Annexin V/PI- Assay: Flow Based Medium Throughput Assessment of Apoptotic Response to Two and Three Drug Combinations
Dennis Juarez, David Fruman
Disclaimer
DISCLAIMER – FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY; USE AT YOUR OWN RISK
The protocol content here is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, medical, clinical, or safety advice, or otherwise; content added to protocols.io is not peer reviewed and may not have undergone a formal approval of any kind. Information presented in this protocol should not substitute for independent professional judgment, advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Any action you take or refrain from taking using or relying upon the information presented here is strictly at your own risk. You agree that neither the Company nor any of the authors, contributors, administrators, or anyone else associated with protocols.io, can be held responsible for your use of the information contained in or linked to this protocol or any of our Sites/Apps and Services.
Abstract
Basic principals and protocol for medium throughput cell viability screening in suspension cells using Annexin V/PI staining on the Attune NXT used in the Fruman lab.
Steps
Basic Principals and Planning Before Proceeding
In vitro viability experiments should not be underestimated; especially, when carried out in a higher throughput fashion.
With a structured an organized plan, a 96 well two drug combination response surface experiment can be plated in 30 minutes; whereas, a poorly thought out and planned experiment can eat away several hours of your day and can lead to non-meaningful results as prolonged experimental setup can affect your media quality and cell quality.
Several dilutions are required. To standardize the discussion, it's crucial to understand these key terms:
Stock Concentration: Refers to the concentration of the aliquots in long-term storage. Often stock concentrations are based on solubility of a compound or a practical concentration for aliquoting. As such, stock concentrations can be many times more concentrated than the final concentration.
Working Concentration: Refers to the concentration of any intermediate dilution of a drug in vehicle or media. As such, they are any concentration besides 1x and the stock concentration.
Final Concentration: Refers to the concentration of a drug which a cell is exposed to for the duration of the experiment. This is also known as 1x.
Cells in culture can only tolerate small amounts of the vehicle in which a drug is dissolved in.
As such, you should minimize and standardize the amount of vehicle used in an experiment across all treatments.
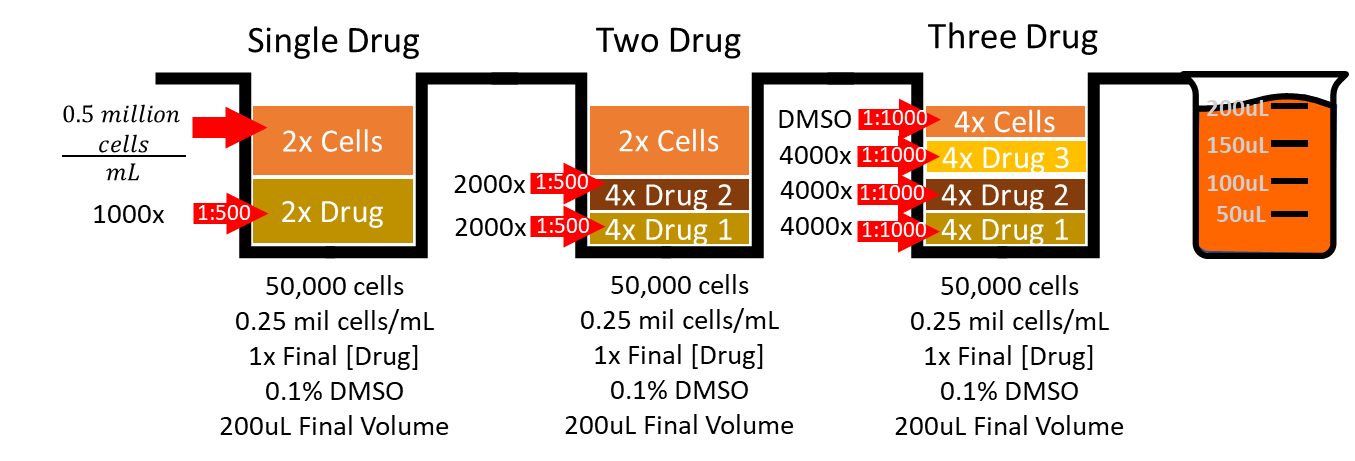
I cap all experiments at 0.1% DMSO in the final experimental condition (1:1000 dilution of DMSO in media).
Single drug treatments are thus prepared at working dilutions that are 1000x their final concentration with DMSO.
Each agent of two drug treatments are prepared at working dilutions that are 2000x their final concentration.
Each agent of three drug combination treatments are prepared at working dilutions that are 4000x their final concentration.
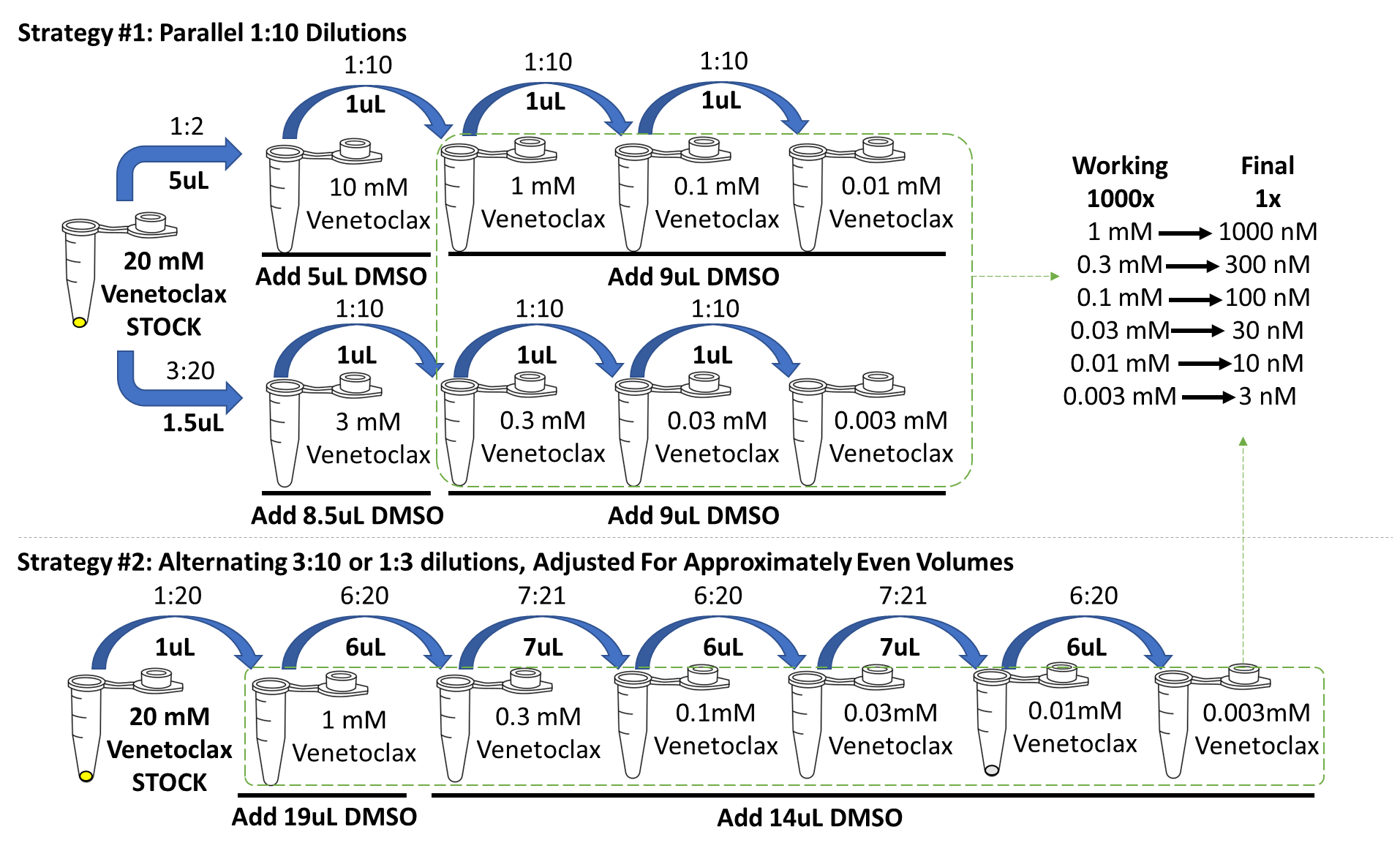
Precision is key when carrying out these assays. Minimize variation by stepwise dilutions and using volumes that are easy to pipet and verify.
In regards to preparing your working dilutions, stepwise dilution results in greater precision than direct dilution.
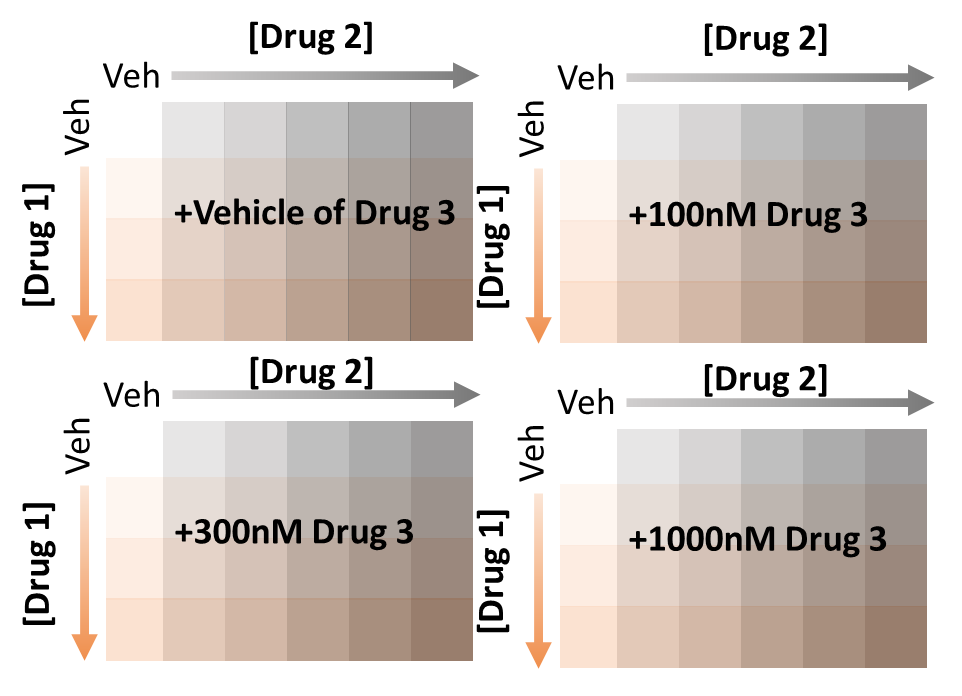
Plan your plate set up to include all single drug controls. To accomplish this, I recommend setting up a matrix.
Prepare Dilutions and Plate Drugs
Prewarm your media.
Prepare your DMSO-based working dilutions sterilely. From your stock solution, make your DMSO-based working dilutions per your experimental design in step 3.
Dilute your DMSO-based working dilutions into prewarmed media from step 7 as depicted in step 3. Only make as much as you need for each drug.
Calculate this by multiplying the volume you will use per well by the number of wells that will get the specific drug dose. Make extra.
Think of the vehicle column and rows of your matrix as a drug and prepare an appropriate dilution per step 3 of DMSO in media. Usually you'll need more of this than the other drug doses.
Using 8 channel reservoirs and a multichannel pipet, distribute your drugs into a 96 well flat bottom.
- To minimize tip usage, you can reuse tips for multiple wells receiving the same drug.
- In order to minimize well to well contamination with other drugs, deliver your first drug on the bottom of the plate. Your second drug should be delivered on the side wall of the plate. Your third drug will be delivered on the opposite side wall of the plate.
When plating of all the drugs is complete, place the plate in the incubator. Plan to minimize this amount of time without the cells to avoid unnecessary evaporation.
If you have a lot of cell lines that you will be plating, you can count your cells before starting your dilutions and drug plating. If you have a couple of cell lines, then preparing them next will not be too time consuming.
Preparing and Plating Cells
Count your cells and either resuspend in fresh media or dilute cells to get them to either 0.5 million per mL or 1 million per mL if carrying out a triple combination.
If doing a triple combination, don't forget to add 1:1000 DMSO to the cells.
Transfer the appropriately concentrated cells to a reservoir and pull your plate with drugs from the incubator.
Deliver cells by multichannel to an unused side wall.
Incubate from 24-72 hours depending on your experiment.
Annexin V PI Staining and Readout
After completion of incubation, transfer 100 uL of cells to a V-Bottom well plate. Centrifuge at 500g x 5 min
Annexin V PI staining
Resuspend in 100uL of 1:2000 Annexin V and 1:2000 propidium iodide diluted in annexin V binding buffer and transfer to a U-Bottom well plate.
After 5 minutes, the samples should be ready to read on the attune with the high throughput setting checked.

