QuPath Visualization/Segmentation
Michael X. Henderson
Abstract
This protocol describes QuPath visualization/segmentation.
Attachments
Steps
QuPath Visualization/Segmentation
Open QuPath . Click “Create Project.”
Upload series of images into new project on QuPath. Don’t worry about what the images are named or how they are ordered yet.
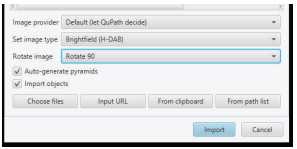
Adjust settings for images prior to import. Our typical settings are shown in the image to the right, although these may change (for example, for fluorescent images).
Image Export for Registration
Click File > Export images > Original pixels > Export format (PNG), Downsample factor (12.0).
Save in QVN folder with appropriate Naming Designation of choice.
Move images to the QVN folder.
Color Deconvolution
This defines what QuPath will see as brown and what it will see as blue. Color settings should be kept constant for a project. Generally, settings should be similar as long as you are using the same chromogen and same microscope. However, we have found that the default settings in QuPath are not ideal so these settings will need to be changed in each project. This can be done with a simple analysis script. Information on Setting Stain Vectors in QuPath is included in the Appendix. Set the color deconvolution by going to the “Image” tab. Draw a rectangle over the desired color from pathology (be as specific as possible).
Click on the “Image” tab.
Draw a rectangle over a pure brown part of the image (9 pixels+).
Click on the “DAB” and it will ask you if you want to “Set stain vector from ROI” and click yes.
If you are doing multiple images, go to the “Workflow” tab and click on “Set color deconvolution stains” under it and click “create script” and run the script it has automatically created you for all images. You NEED to do this before setting your thresholder and running it for consistent results.
Segmentation
Name each annotation with abbreviated name designation found in the final column of the QUINT section log and described in Step 7.
Right click on the rectangle annotation in the annotation tab and select “Set Properties”.
Write the abbreviated name you would like your input file to be denoted as in the ‘Name’ box and select ‘OK’.
Repeat for all desired annotations.
Load your classifier for this project: Classify > Pixel classification > Load pixel classifier.
Choose the correct classifier and “Any annotations.” Click “Create Objects.”
Create objects: leave settings as they are, and click “OK.”
Click “Annotations” tab. Navigate to Annotations tab on the left side of the program screen and click it. Find the Annotation (Geometry) you just generated. Right click the row and select “Unlock”.
Remove artifactual stain (see Appendix for examples; bubbles, edge effect, vasculature).
To erase, hold down the Alt key while erasing artifacts.
After completing erase of artifact select “Automate” > Show script editor.
Script Editor: enter the script listed below into the box at line “1” and press Crtl + R to run. This will create your segmentation images that will be used in Nutil.
Code to Run:
import qupath.lib.images.servers.LabeledImageServer
def imageData = getCurrentImageData()
// Define output path (relative to project)
def name = GeneralTools.getNameWithoutExtension(imageData.getServer().getMetadata().getName())
def pathOutput = buildFilePath(PROJECT_BASE_DIR, 'export', name)
mkdirs(pathOutput)
// Export at full resolution
double downsample = 1.0
// Create an ImageServer where the pixels are derived from annotations
def labelServer = new LabeledImageServer.Builder(imageData)
.backgroundLabel(0, ColorTools.WHITE) // Specify background label (usually 0 or 255)
.downsample(downsample) // Choose server resolution; this should match the resolution at which tiles are exported
.addLabel('Positive', 1) // Choose output labels (the order matters!)
.multichannelOutput(false) // If true, each label refers to the channel of a multichannel binary image (required for multiclass
probability)
.build()
// Export each region
int i = 0
for (annotation in getAnnotationObjects()) {
name = annotation.getName()
if (annotation.getROI().getRoiName() == "Rectangle") {
def region = RegionRequest.createInstance(
labelServer.getPath(), downsample, annotation.getROI())
i++
def outputPath = buildFilePath(pathOutput, name + '.png')
writeImageRegion(labelServer, region, outputPath)
}}
Find exported images in your folder scheme under QuPath\export . The segmentation image should be a black and white image with objects in black. The images should be the exact same dimensions of the earlier region of interest image you created as a PNG with a downsize factor of 12.
Plate the image and place into “ Input ” folder that will be used in final Nutil step.