Preparation of single-cell suspensions of mouse glomeruli for high-throughput analysis
Ben Korin, Jun-Jae Chung, Shimrit Avraham, Andrey S. Shaw

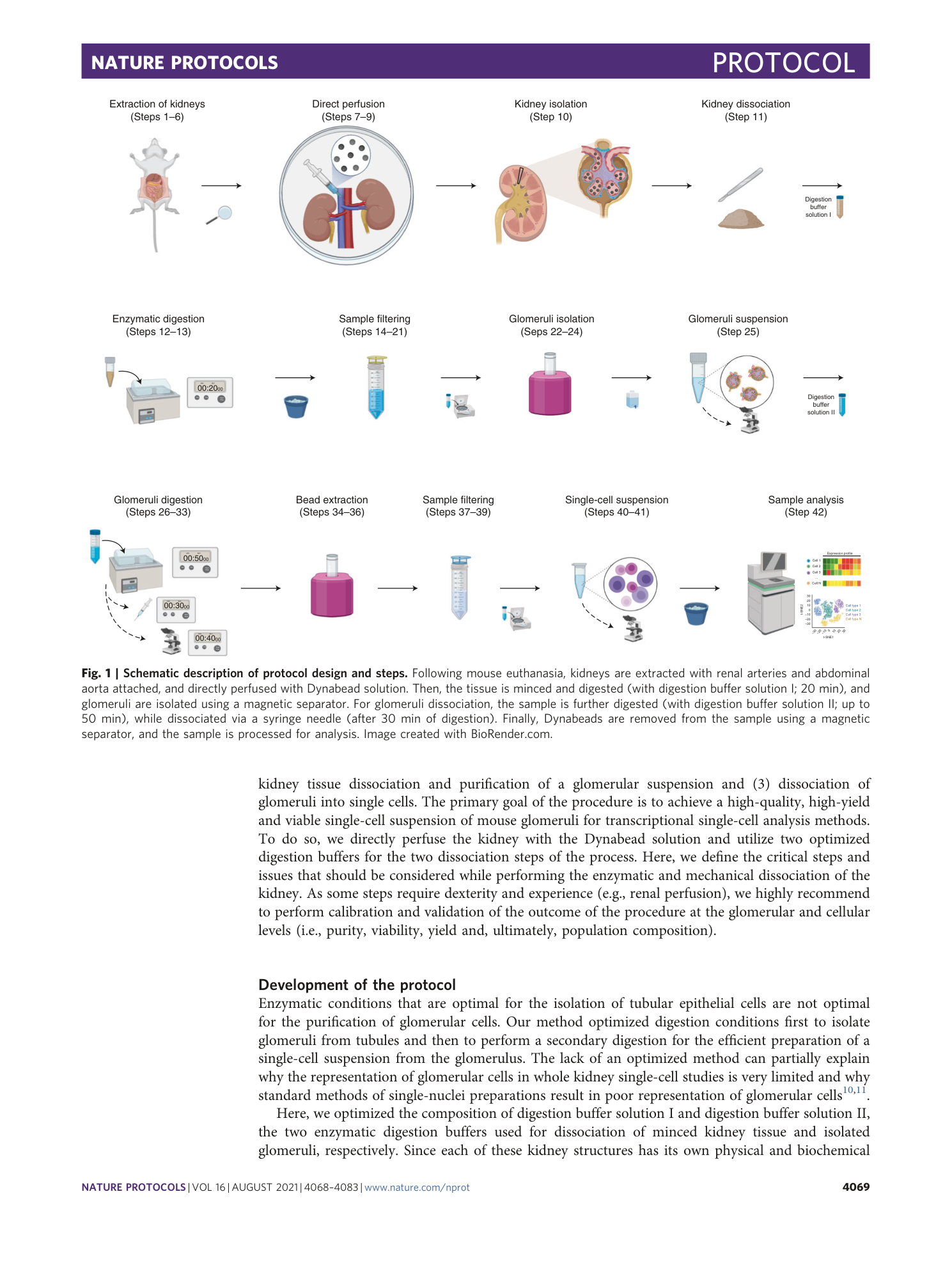














Extended
Extended Data Fig. 1 Preparation of a semi-dulled needle for renal perfusion.
Representative image of a semi-dulled 27½ gauge needle used for direct perfusion via the renal arteries. Images were taken using 1080P Full HD Digital Microscope.
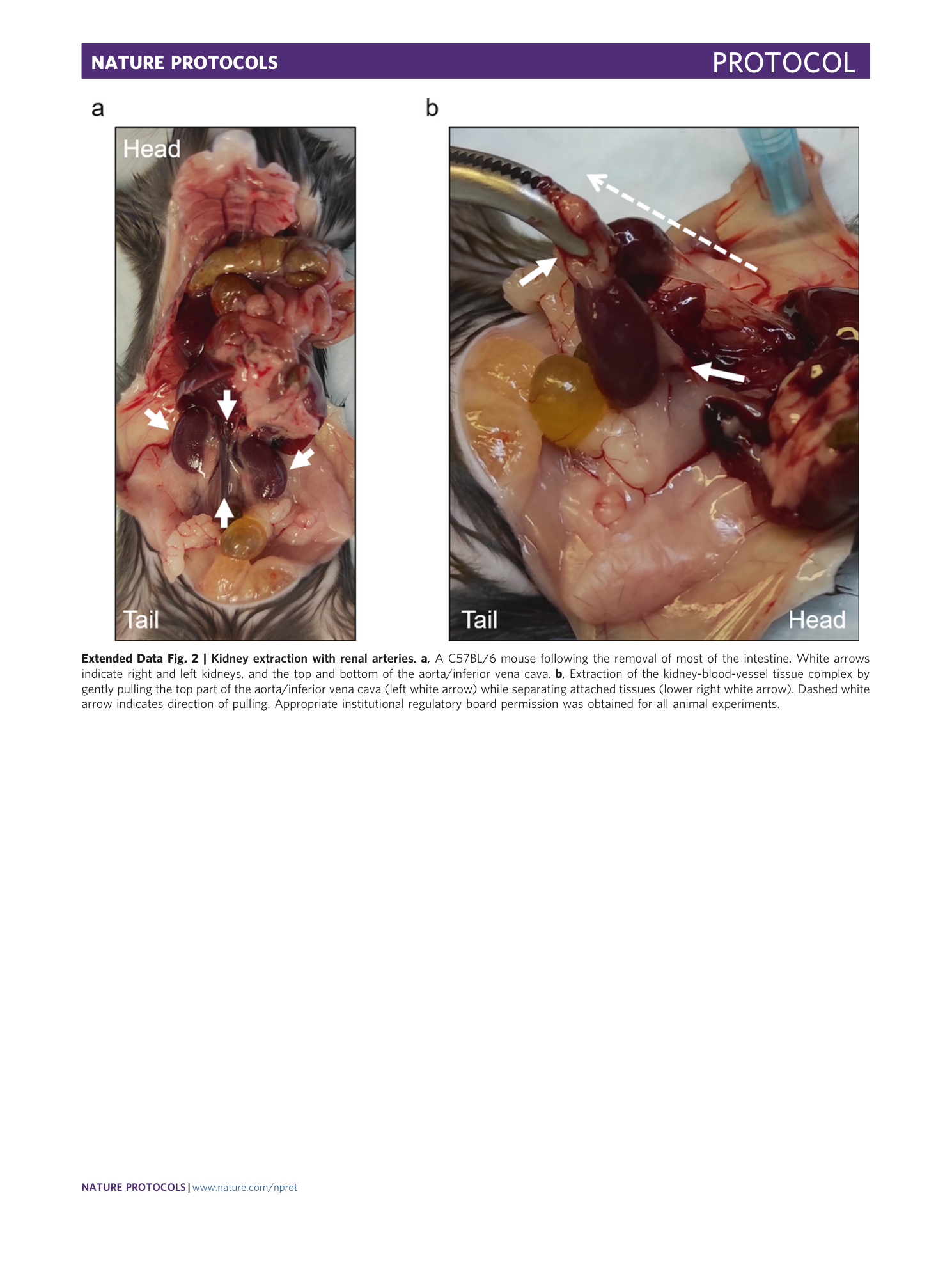
Extended Data Fig. 2 Kidney extraction with renal arteries.
a , A C57BL/6 mouse following the removal of most of the intestine. White arrows indicate right and left kidneys, and the top and bottom of the aorta/inferior vena cava. b , Extraction of the kidney-blood-vessel tissue complex by gently pulling the top part of the aorta/inferior vena cava (left white arrow) while separating attached tissues (lower right white arrow). Dashed white arrow indicates direction of pulling. Appropriate institutional regulatory board permission was obtained for all animal experiments.
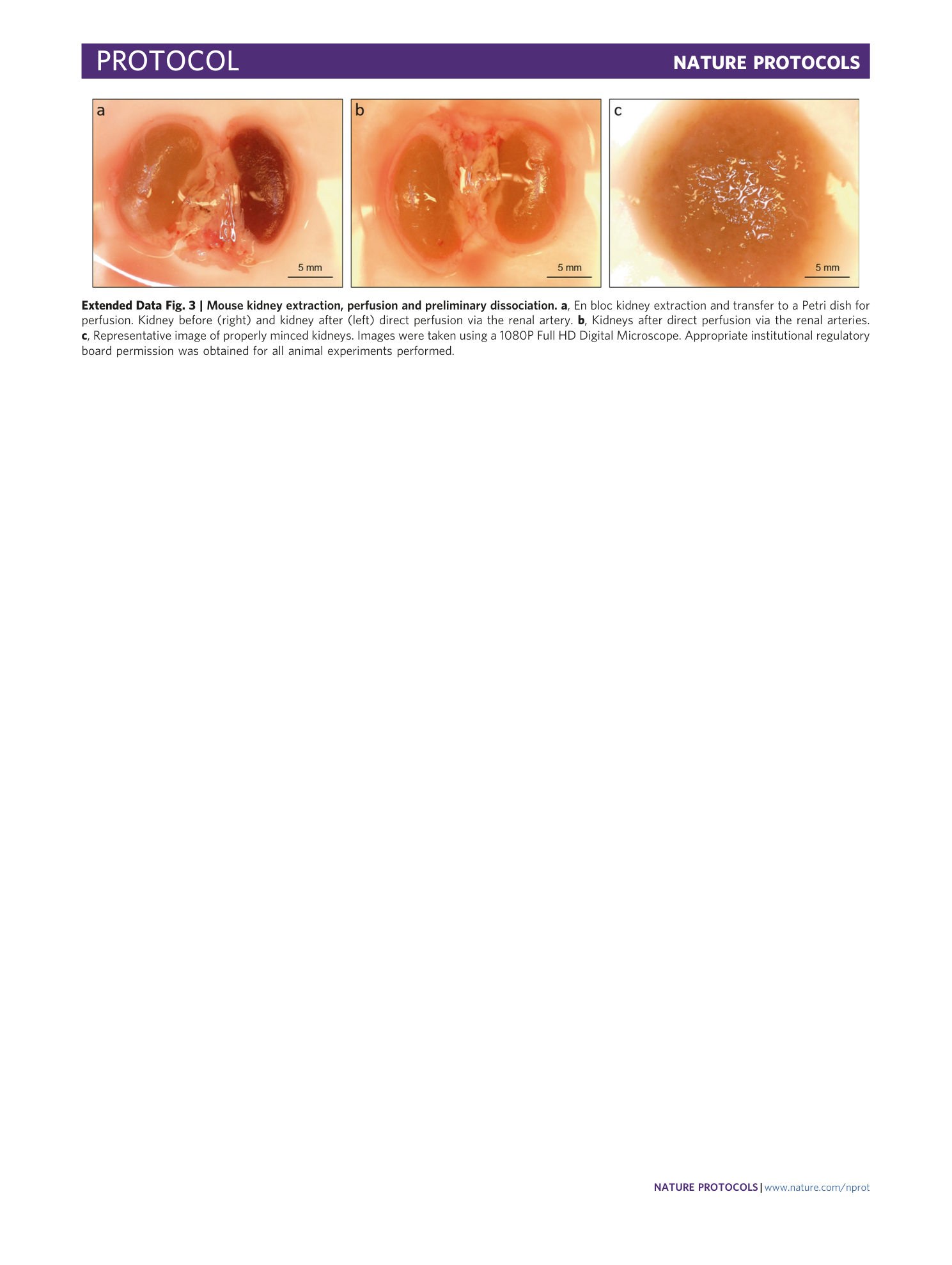
Extended Data Fig. 3 Mouse kidney extraction, perfusion and preliminary dissociation.
a , En bloc kidney extraction and transfer to a Petri dish for perfusion. Kidney before (right) and kidney after (left) direct perfusion via the renal artery. b , Kidneys after direct perfusion via the renal arteries. c , Representative image of properly minced kidneys. Images were taken using a 1080P Full HD Digital Microscope. Appropriate institutional regulatory board permission was obtained for all animal experiments performed.
Extended Data Fig. 4 Validation of glomeruli purity following magnetic separation and washes.
a , Representative image of glomeruli and magnetic Dynabeads sample following first enzymatic digestion; before washes, tubular contamination is visible. b – d , The sample was washed with 10 ml HBSS −/− , and 10 µl aliquots were taken after the third ( b ), fourth ( c ), and fifth ( d ) washes to check for glomeruli purity under the microscope. e , Representative image of the resuspended glomeruli sample. Images were taken using the Leica Thunder Imaging System. Appropriate institutional regulatory board permission was obtained for all animal experiments.
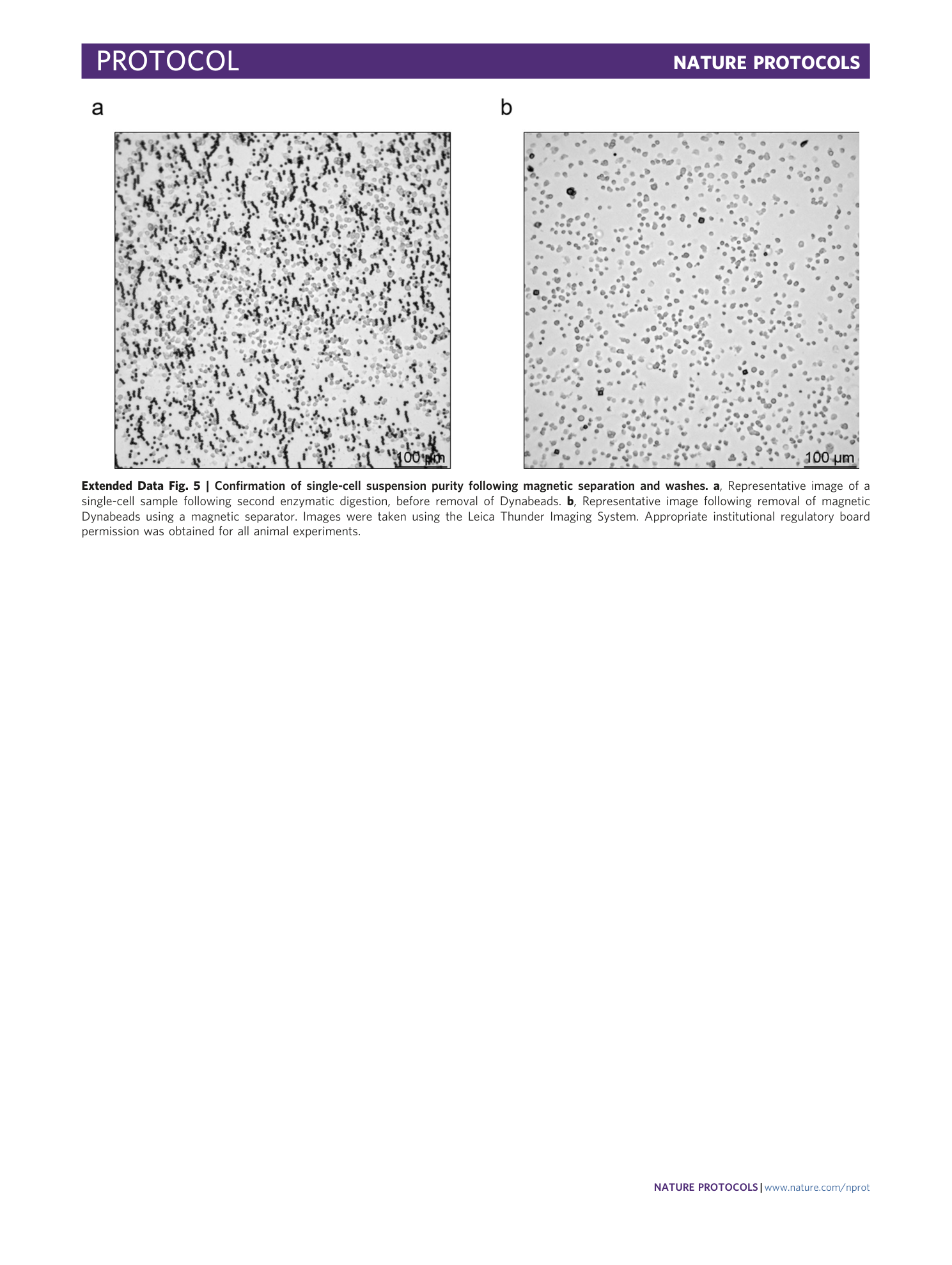
Extended Data Fig. 5 Confirmation of single-cell suspension purity following magnetic separation and washes.
a , Representative image of a single-cell sample following second enzymatic digestion, before removal of Dynabeads. b , Representative image following removal of magnetic Dynabeads using a magnetic separator. Images were taken using the Leica Thunder Imaging System. Appropriate institutional regulatory board permission was obtained for all animal experiments.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Video 1
Dissection of aorta and direct renal perfusion . Kidneys are placed in a Petri dish with HBSS −/− and further handled using a dissecting microscope. Dumont forceps are used to remove muscle and fatty tissue over the aorta and inferior vena cava. Then, Vannas spring scissors are used to dissect the abdominal aorta to expose the openings to the renal arteries. Next, the kidney is perfused by inserting the tip of a semi-dulled needle into the opening of the renal artery and slowly injecting the solution. The video was recorded using a Dino-Lite Edge Digital Microscope. Appropriate institutional regulatory board permission was obtained for all animal experiments.

