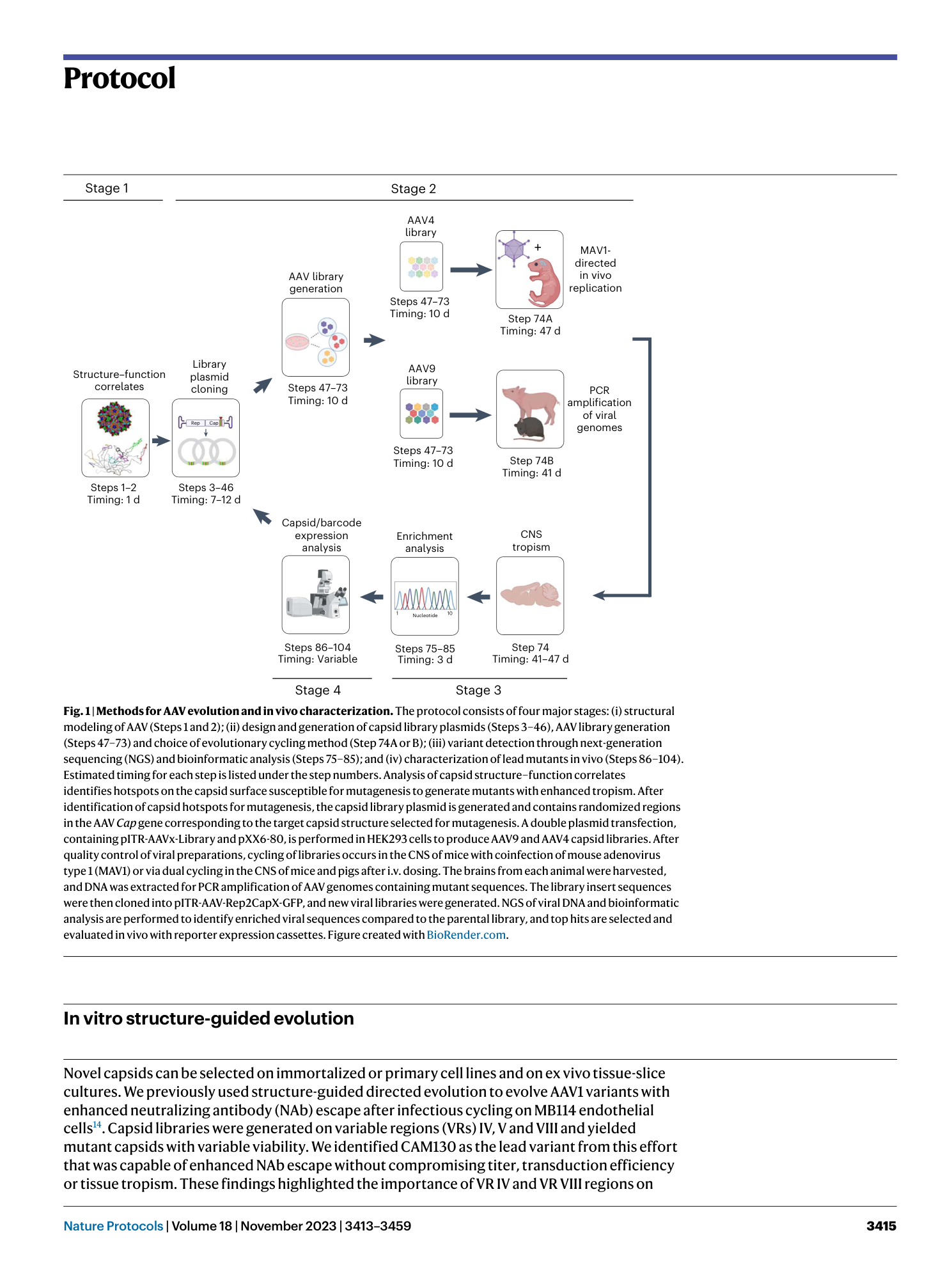
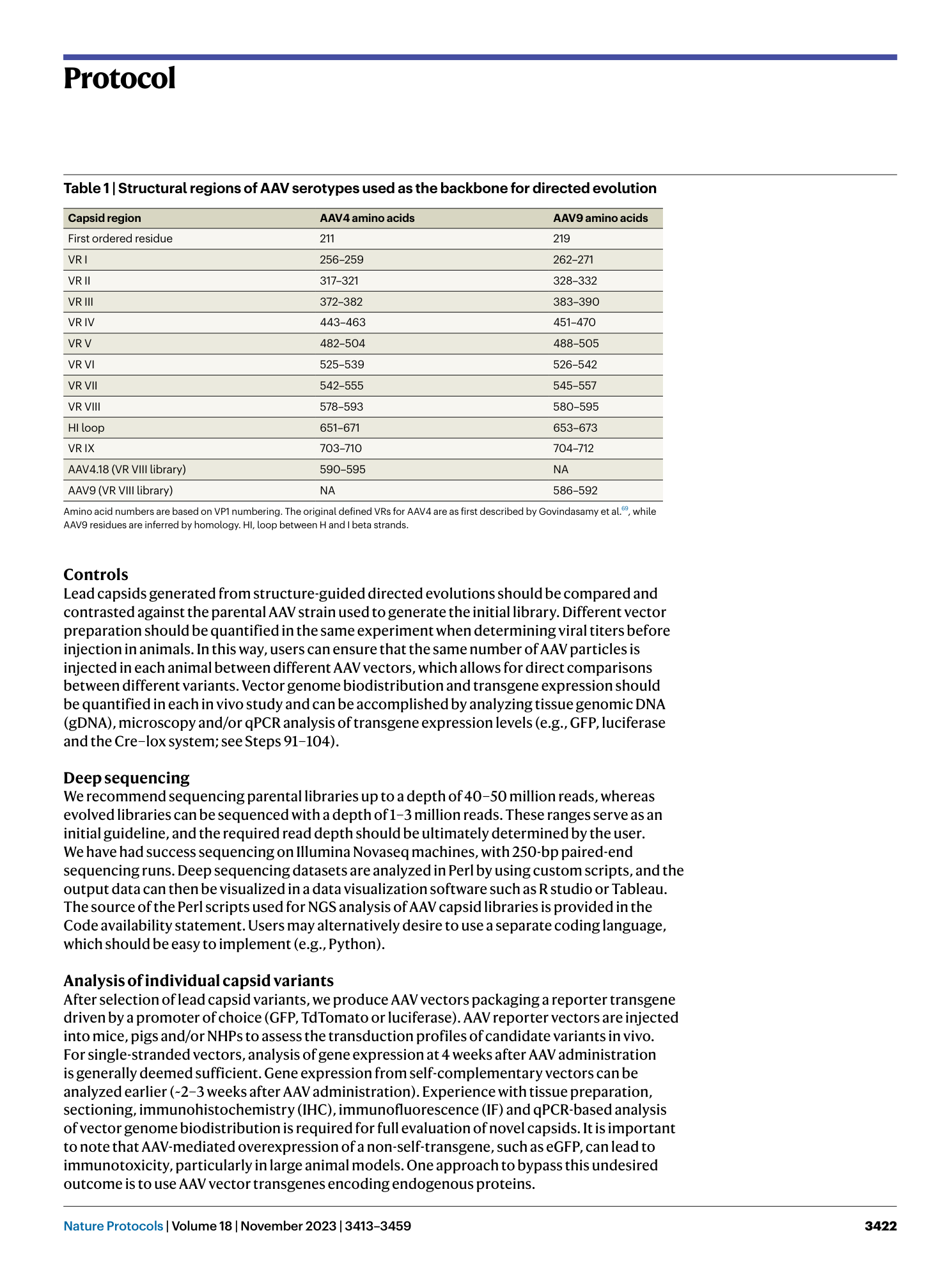
Structure-guided AAV capsid evolution strategies for enhanced CNS gene delivery
Trevor J. Gonzalez, Aaron Mitchell-Dick, Leo O. Blondel, Marco M. Fanous, Joshua A. Hull, Daniel K. Oh, Sven Moller-Tank, Ruth M. Castellanos Rivera, Jorge A. Piedrahita, Aravind Asokan
AAV capsid evolution
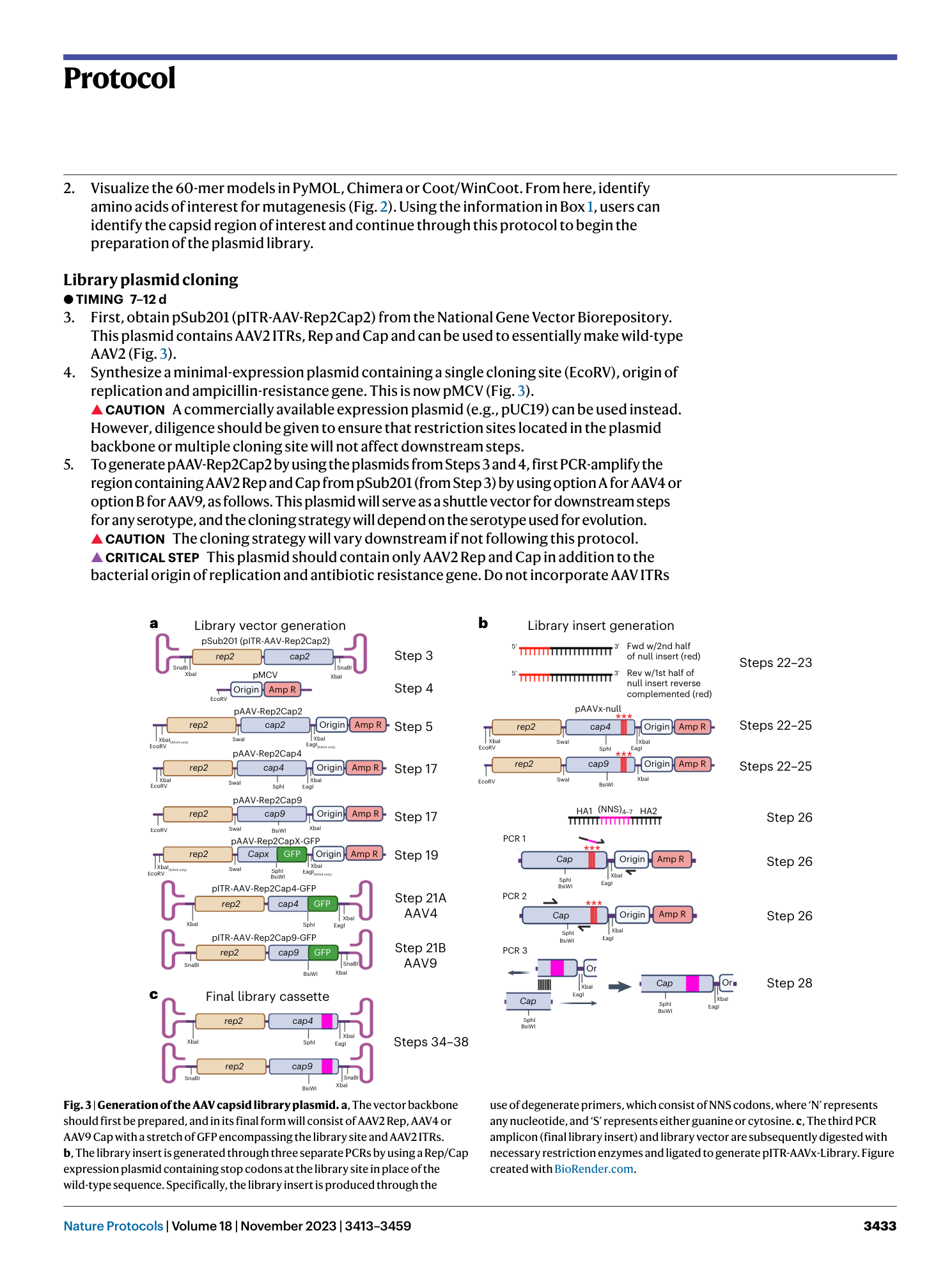
CNS gene delivery
structure-guided design
library cycling
humoral immunity evasion









































Extended
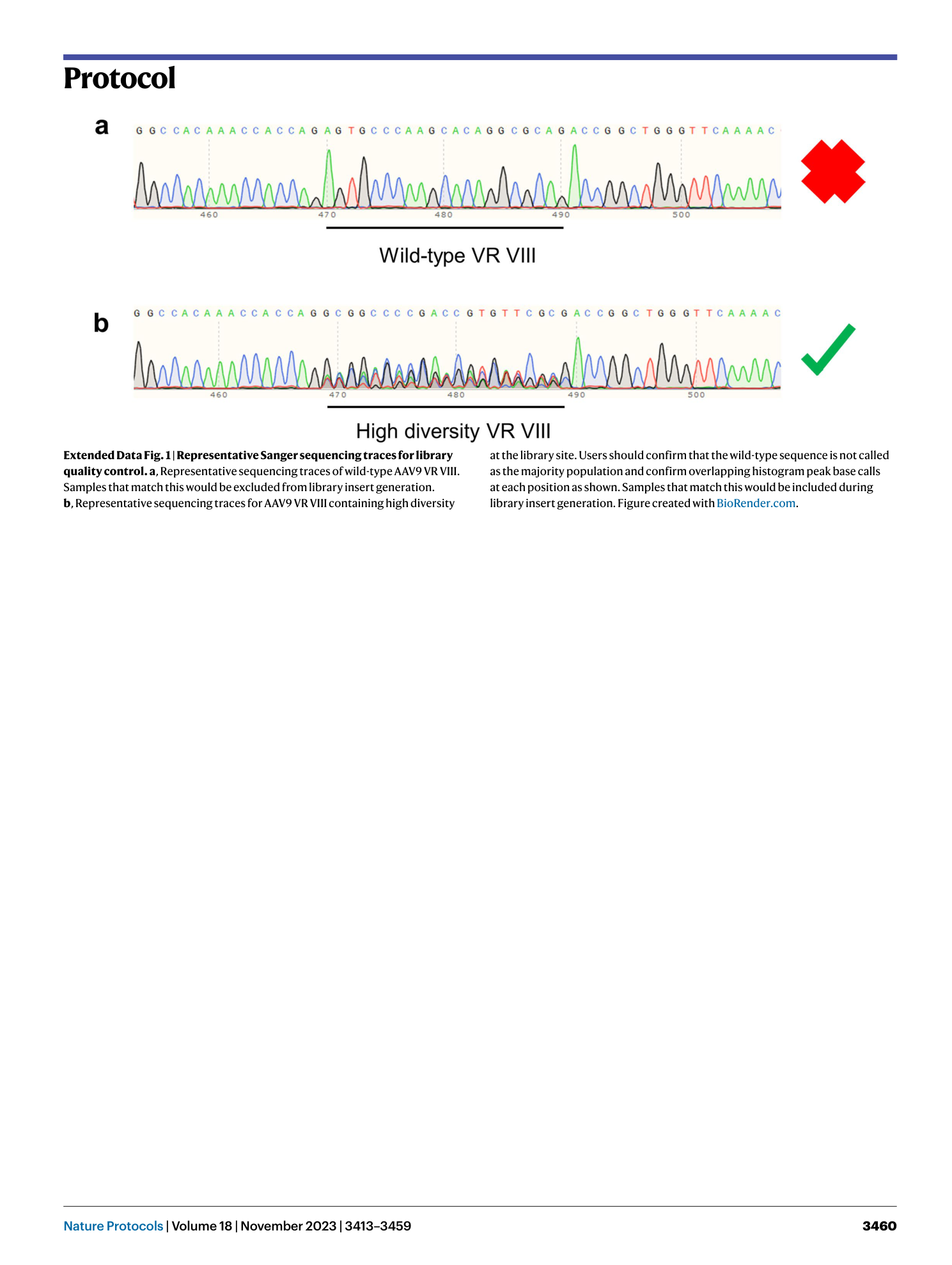
Extended Data Fig. 1 Representative Sanger sequencing traces for library quality control.
a , Representative sequencing traces of wild-type AAV9 VR VIII. Samples that match this would be excluded from library insert generation. b , Representative sequencing traces for AAV9 VR VIII containing high diversity at the library site. Users should confirm that the wild-type sequence is not called as the majority population and confirm overlapping histogram peak base calls at each position as shown. Samples that match this would be included during library insert generation. Figure created with BioRender.com .
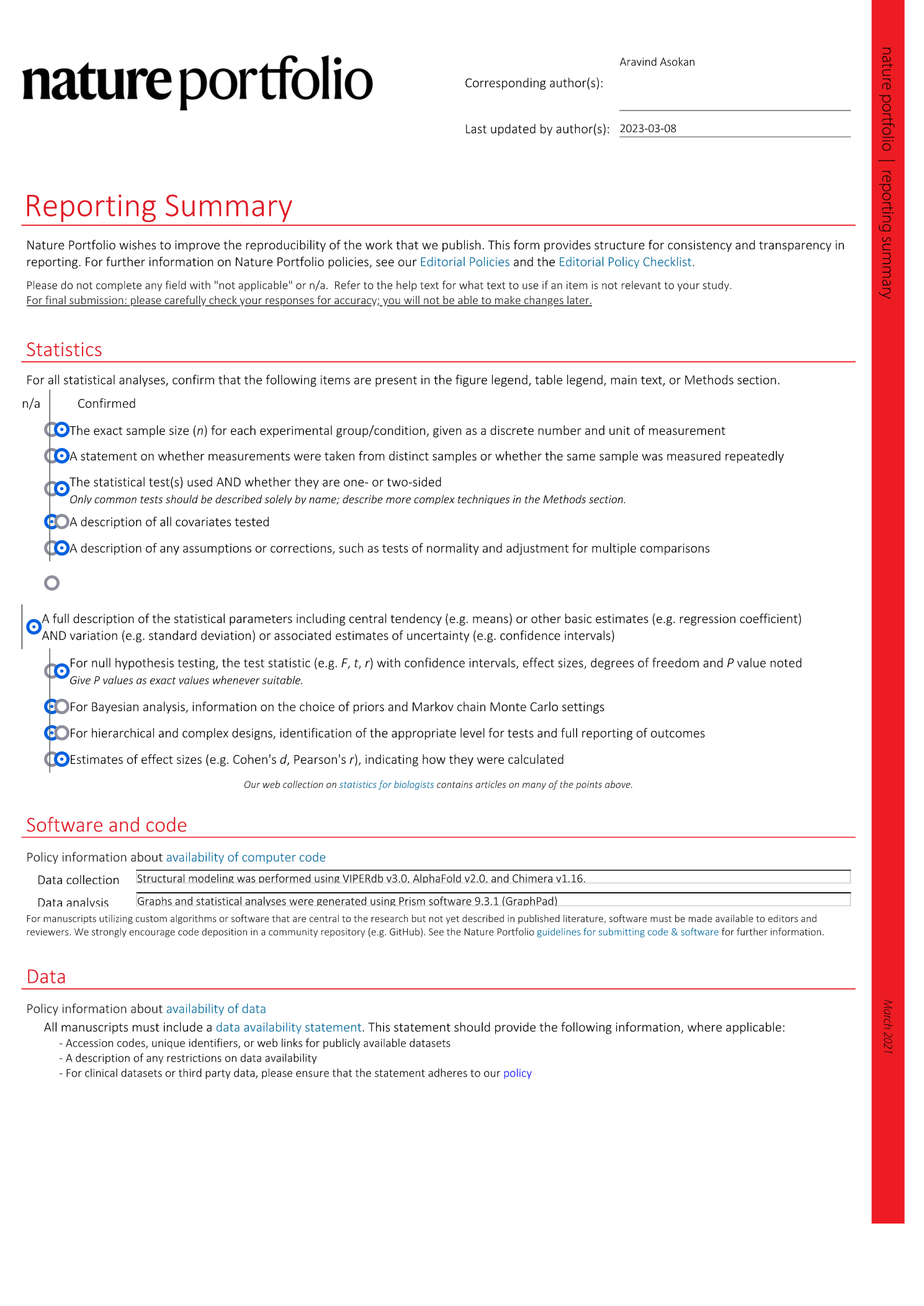
Extended Data Fig. 2 Generation of iodixanol gradients for AAV purification.
Gradients can be created either by overlaying ( a ) or underlaying ( b ) of different densities in 17-ml ultracentrifuge tubes. These densities include 17%, 25%, 40% and 60% iodixanol. Virus is added on top of the completed gradient before spinning in an ultracentrifuge. Either method can be used successfully, and the choice of method is based on user preference. Figure created with BioRender.com .
Extended Data Fig. 3 ICV injection station.
a , Ice anesthetization setup. Two large gloves are filled with ice to create a sandwich chamber. When ready to begin, pups are placed between the two gloves of ice and incubated for 3–5 min. During this time, the pup will become unresponsive, and a loss of its pink body color will be observed. b , Stereotaxic injection apparatus with injection pump and Hamilton syringe. Once pups are anesthetized, mount pups on the stage and zero out your X and Y coordinates by moving your needle above the lambda point. The injection site is located 0.8 mm (X), followed by 1.5 mm (Y) up toward the coronal suture and −1.5 mm (Z).

