Medulloblastoma and high-grade glioma organoids for drug screening, lineage tracing, co-culture and in vivo assay
Chiara Lago, Matteo Gianesello, Lucia Santomaso, Gloria Leva, Claudio Ballabio, Marica Anderle, Francesco Antonica, Luca Tiberi





























Extended
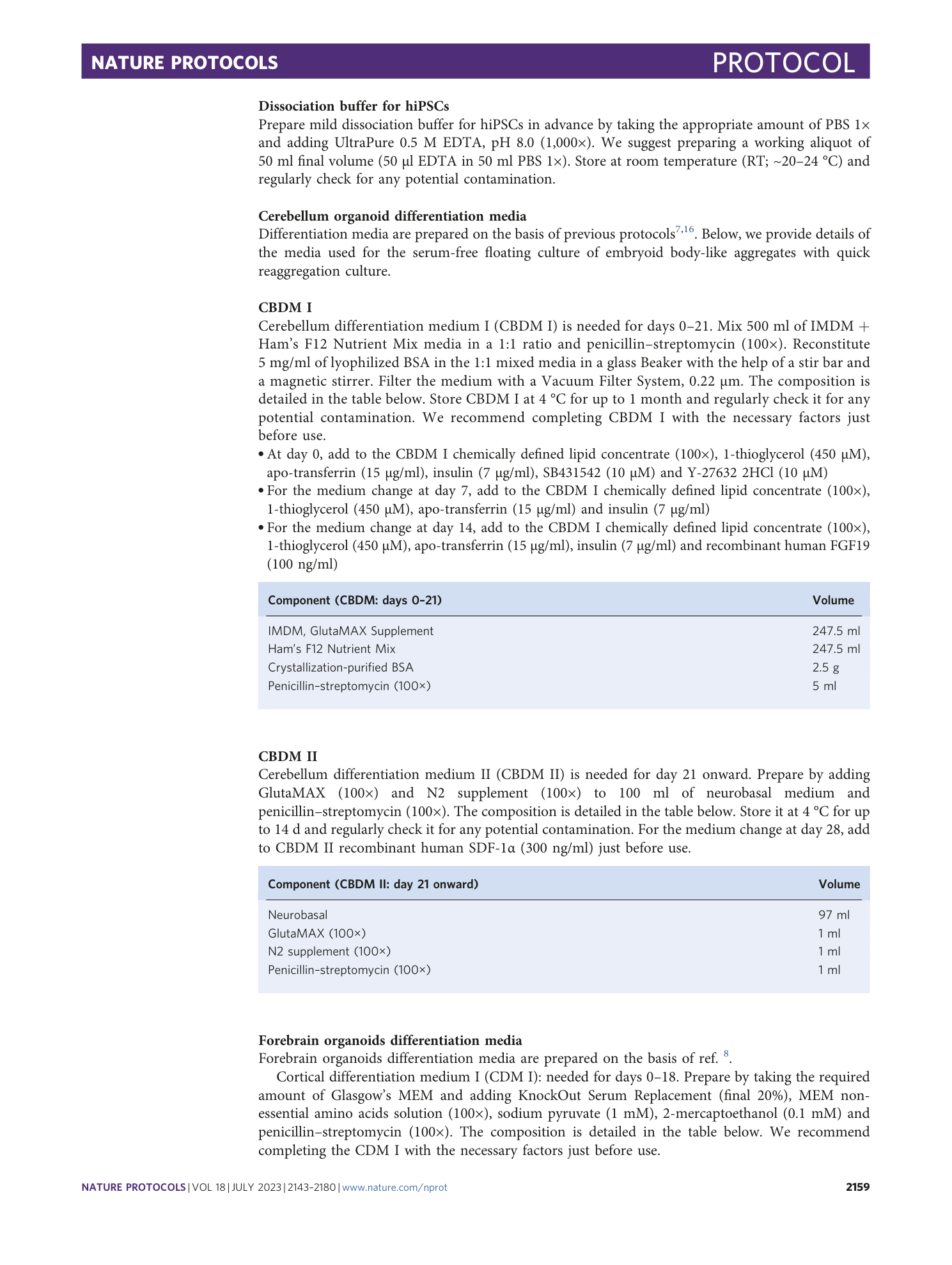
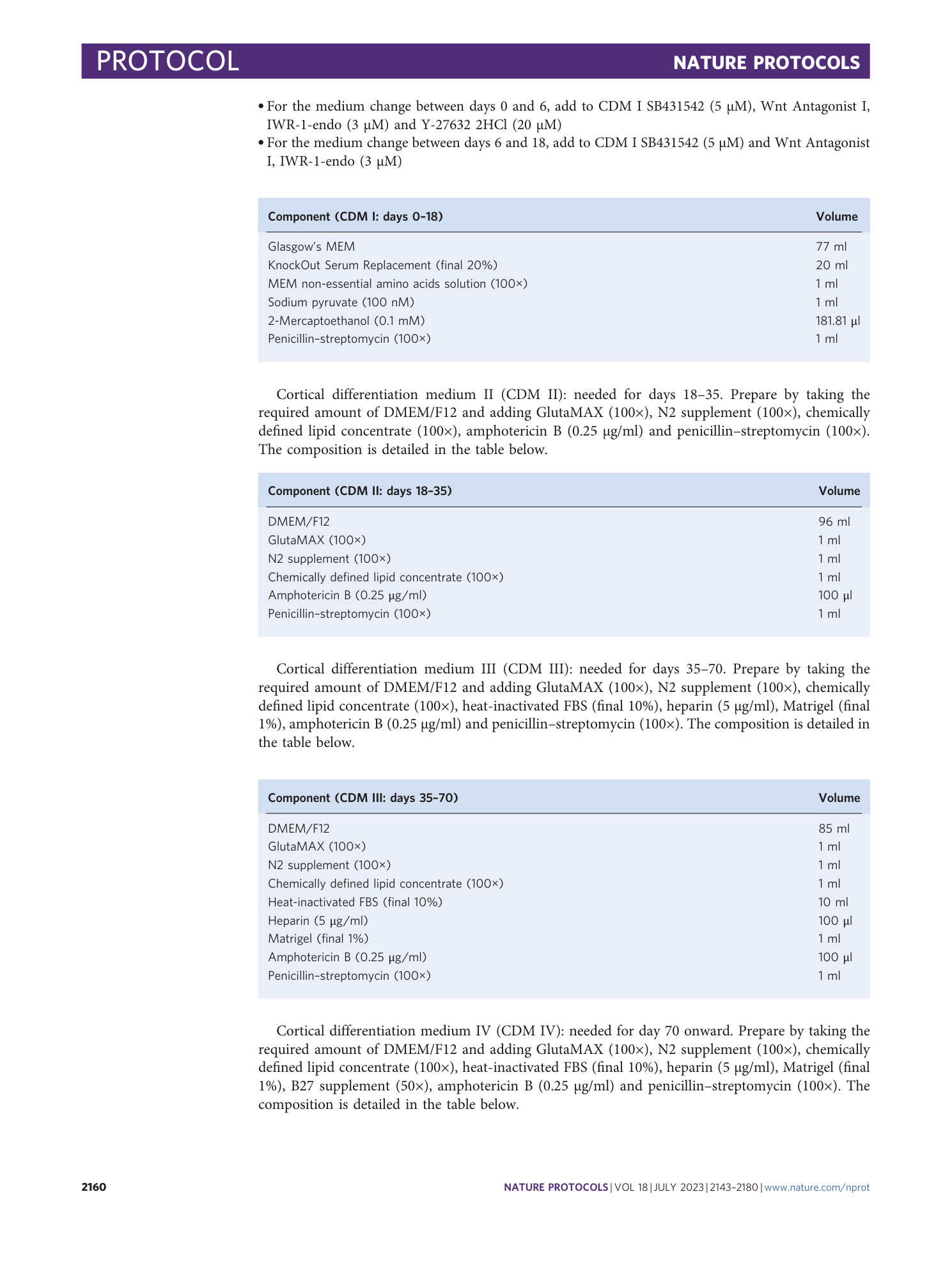
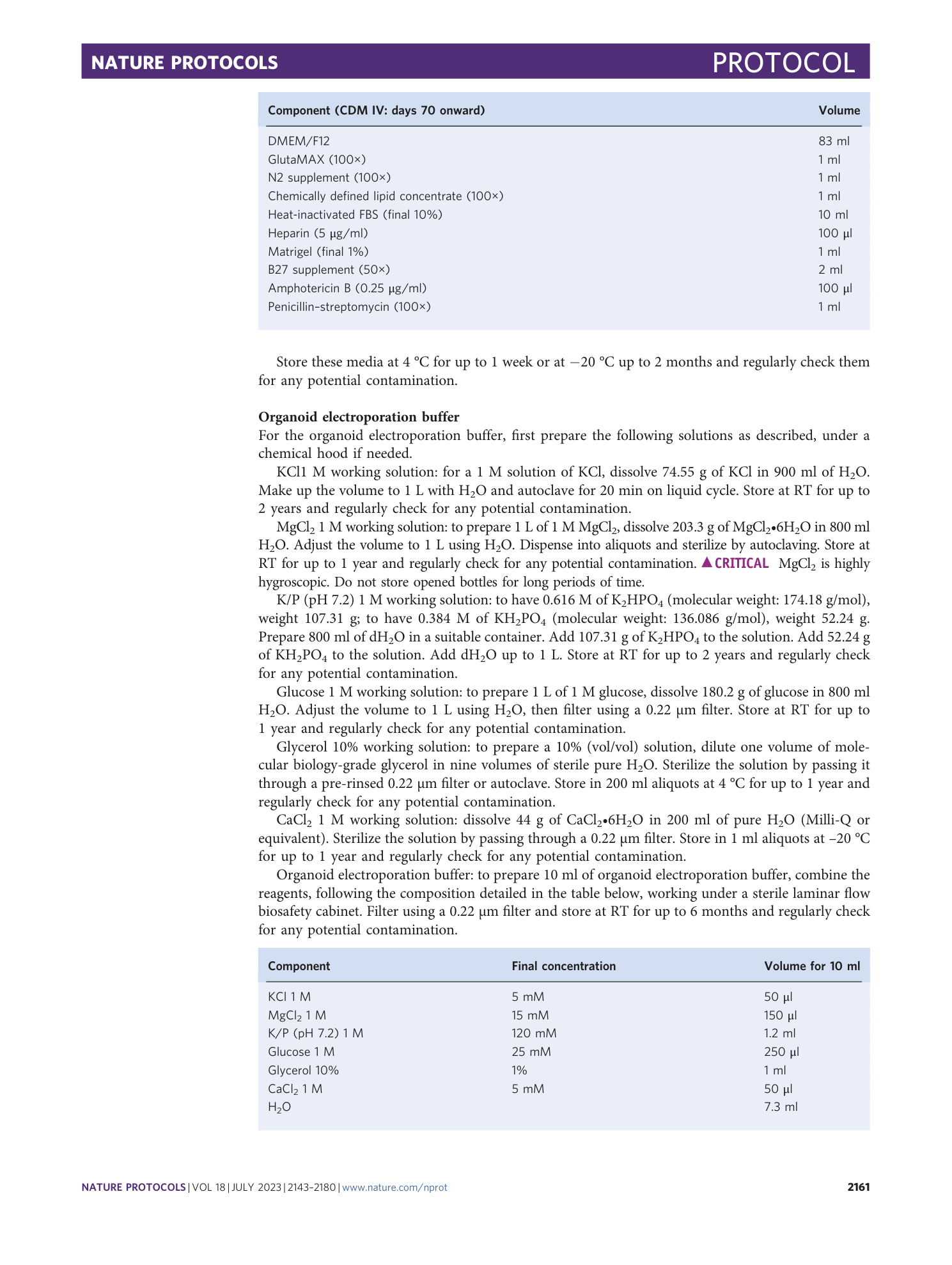
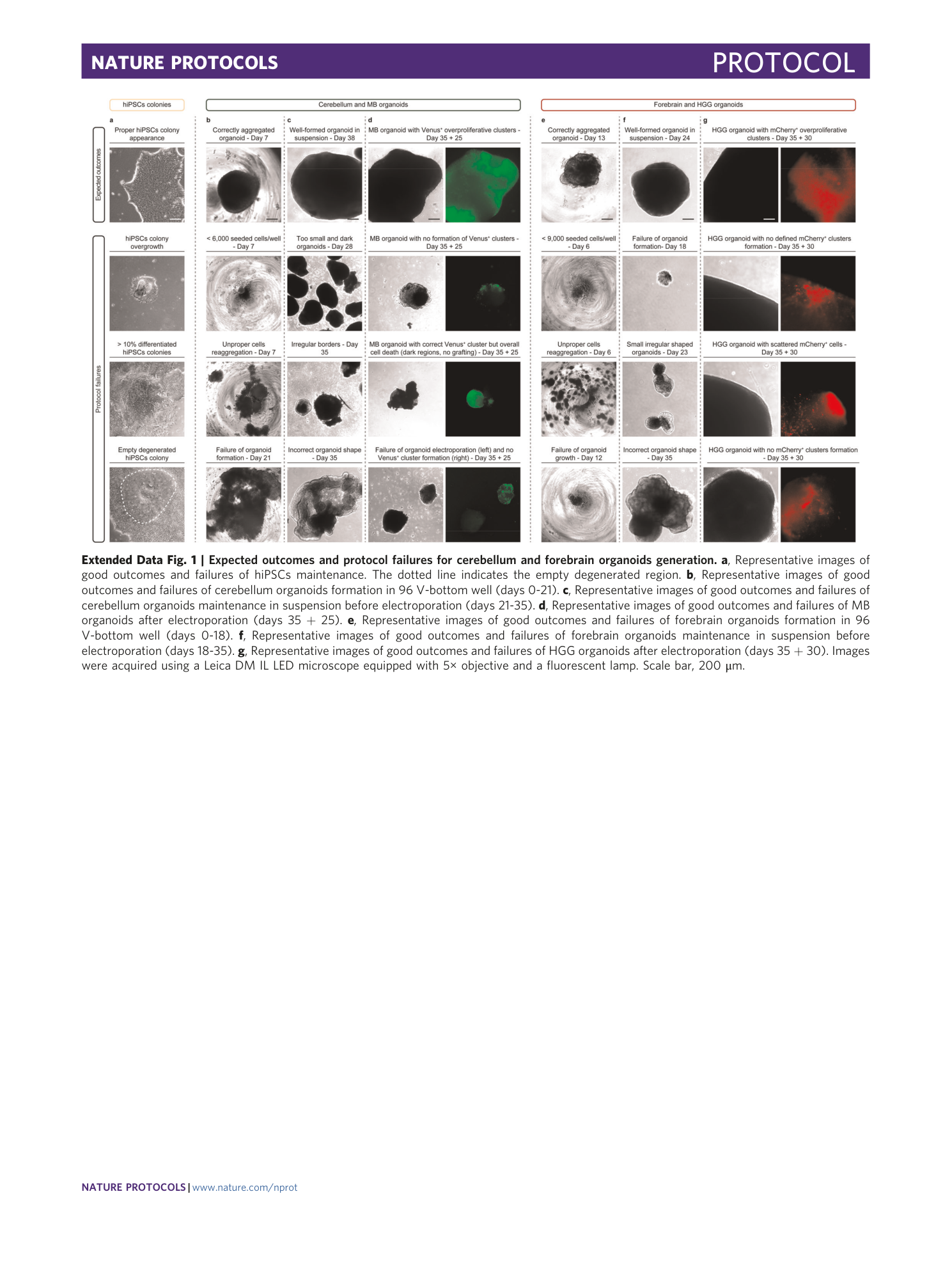
Extended Data Fig. 1 Expected outcomes and protocol failures for cerebellum and forebrain organoids generation.
a , Representative images of good outcomes and failures of hiPSCs maintenance. The dotted line indicates the empty degenerated region. b , Representative images of good outcomes and failures of cerebellum organoids formation in 96 V-bottom well (days 0-21). c , Representative images of good outcomes and failures of cerebellum organoids maintenance in suspension before electroporation (days 21-35). d , Representative images of good outcomes and failures of MB organoids after electroporation (days 35 + 25). e , Representative images of good outcomes and failures of forebrain organoids formation in 96 V-bottom well (days 0-18). f , Representative images of good outcomes and failures of forebrain organoids maintenance in suspension before electroporation (days 18-35). g , Representative images of good outcomes and failures of HGG organoids after electroporation (days 35 + 30). Images were acquired using a Leica DM IL LED microscope equipped with 5× objective and a fluorescent lamp. Scale bar, 200 μm.
Extended Data Fig. 2 Necessary equipment for transplantation procedure.
a , Representative image of the necessary equipment to perform the transplantation procedure of organoids in immunocompromised mice (Step 36A). b , Representative image showing the equipment setup of Hamilton syringe and pups adaptor on the stereotactic apparatus.

