ESTABLISHMENT OF A SPECIMEN/TISSUE BANK AND ASSOCIATED DNA REFERENCE DATA FOR eDNA ANALYSIS
Luca Mirimin, Dulaney Miller, Sara Fernandez
Abstract
This protocol is intended to provide guidelines on the curation and establishment of a specimen/tissue bank and associated DNA sequence data to be used as reference material/data for subsequent environmental DNA (eDNA) analysis, with particular emphasis on marine non-indigenous and invasive species.
Before start
To minimize risk of cross-sample contamination, note that all re-usable materials (e.g. scalpels, scissors, tweezers) should be decontaminated to remove any traces of DNA. It is highly recommended to carry out these protocols in dedicated and PCR-free laboratories/rooms.
Ensure that each protocol and list of materials is checked before starting any of the procedures. Specifically, make sure that all key materials(e.g. kits) have not been modified or discontinued by the relevant supplier.
Steps
Introduction
This document includes the following sections:
-
A graphical representation of the overall process
-
Collection of specimens and associated metadata
-
Specimen and tissue bank
-
Isolation of genomic DNA
-
Molecular barcoding
-
Acknowledgements
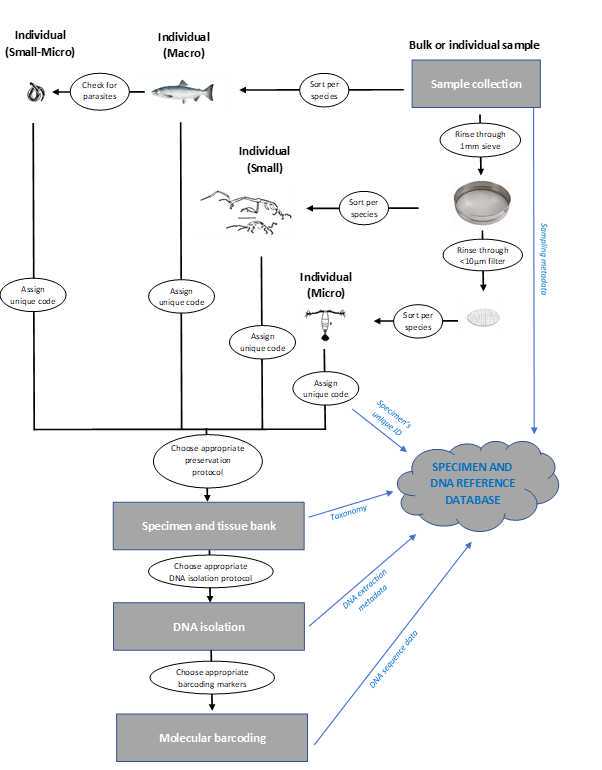
Graphical overview
Collection of specimens and associated metadata
Specimens can be collected following targeted surveys or opportunistically, using rapid methods (collection by hand, dredges, corers, traps, nets, etc.) or dedicated in situ approaches (e.g. SETL settlement plates; https://www.gimaris.com/Projects/SETL-project). When possible, whole specimens should be preserved for future downstream taxonomic identification.
As for metadata, the minimum information would include location (ideally with exact coordinates), date of collection, method of collection, photographs, and name/contact of person who collected the specimen. For an extensive list of recommended metadata, we recommend consulting guidelines provided in Rimet et al. (2021).
Specimen and tissue bank
For samples containing multiple organisms (e.g. dredge, SETL), specimens should be sorted and separated into single species groups. If the goal of the survey includes small- to micro-organisms, any small (>1mm) organism should be collected by rinsing with clear seawater (or artificial seawater) any substrate or specimen through a 1mm sieve, whereas the flow-through water should be inspected with a microscope for the presence of micro-organism.
A unique specimen identifier code should be allocated to each specimen collected. The format and style of such code will depend on the intended database/repository.
Preservation conditions will depend on the organism and can vary substantially, however such conditions should be chosen with the purpose of (i) limit DNA degradation during storage and (ii) ensure that key taxonomic features are retained for subsequent identification. However, in the context of marine non-indigenous species, many taxa (including most invertebrates) can be preserved frozen (-20°C to -80°C), using 70-100%
WARNING: caution should be exercised when handling ethanol and formalin. Please consult the relevant Safety Data Sheets for further information.
Isolation of genomic DNA
DNA isolation protocols should be adapted to each organisms following the manufacturer's recommendations. However, in the context of marine non-indigenous species, two DNA isolation kits have been used with highly successful rates, including the
Subsequent to DNA isolation, template DNA should be quantified using a Qubit Fluorometer (Invitrogen), whereas quality of extracts should be assessed using a small-volume spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific™).
Equipment
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| Invitrogen™ Qubit™ 3 Fluorometer | NAME |
| Accurately measures DNA, RNA, and protein using the highly sensitive fluorescence-based Qubit quantitation assays | TYPE |
| Invitrogen™ Q33216 | BRAND |
| Q33216 | SKU |
Equipment
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| NanoDrop™ One UV-Vis Spectrophotometer | NAME |
| spectrophotometer | TYPE |
| Thermo Scientific | BRAND |
| ND-ONE-W | SKU |
| Sample Volume (Metric): Minimum 1µL; Spectral Bandwidth: ≤1.8 nm (FWHM at Hg 254 nm); System Requirements: Windows™ 8.1 and 10, 64 bit; Voltage: 12 V (DC); Wavelength Range: 190–850 nm | SPECIFICATIONS |
Molecular barcoding
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assay # | Target Taxa | Target Gene | Amplicon Length Range (bp) | Forward Primer Name | Forward Primer Sequence (5'-3') | Forward Primer Source Reference | Reverse Primer Name | Reverse Primer Sequence (5'-3') | Reverse Primer Source Reference | ||
| 1 | Marine metazoans | COI | 658 | LoboF1 | KBTCHACAAAYCAYAARGAYATHGG | Lobo et al. 2013 | LoboR1 | TAAACYTCWGGRTGWCCRAARAAYCA | Lobo et al. 2013 | ||
| 2 | Marine metazoans | COI | 313 | mICOIintF‐XT | GGWACWRGWTGRACWNTNTAYCCYCC | Leray et al 2013 | jgHCO2198a | TANACYTCNGGRTGNCCRAARAAYCA | Leray et al 2013 | ||
| 3 | Marine metazoans | COI | 710 | jgLCO1490 | TITCIACIAAYCAYAARGAYATTGG | Geller et al 2013 | jgHCO2198b | TAIACYTCIGGRTGICCRAARAAYCA | Geller et al 2013 | ||
| 4 | Marine metazoans | 16S rRNA | 567 | 16sar-L | CGCCTGTTTATCAAAAACAT | Palumbi et al 2002 | 16sbr-H | CCGGTCTGAACTCAGATCACGT | Palumbi et al 2002 | ||
| 5 | (Freshwater) Diatoms | RuBisCO | 312 | Diat_rbcL_708F | AGGTGAARYWAAAGGTTCWTAYTTAAA | Vasselon et al 2017 | Diat_rbcL_R3 | CCTTCTAATTTACCWACWACTG | Vasselon et al 2017 |
Assay 1 (COI - Lobo et al 2013)
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| Reagent name and starting concentration | Amount per reaction (µL) | Final concentration (per reaction) |
| Moleculr grade water | to 10 μL | - |
| 5X Platinum™ II PCR Buffer | 2 | 1X |
| 10 mM dNTP mix | 0.2 | 0.2 mM each |
| 10 μM forward primer | 0.2 | 0.2 μM |
| 10 μM reverse primer | 0.2 | 0.2 μM |
| Platinum™ II Taq Hot-Start DNA Polymerase | 0.08 | 0.04 U/μL |
| Template DNA | 1-2 | <200 ng/rxn |
| Total | 10 |
PCR reagents and concentrations for Assay 1
Thermal cycling conditions:
94ºC-1min
94ºC-30secs
45ºC-60secs x5
72ºC-60secs
94ºC-30secs
54ºC-90secs x45
72ºC-60secs
4ºC-+∞
Assay 2 (COI - Leray et al 2013)
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reagent name and starting concentration | Amount per reaction (µL) | Final concentration (per reaction) | |
| Moleculr grade water | to 20µL | - | |
| 5X GoTaq PCR Buffer | 4 | 1X | |
| 10 mM dNTP mix | 0.4 | 0.2 mM each | |
| 10 μM forward primer | 1 | 0.5 µM | |
| 10 μM reverse primer | 1 | 0.5 μM | |
| GoTaq DNA Polymerase | 0.15 | 0.04 U/μL | |
| Template DNA | 2 | <200 ng/rxn | |
| Total | 20 |
Thermal cycling conditions:
95ºC-1min
95ºC-15secs
46ºC-15secs x40
72ºC-10secs
72ºC-3min
4ºC-+∞
Assay 3 (COI - Geller et al 2013)
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reagent name and starting concentration | Amount per reaction (µL) | Final concentration (per reaction) | |
| Moleculr grade water | to 20µL | - | |
| 5X GoTaq PCR Buffer | 4 | 1X | |
| 10 mM dNTP mix | 0.4 | 0.2 mM each | |
| 10 μM forward primer | 1 | 0.5 µM | |
| 10 μM reverse primer | 1 | 0.5 μM | |
| GoTaq DNA Polymerase | 0.15 | 0.04 U/μL | |
| Template DNA | 2 | <200 ng/rxn | |
| Total | 20 |
Thermal cycling conditions:
95ºC-5min
95ºC-1min
48ºC-1min x40
72ºC-1min
72ºC-5min
4ºC-+∞
Assay 4 (16S rRNA - Palumbi et al 2002)
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reagent name and starting concentration | Amount per reaction (µL) | Final concentration (per reaction) | |
| Moleculr grade water | to 20µL | - | |
| 5X GoTaq PCR Buffer | 4 | 1X | |
| 10 mM dNTP mix | 0.4 | 0.2 mM each | |
| 10 μM forward primer | 1 | 0.5 µM | |
| 10 μM reverse primer | 1 | 0.5 μM | |
| GoTaq DNA Polymerase | 0.15 | 0.04 U/μL | |
| Template DNA | 2 | <200 ng/rxn | |
| Total | 20 |
Thermal cycling conditions:
95ºC-5min
94ºC-1min
55ºC-1min x40
72ºC-2min
72ºC-7min
4ºC-+∞
Assay 5 (RuBisCO - Vasselon et al 2017)
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reagent name and starting concentration | Amount per reaction (µL) | Final concentration (per reaction) | |
| Moleculr grade water | to 20µL | - | |
| 5X GoTaq PCR Buffer | 4 | 1X | |
| 10 mM dNTP mix | 0.4 | 0.2 mM each | |
| 10 μM forward primer | 1 | 0.5 µM | |
| 10 μM reverse primer | 1 | 0.5 μM | |
| GoTaq DNA Polymerase | 0.15 | 0.04 U/μL | |
| Template DNA | 2 | <200 ng/rxn | |
| Total | 20 |
Thermal cycling conditions:
94ºC-1min
95ºC-30secs
46ºC-30secs x40
72ºC-30secs
72ºC-10min
4ºC-+∞
Successful amplification and confirmation of expected size of PCR products should be carried out by agarose gel electrophoresis .
(Optional) A PCR clean-up step can be included at this stage, but in many cases it is not necessary.
DNA sequences should be obtained by Sanger sequencing using the Forward and/or reverse primers.
Raw DNA sequence data should be inspected using any suitable software (e.g. MEGA, Geneious) and curated to ensure high quality (error-free) of final data.
Linking DNA sequence data to public repositories such as GenBank GenBank and BOLD BOLD is strongly encouraged.