SorTn-seq: a high-throughput functional genomics approach to discovering regulators of bacterial gene expression
Leah M. Smith, Simon A. Jackson, Paul P. Gardner, Peter C. Fineran
functional genomics
SorTn-seq
bacterial gene expression
Tn5 mutagenesis
fluorescence-activated cell sorting







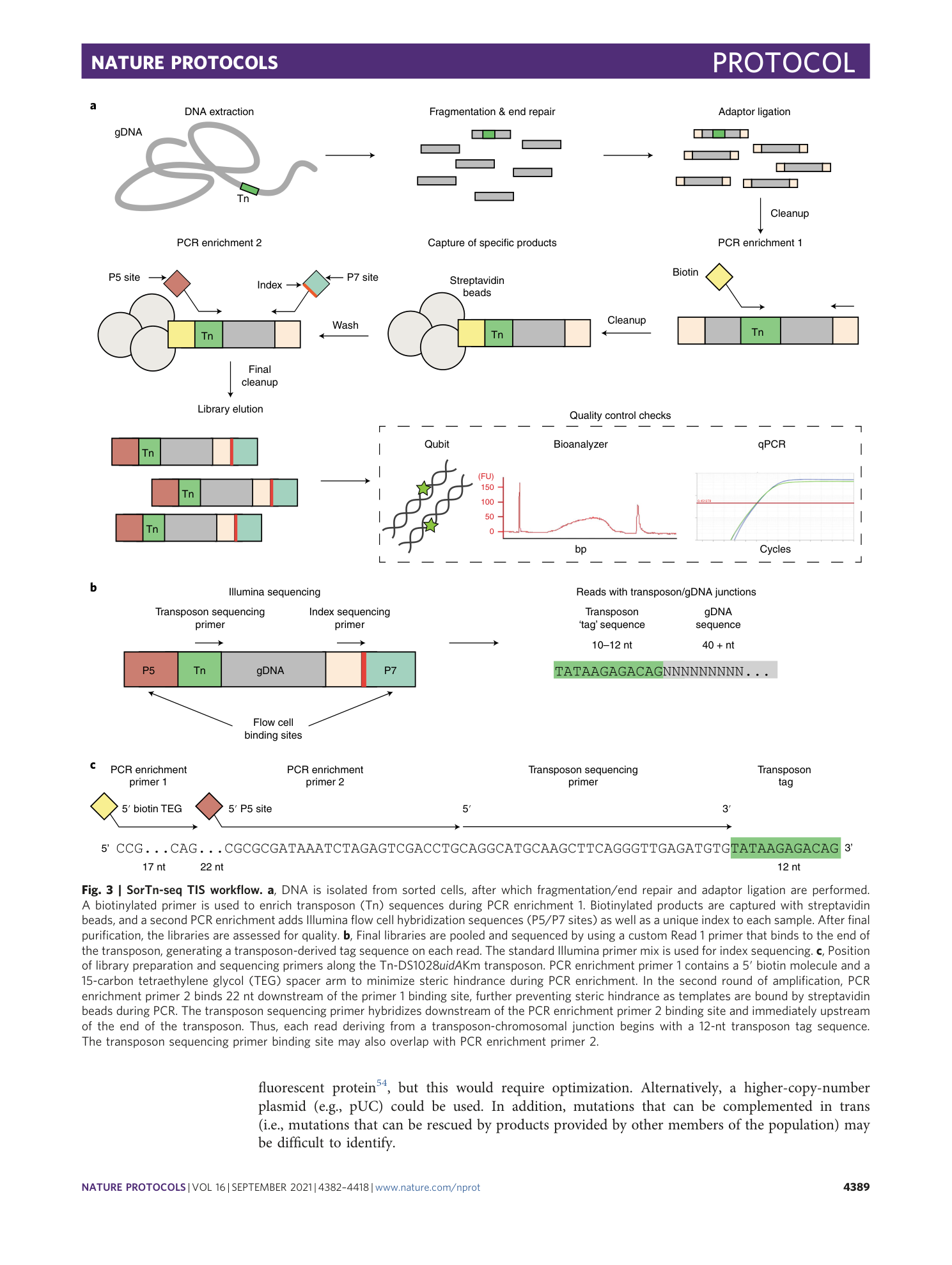
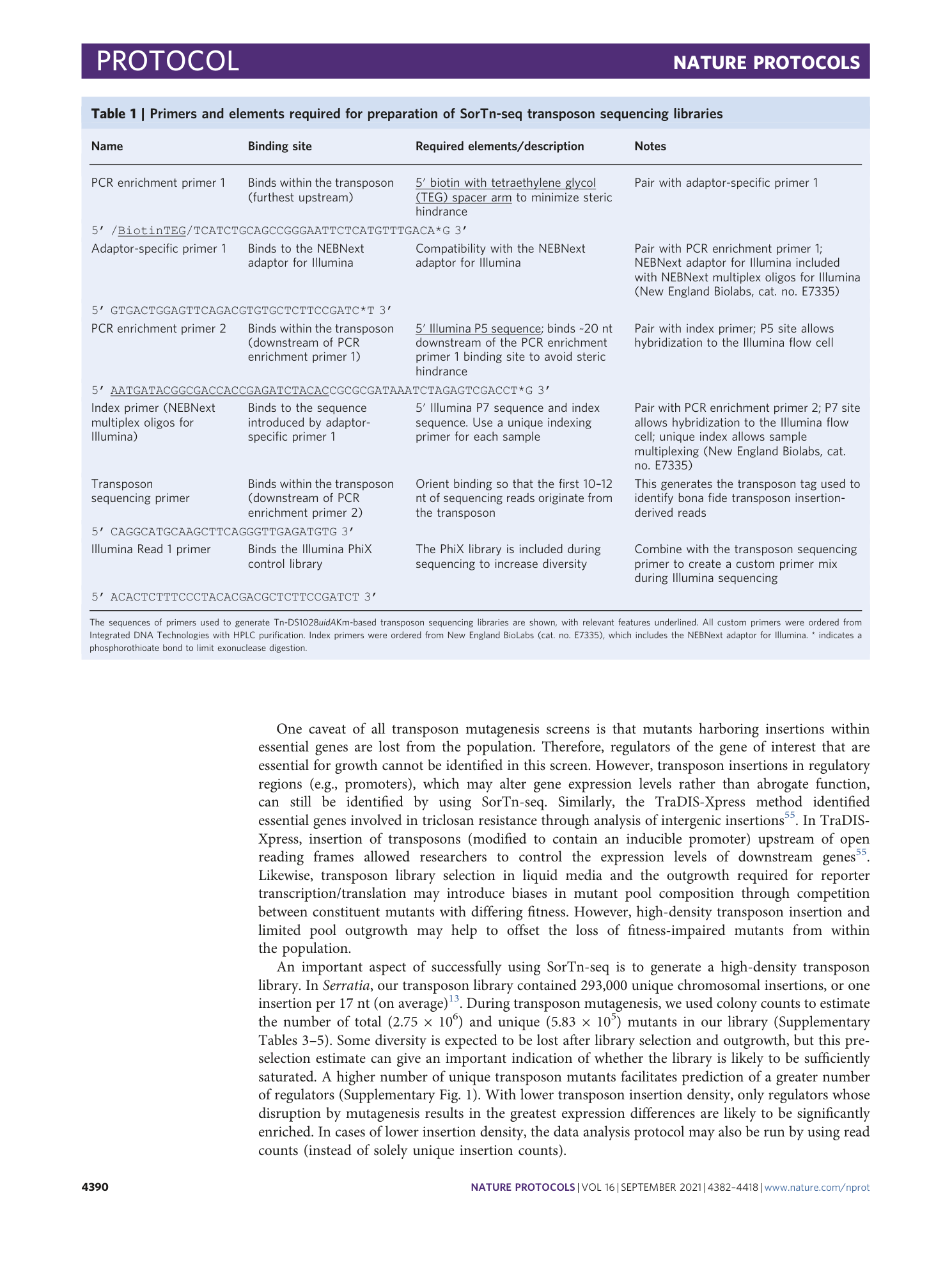
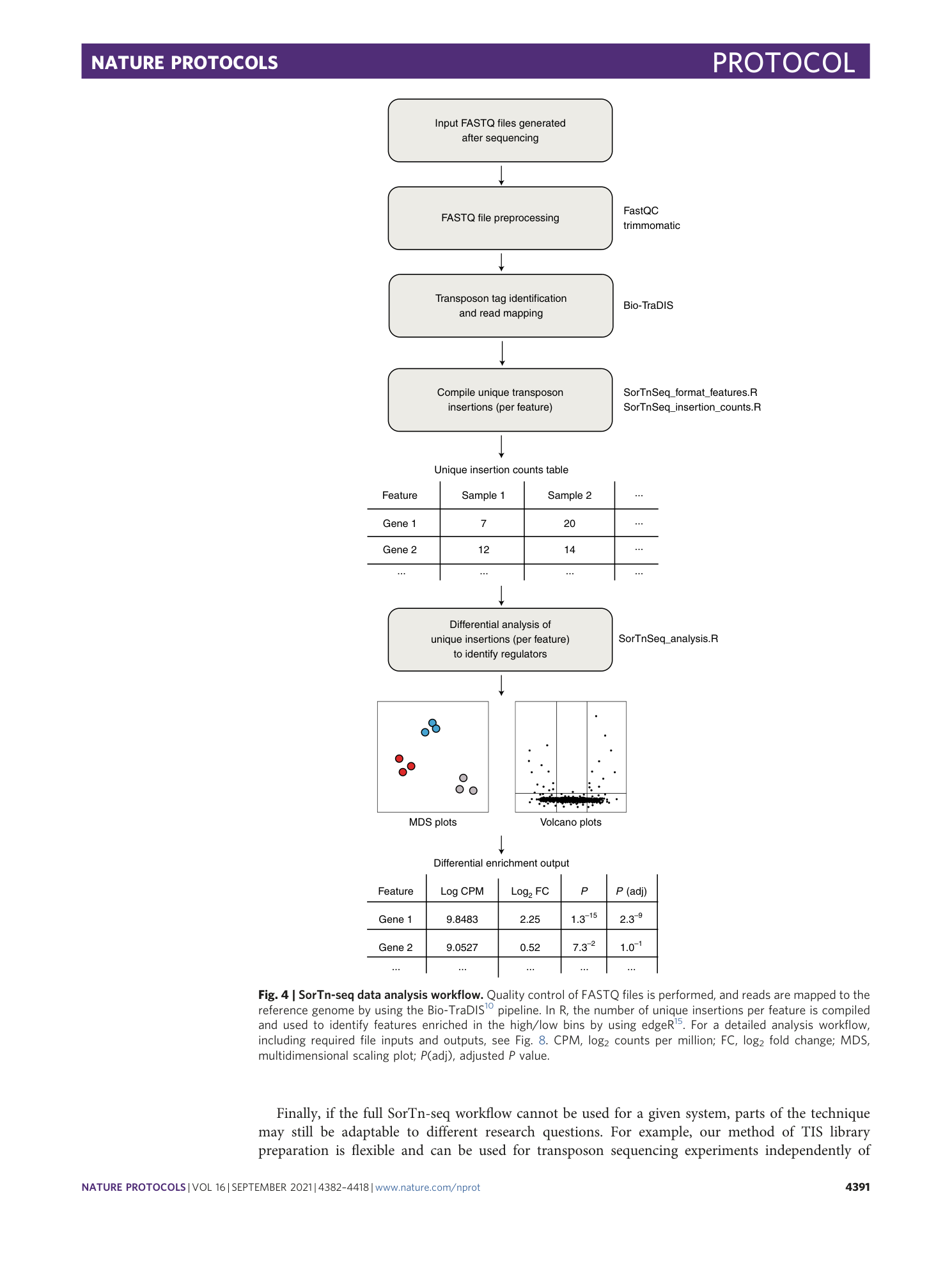










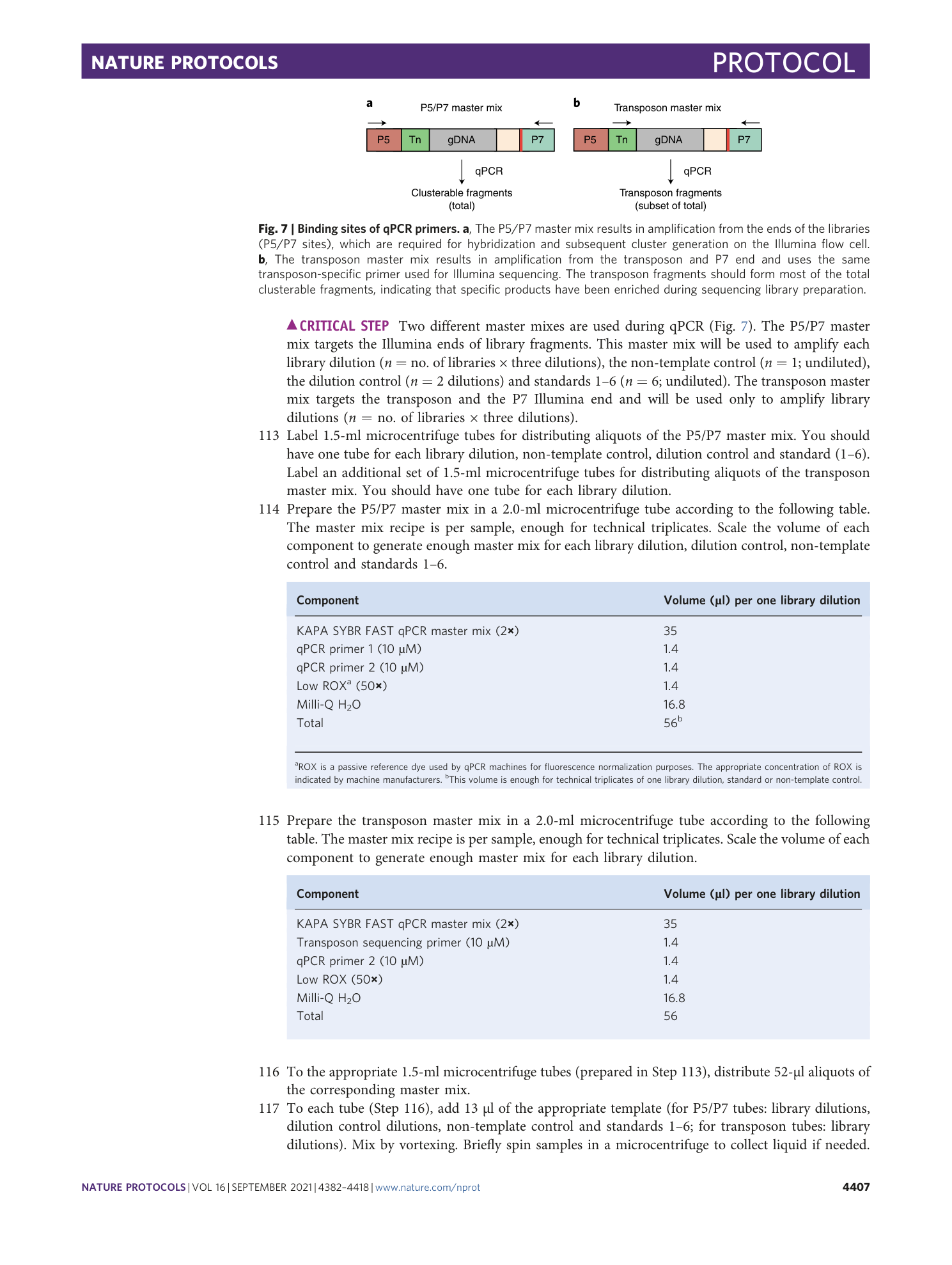

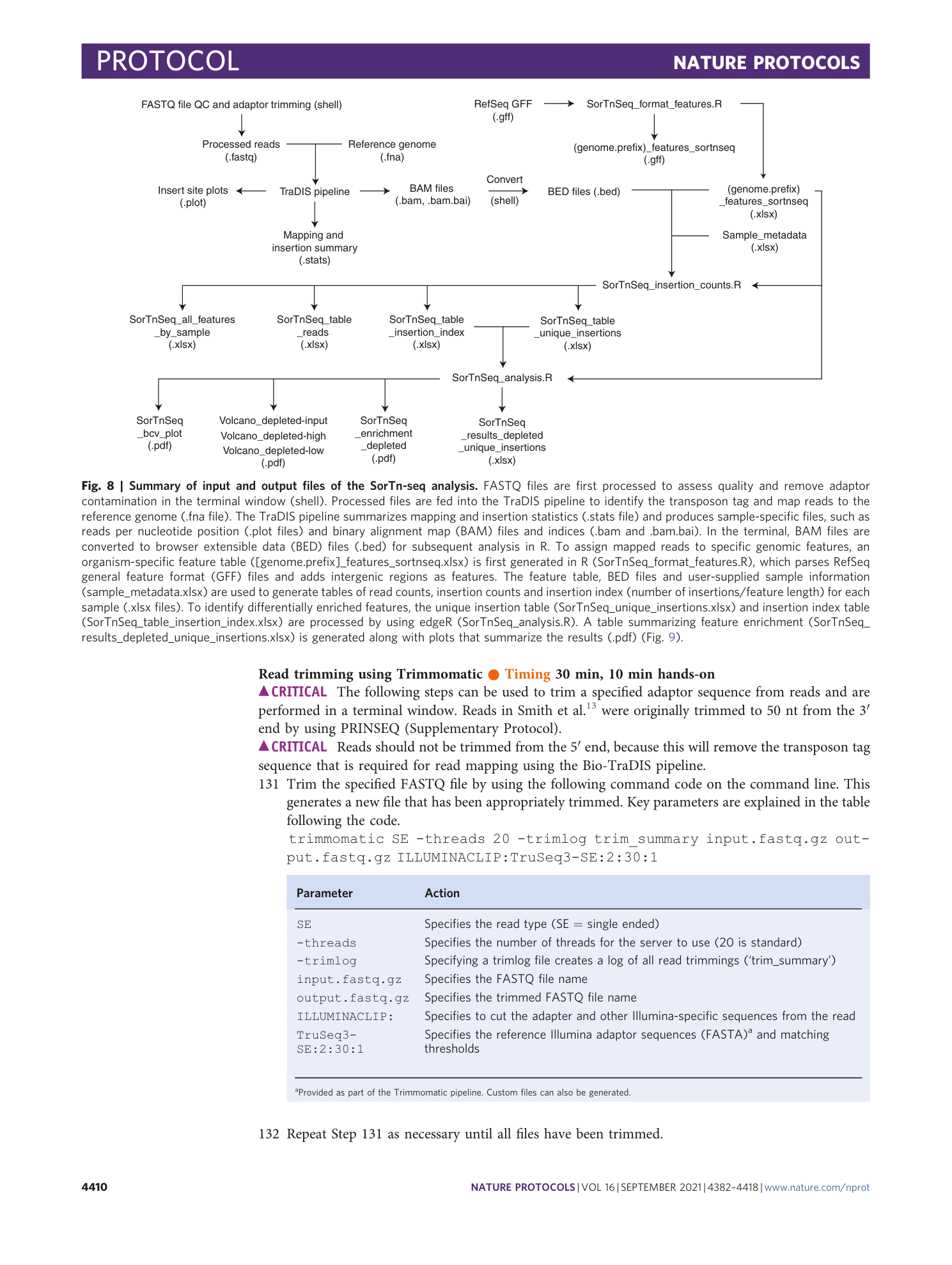





Extended
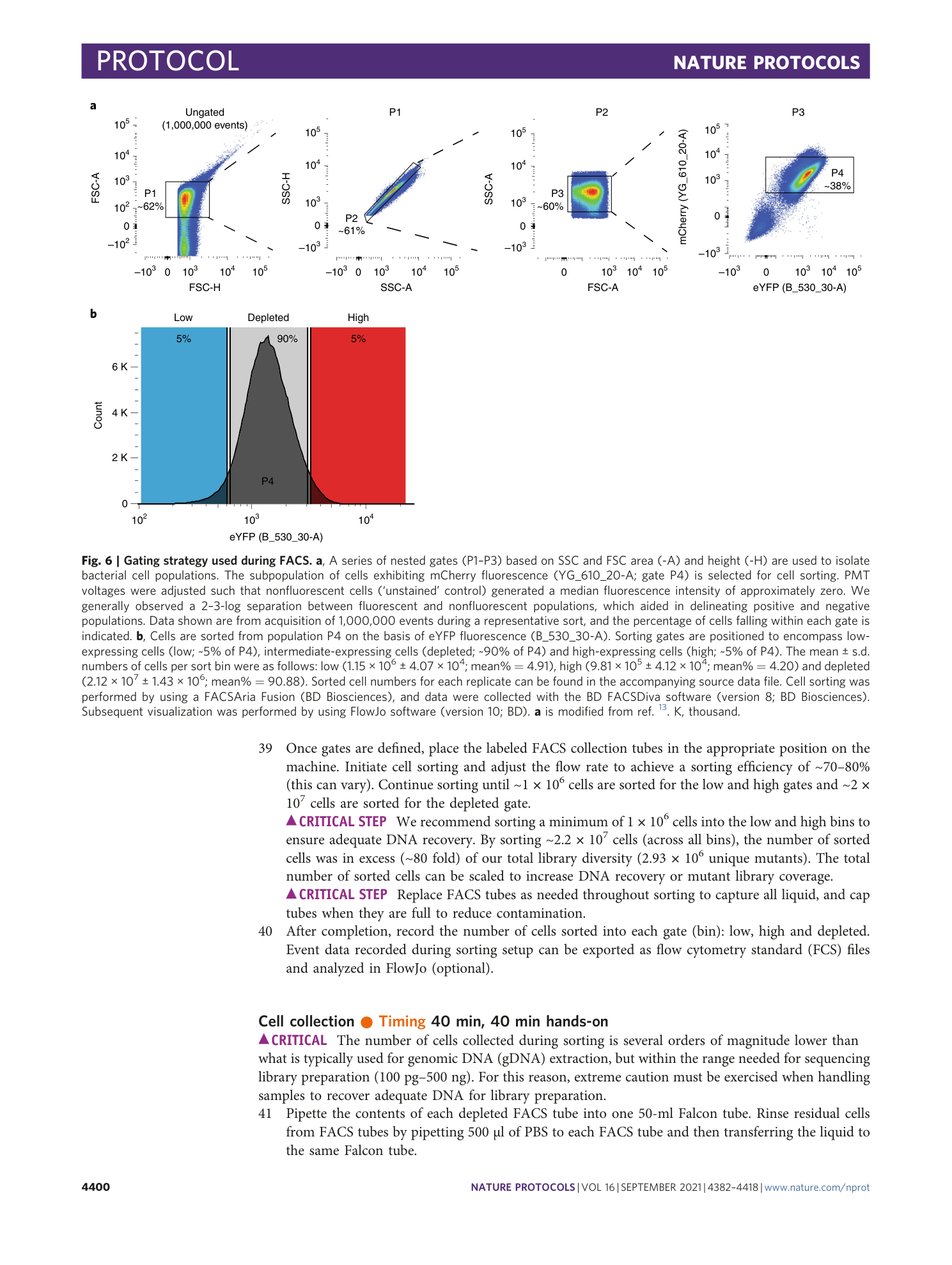
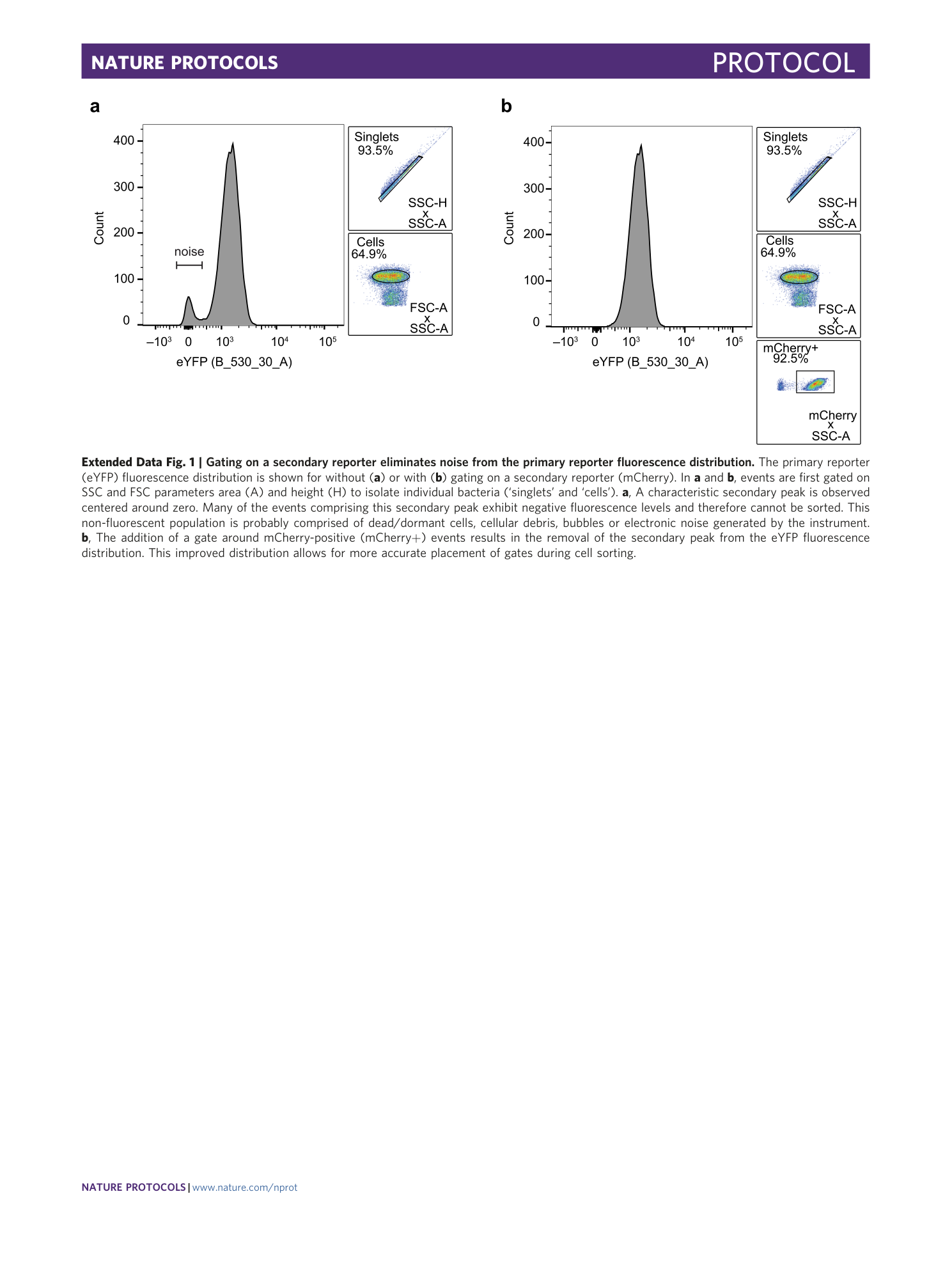
Extended Data Fig. 1 Gating on a secondary reporter eliminates noise from the primary reporter fluorescence distribution.
The primary reporter (eYFP) fluorescence distribution is shown for without ( a ) or with ( b ) gating on a secondary reporter (mCherry). In a and b , events are first gated on SSC and FSC parameters area (A) and height (H) to isolate individual bacteria (‘singlets’ and ‘cells’). a , A characteristic secondary peak is observed centered around zero. Many of the events comprising this secondary peak exhibit negative fluorescence levels and therefore cannot be sorted. This non-fluorescent population is probably comprised of dead/dormant cells, cellular debris, bubbles or electronic noise generated by the instrument. b , The addition of a gate around mCherry-positive (mCherry+) events results in the removal of the secondary peak from the eYFP fluorescence distribution. This improved distribution allows for more accurate placement of gates during cell sorting.
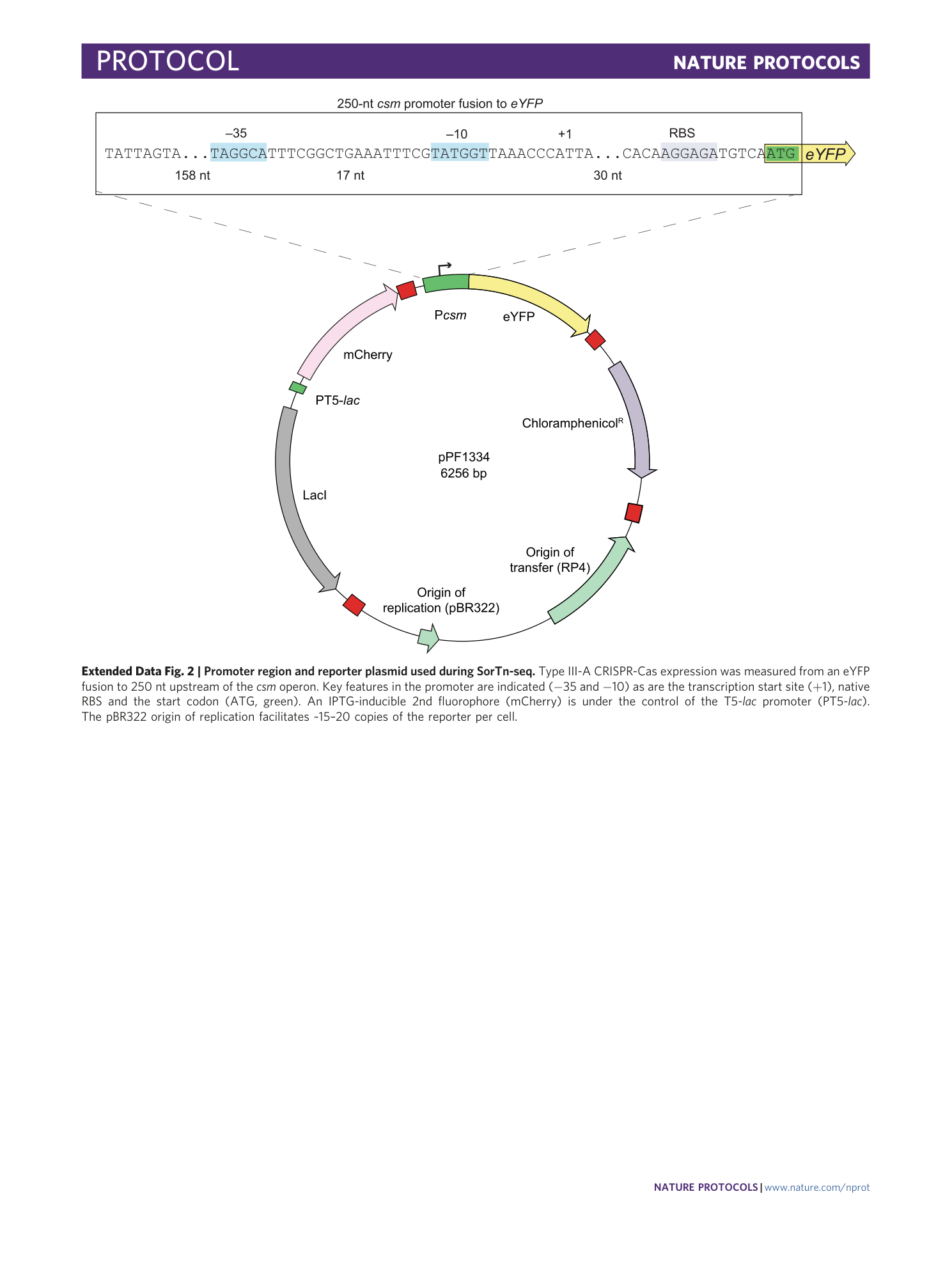
Extended Data Fig. 2 Promoter region and reporter plasmid used during SorTn-seq.
Type III-A CRISPR-Cas expression was measured from an eYFP fusion to 250 nt upstream of the csm operon. Key features in the promoter are indicated (−35 and −10) as are the transcription start site (+1), native RBS and the start codon (ATG, green). An IPTG-inducible 2nd fluorophore (mCherry) is under the control of the T5- lac promoter (PT5- lac ). The pBR322 origin of replication facilitates ~15–20 copies of the reporter per cell.
Extended Data Fig. 3 Transposon delivery vector and transposon organization.
a , Organization of the pKRCPN2 transposon delivery vector. b , Schematic of the transposon Tn-DS1028 uidA Km, which contains a transcriptional uidA reporter, origin of replication (R6Kγ) and kanamycin resistance gene (Km R ).
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–3, Supplementary Tables 1–8 and Supplementary Protocol
Supplementary Data 1
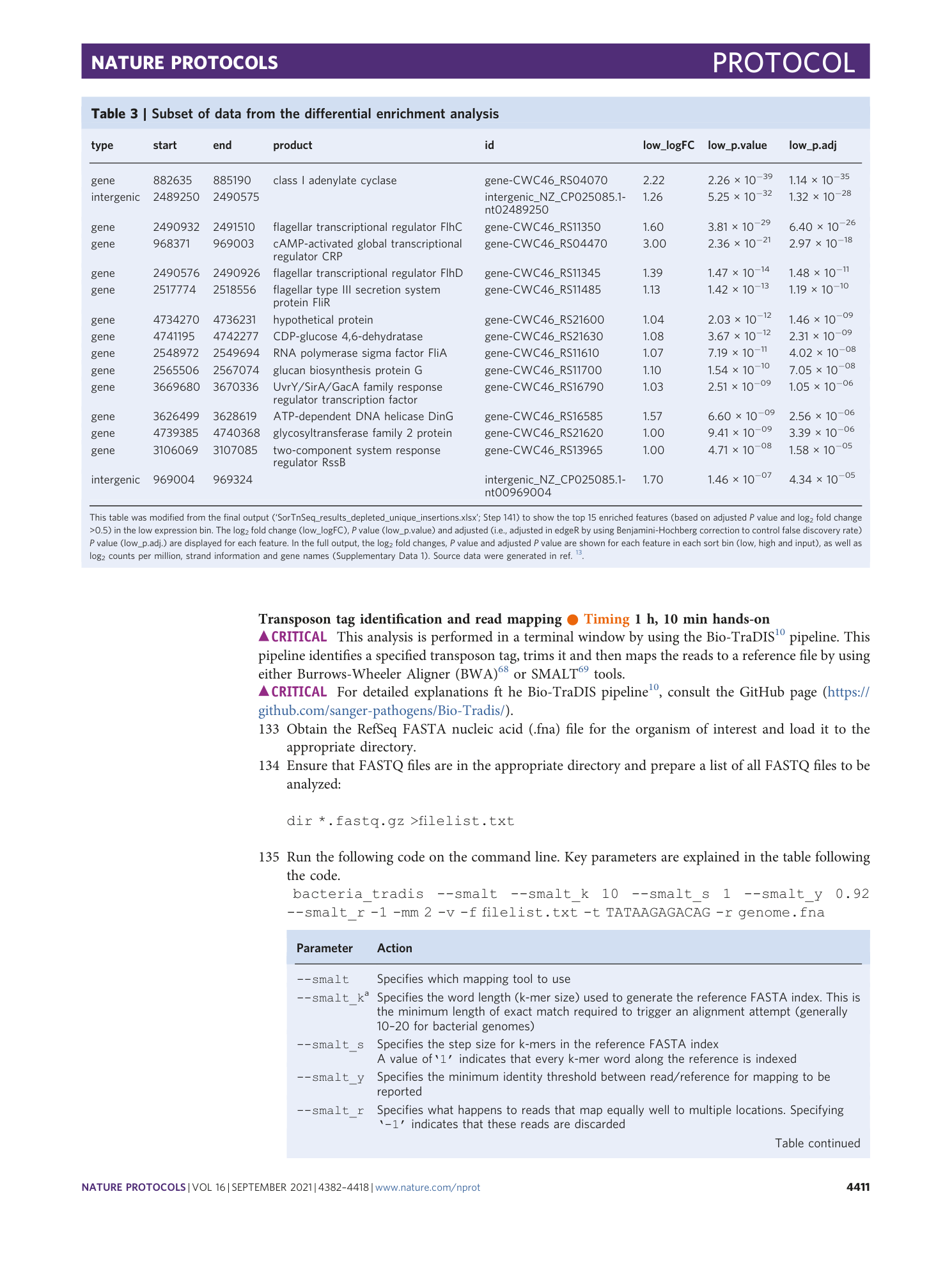
Results of the SorTn-seq differential enrichment analysis

