Isolation of ready-made rat microvessels and its applications in effective in vivo vascularization and in angiogenic studies in vitro
Xuetao Sun, Yasaman Aghazadeh, Sara S. Nunes














Extended
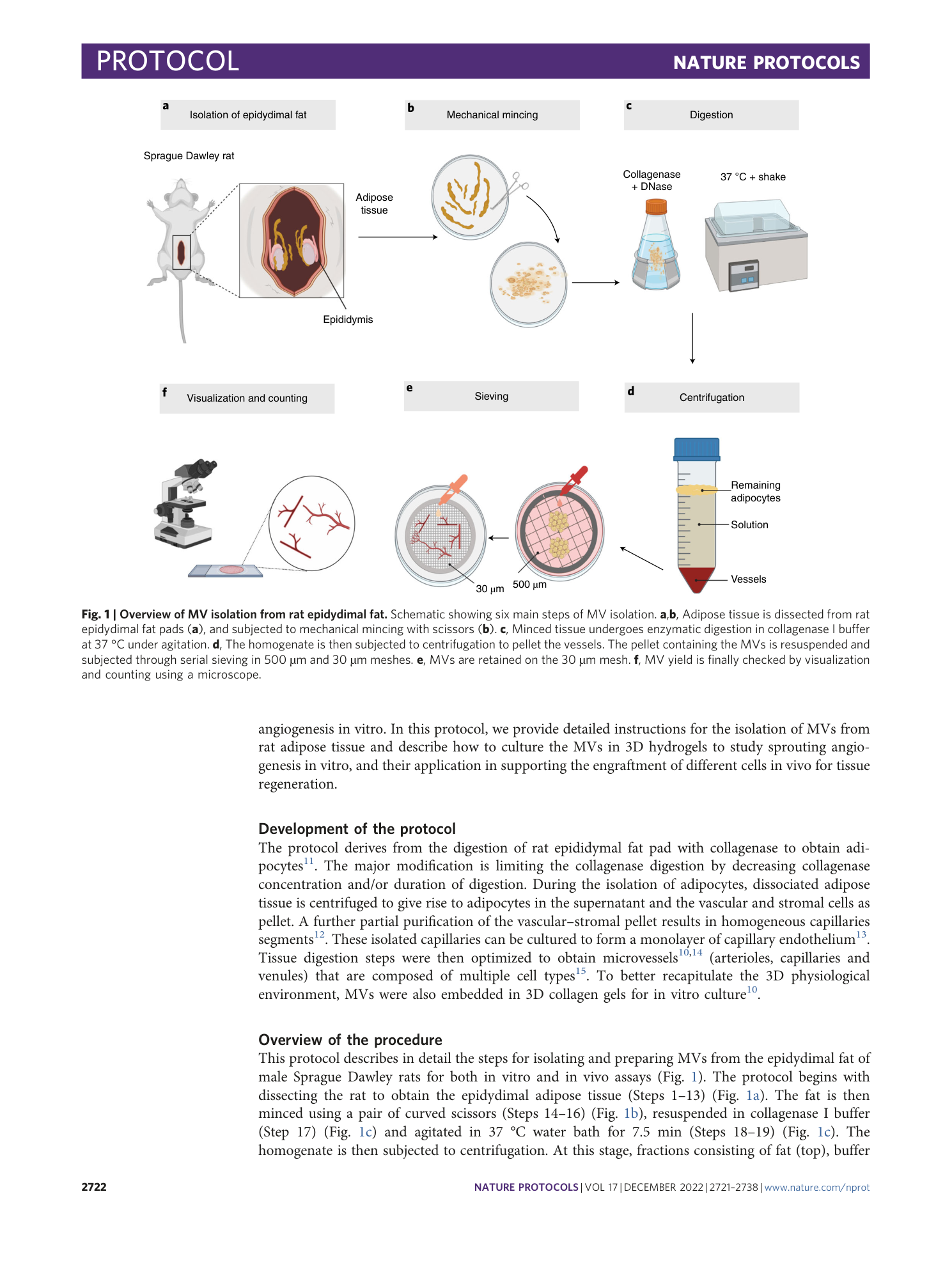
Extended Data Fig. 1 Optimization of enzymatic treatment.
Digestion time should be experimentally optimized for each lot of collagenase I. We often test approximately five lots at a time, keeping the collagenase concentration constant (2 mg/ml) but varying the incubation time to find the optimal incubation time for a specific lot. a – c , Adipose tissue is harvested ( a ), minced ( b ) and subjected to collagenase digestion ( c ). The enzymatic digestion is monitored over time by sampling it every ~2–3 min for up to ~15 min and observing under the microscope. This will define the optimal incubation time (i.e., the timepoint when MVs are abundant). d – g , Once defined, we repeat that isolation procedure at the optimized timepoint, purify the MVs by sieving ( d – f ) and then cast MVs in 3D gels at 20,000 MVs/ml of gel ( g ). h , MV growth is monitored for 1 week. i , Lot selection is based on MV growth in 3D and yield. We select the lot that produces the highest MV yield within the ones that show robust angiogenic growth. Of note, most MVs once cast in 3D collagen gels will grow well; however, yields vary a lot depending on the lot. Once a protocol is established for a new lot, a second experimenter repeats the isolation using the new lot and optimized protocol. The current optimized incubation time in our lab lot is 7.5 min. j , Yields range from 5,000 to 10,000 MVs per milliliter of fat, with three people performing the isolation. Refer to main text for details for a , b and d – g .
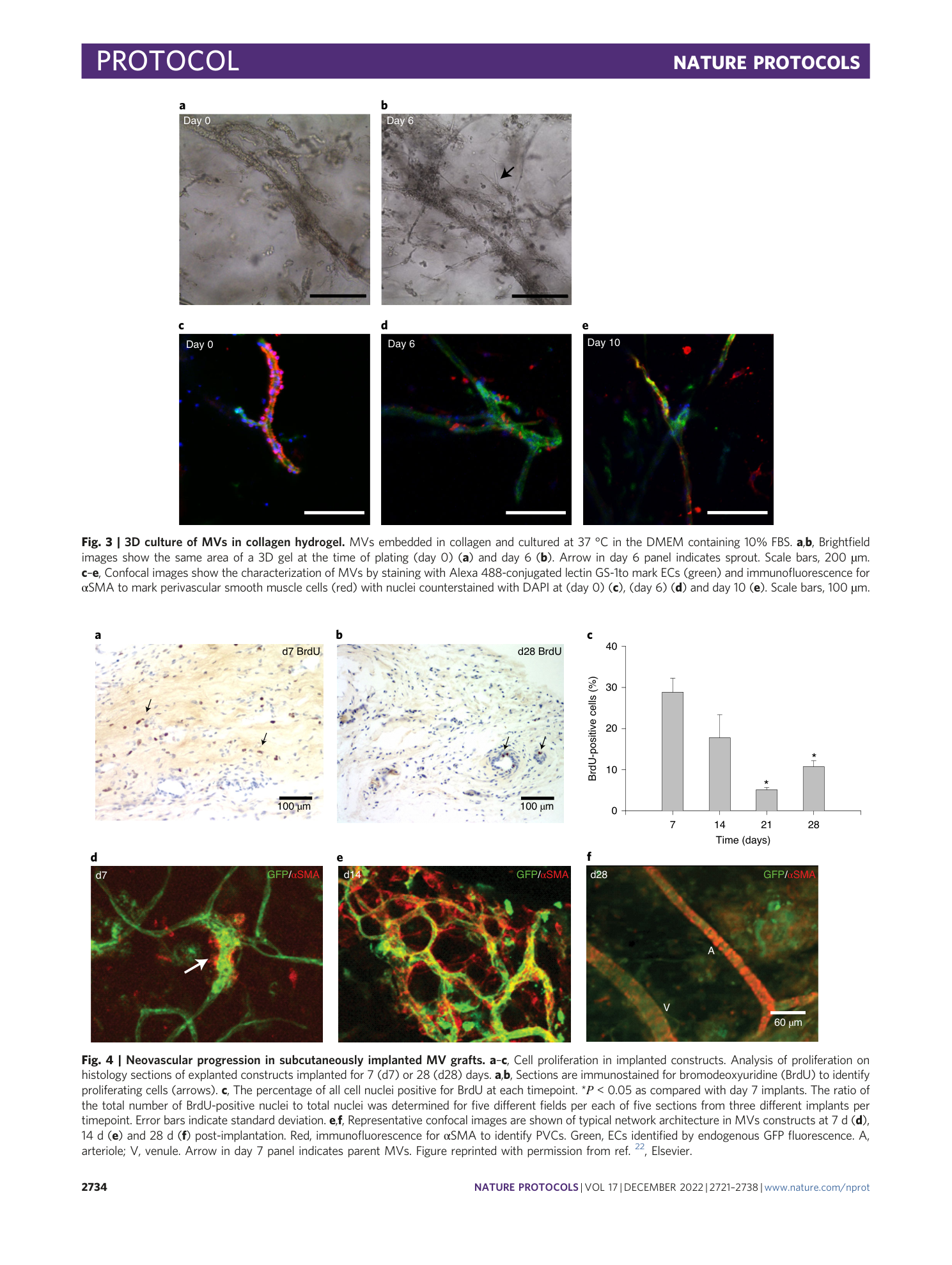
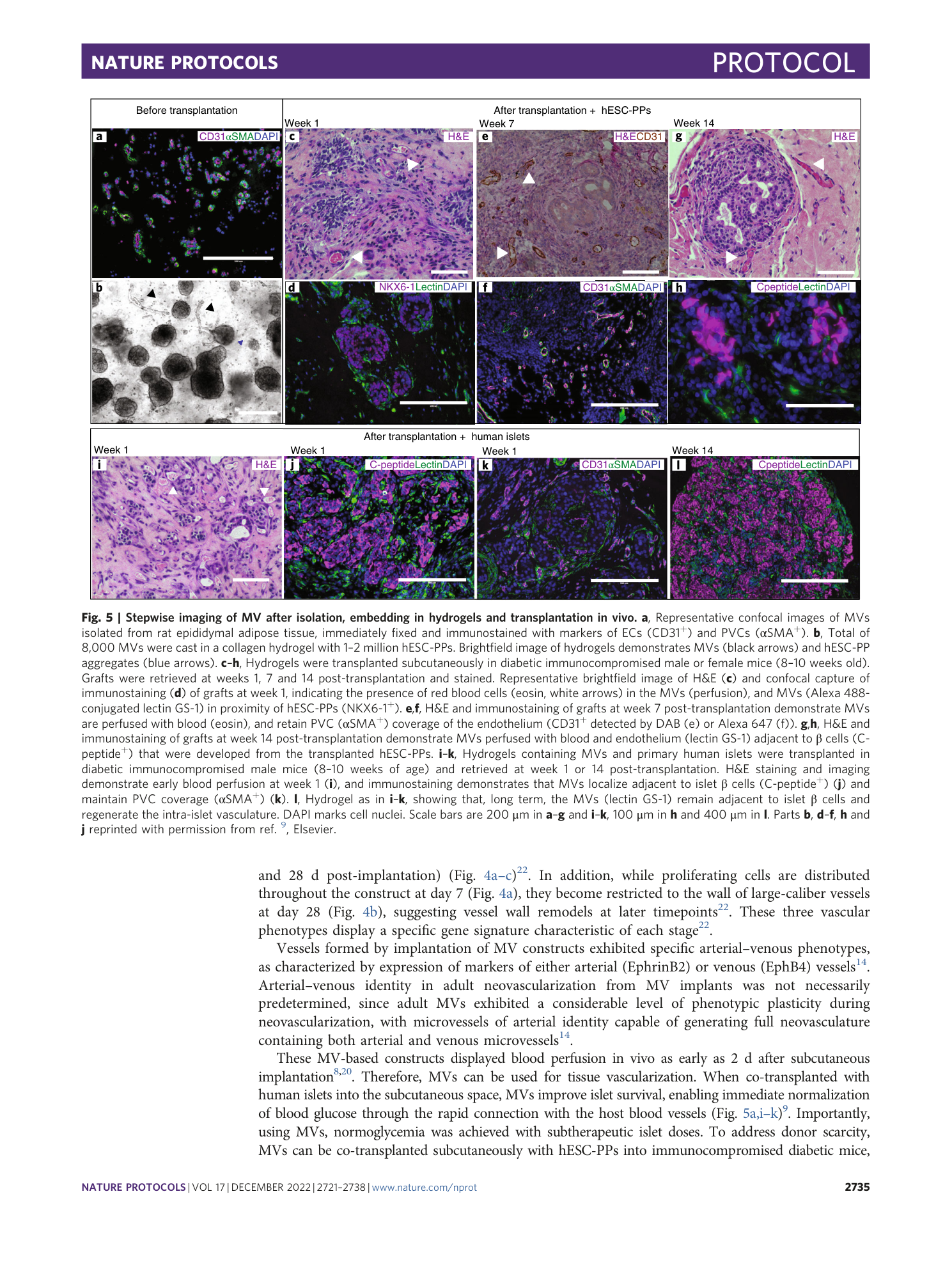
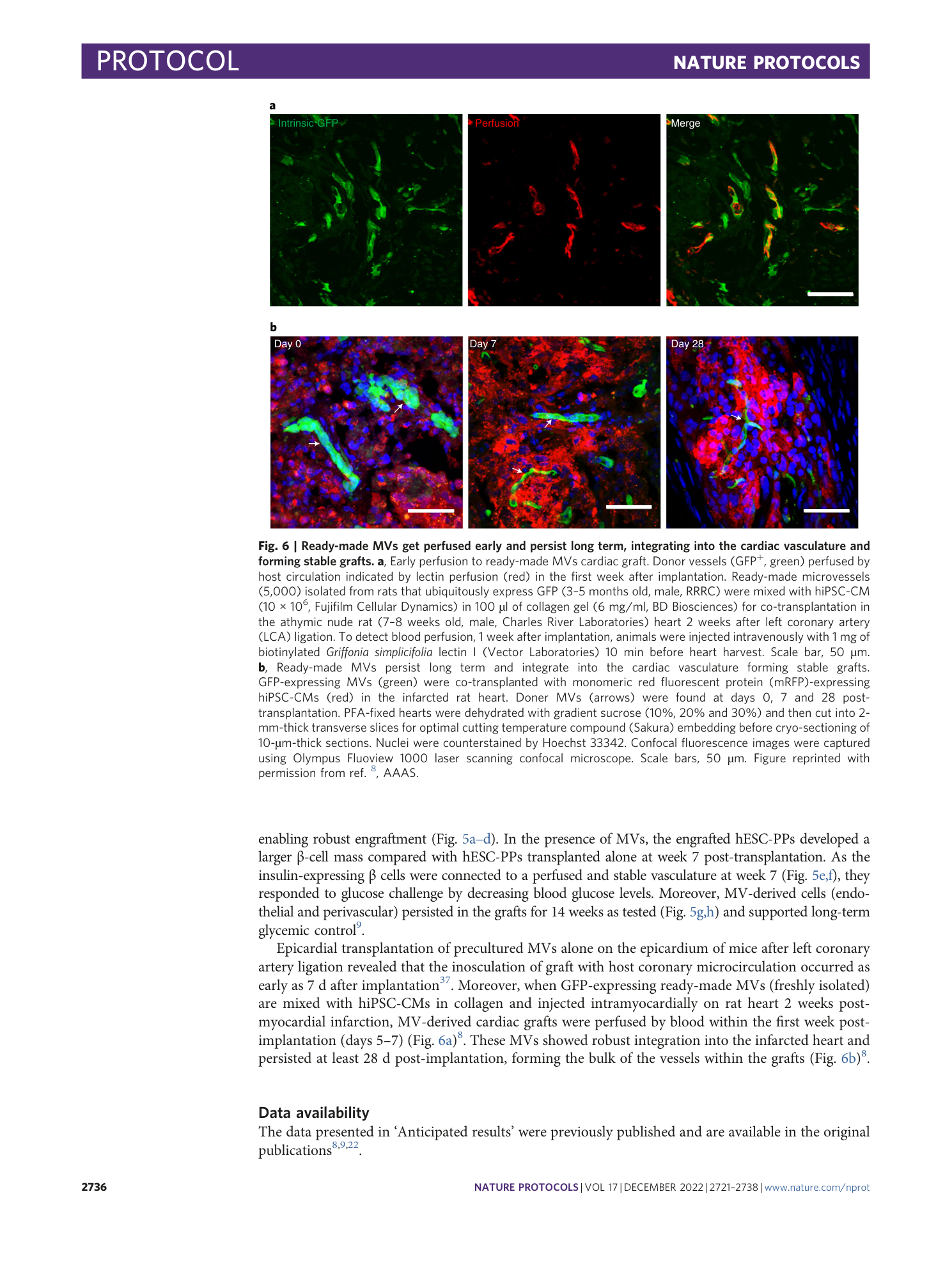
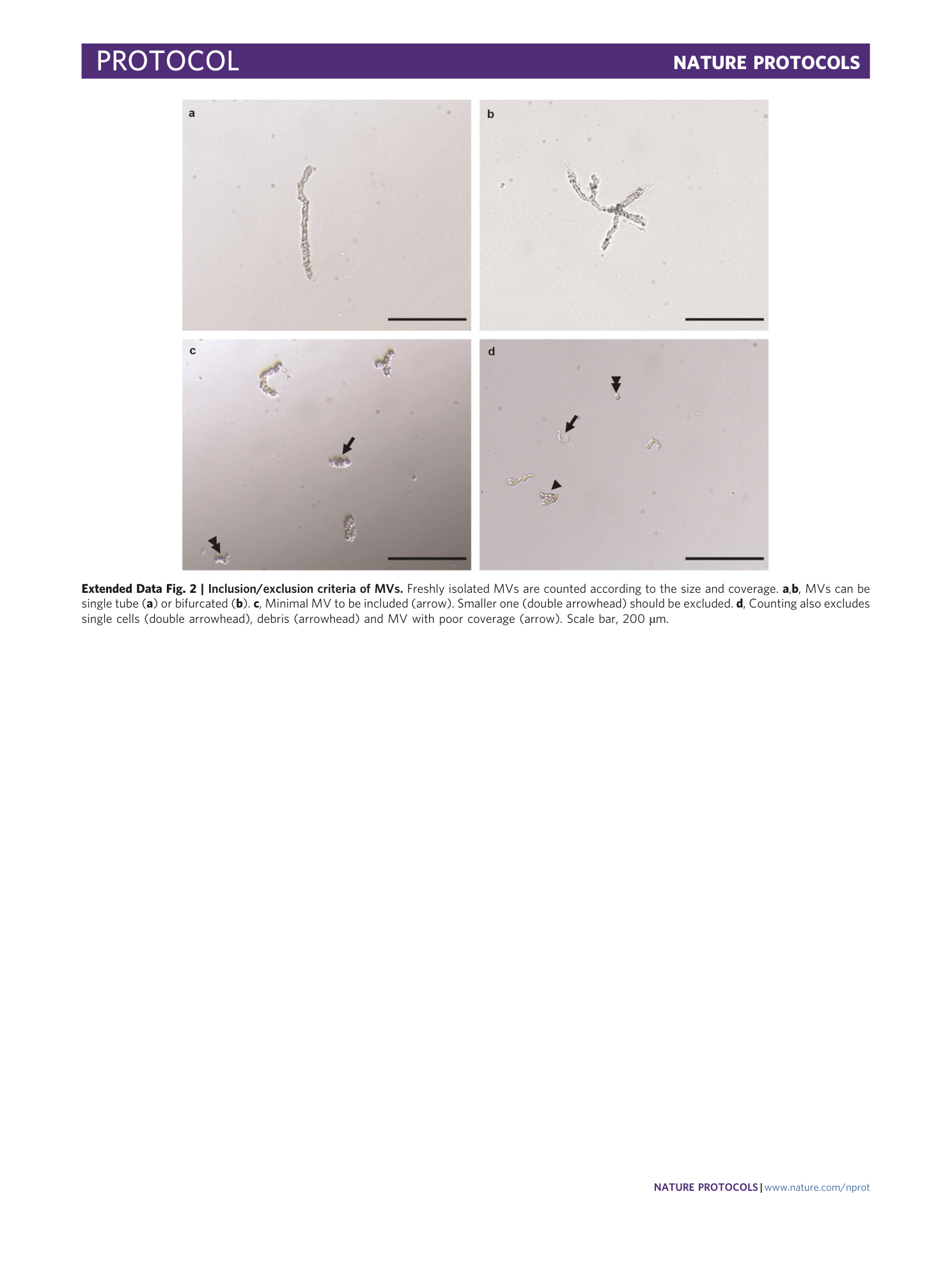
Extended Data Fig. 2 Inclusion/exclusion criteria of MVs.
Freshly isolated MVs are counted according to the size and coverage. a , b , MVs can be single tube ( a ) or bifurcated ( b ). c , Minimal MV to be included (arrow). Smaller one (double arrowhead) should be excluded. d , Counting also excludes single cells (double arrowhead), debris (arrowhead) and MV with poor coverage (arrow). Scale bar, 200 µm.
Extended Data Fig. 3 pH of collagen hydrogel.
a , Stock collagen is acidic. b , pH of working collagen hydrogel is ~7.4 as verified by pH strips.
Extended Data Fig. 4 Handling collagen constructs.
After the collagen hydrogels have become completely solidified, keep constructs in medium until implantation. a , Tilt the plate to a 45° angle to help hydrogel detach from the bottom of the well. b , Place the forceps around the hydrogels, and pick it up without applying pressure. c , Using a second pair of forceps, gently open the incision made in the dorsal area of the mouse and gently push the hydrogel inside the opening.

