Creating hierarchical pores in metal–organic frameworks via postsynthetic reactions
Kun-Yu Wang, Zhentao Yang, Jiaqi Zhang, Sayan Banerjee, Elizabeth A. Joseph, Yu-Chuan Hsu, Shuai Yuan, Liang Feng, Hong-Cai Zhou
Metal-organic frameworks
hierarchical pores
postsynthetic reactions
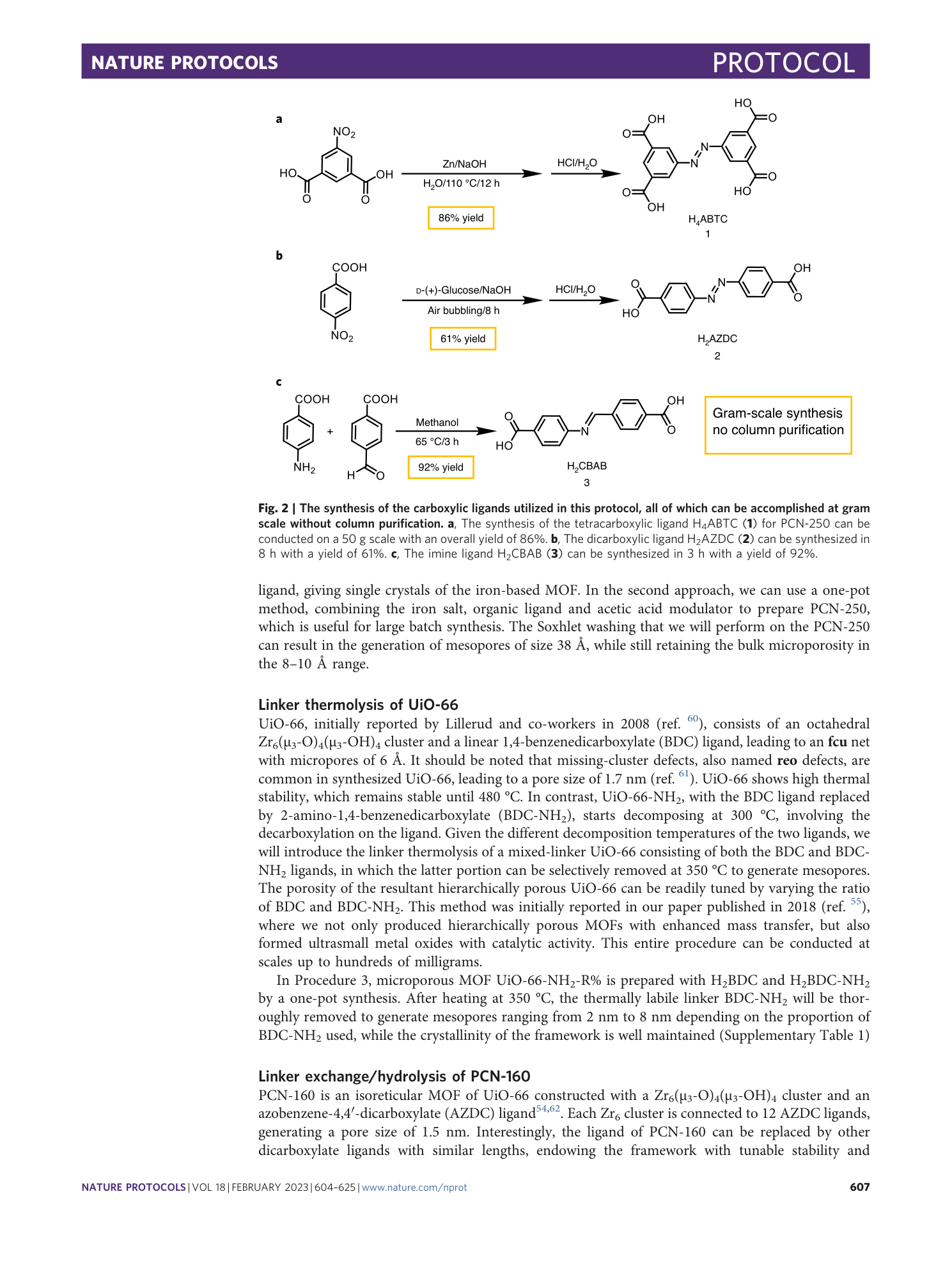
Soxhlet washing
mesopore generation


















Extended
Extended Data Fig. 1 The equipment setup to synthesize the H 4 ABTC ligand.
a , Initial setup for the synthesis. b , The appearance of the yellow precipitate after 12 h.
Extended Data Fig. 2 Color change of PCN-250 before and after activation.
a , The brown color of PCN-250 before activation. b , The black color of PCN-250 after 12 h activation at 240 °C.
Extended Data Fig. 3 Equipment setup for the Soxhlet washing of PCN-250.
a , Soxhlet extraction setup using a 500 ml round-bottom flask and a magnetic stir bar. b , The Soxhlet extractor with the PCN-250 and a water condenser.
Extended Data Fig. 4 Color of the mixed-linker UiO-66 before and after thermolysis.
a , The pale-yellow UiO-66-NH 2 -5% powder. b , The brown UiO-66-NH 2 -5% powder after heating at 350 °C. c , The pale-yellow UiO-66-NH 2 -28% powder. d , The dark-brown UiO-66-NH 2 -28% powder after heating at 350 °C.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–16, and Supplementary Table 1.

