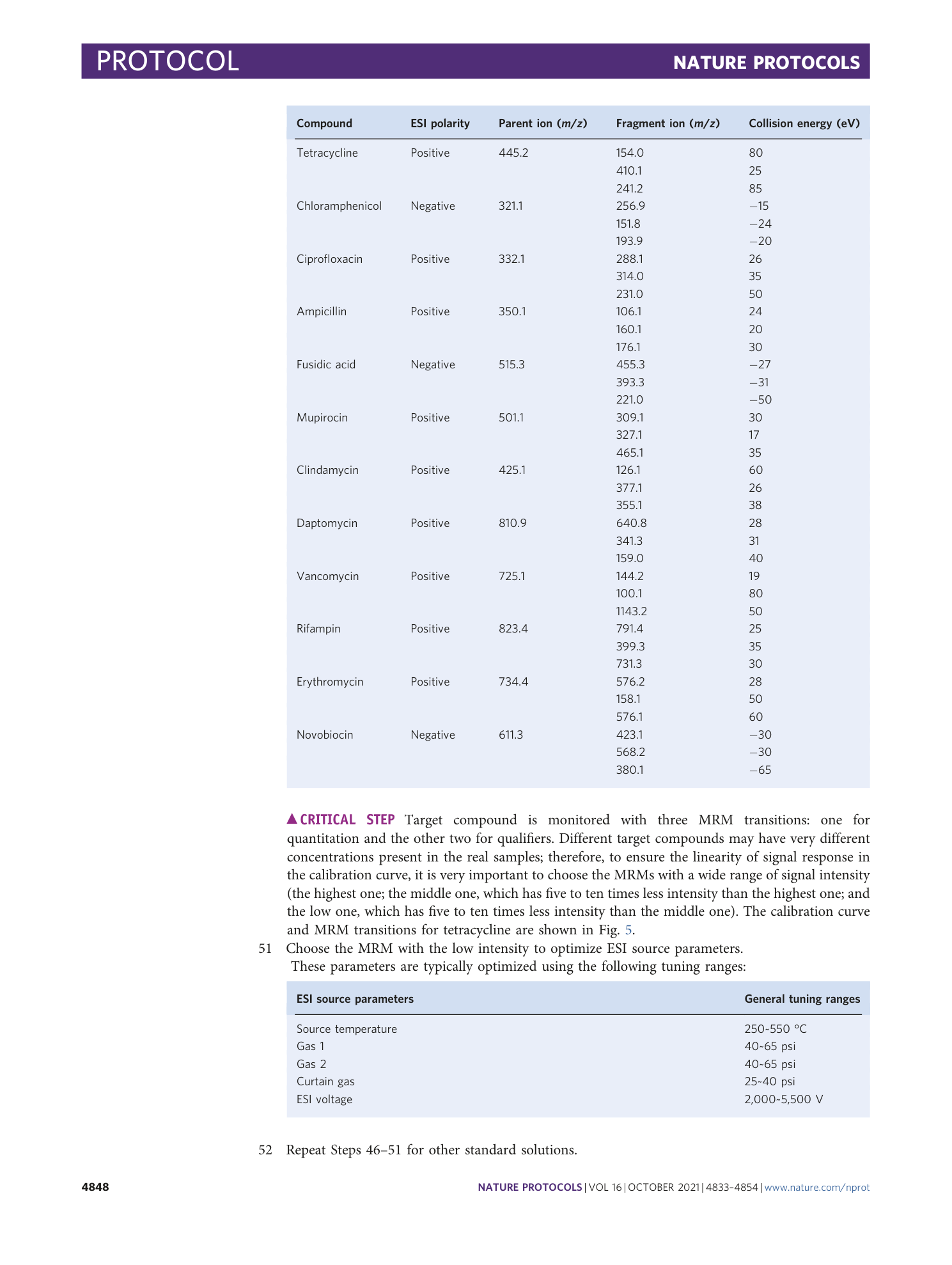





Extended
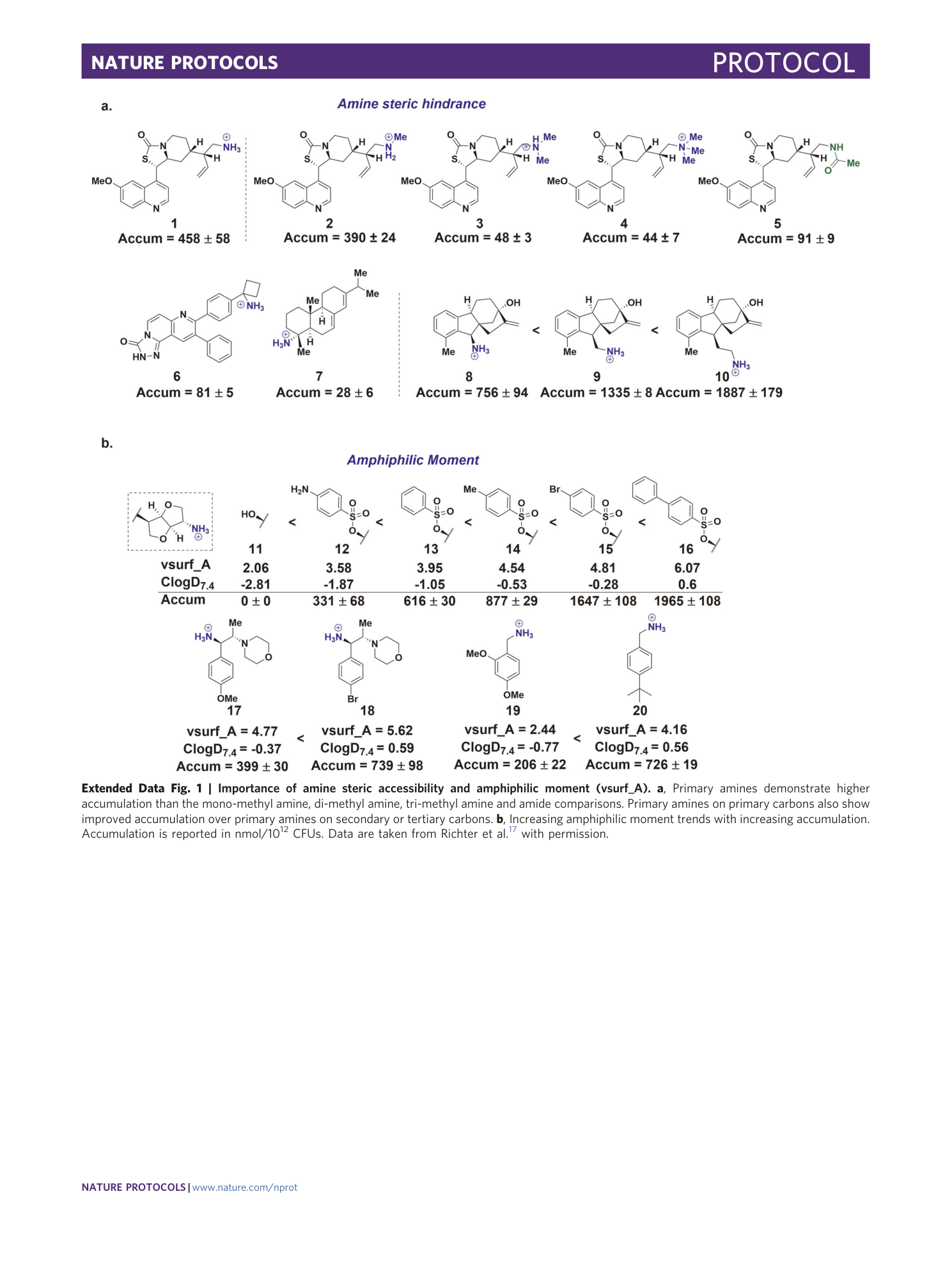
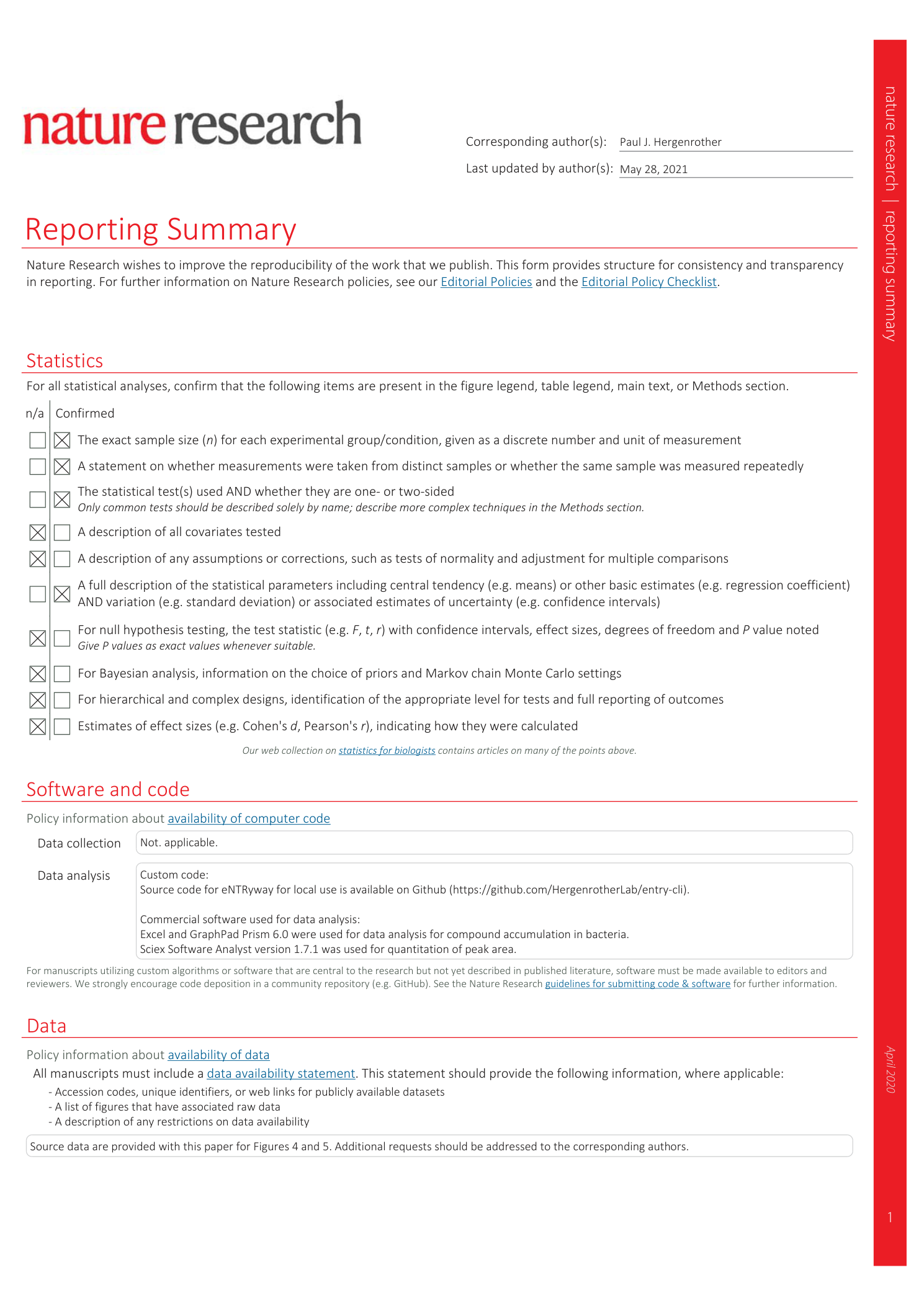
Extended Data Fig. 1 Importance of amine steric accessibility and amphiphilic moment (vsurf_A).
a , Primary amines demonstrate higher accumulation than the mono-methyl amine, di-methyl amine, tri-methyl amine and amide comparisons. Primary amines on primary carbons also show improved accumulation over primary amines on secondary or tertiary carbons. b , Increasing amphiphilic moment trends with increasing accumulation. Accumulation is reported in nmol/10 12 CFUs. Data are taken from Richter et al. 17 with permission.
Extended Data Fig. 2 Screenshot of the ‘input’ box for SMILES strings.
SMILES strings are canonicalized using Open Babel GUI.
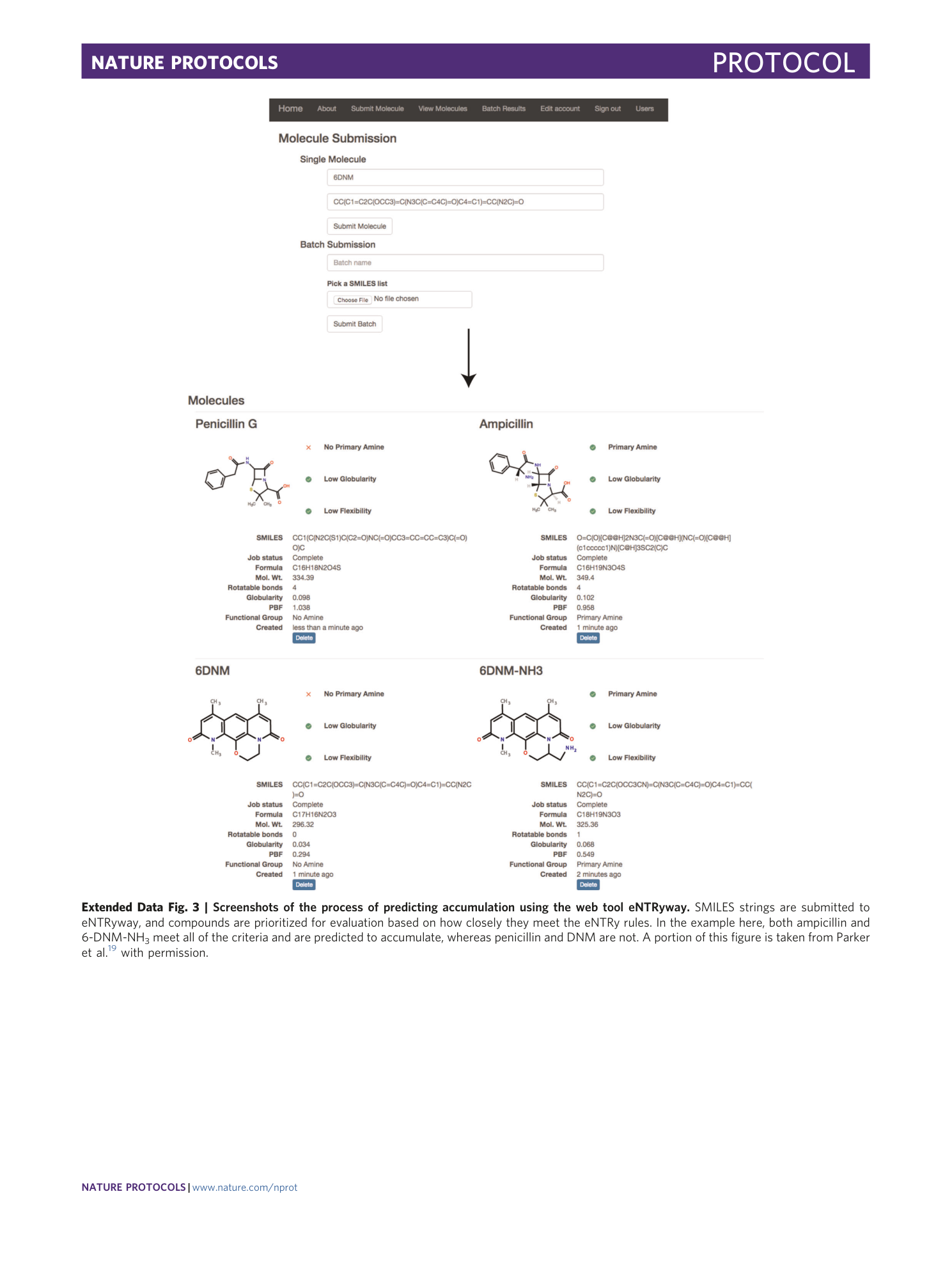
Extended Data Fig. 3 Screenshots of the process of predicting accumulation using the web tool eNTRyway.
SMILES strings are submitted to eNTRyway, and compounds are prioritized for evaluation based on how closely they meet the eNTRy rules. In the example here, both ampicillin and 6-DNM-NH 3 meet all of the criteria and are predicted to accumulate, whereas penicillin and DNM are not. A portion of this figure is taken from Parker et al. 19 with permission.

