OT-2 Modular Cloning Construct Assembly
Ana Mariya Anhel, Ángel Goñi-Moreno, Laura Cutugno
Abstract
This protocol is meant to create modular cloning constructs from different parts into a final plate and, optionally, perform the temperature profile needed to the assembly of the constructs.
The output of running this script will be the final plate(s) with the constructs and the mix needed to perform that assembly, and the corresponding map(s) with the names of the constructs in their corrresponding well which will be given by the user in the input file.
This protocol uses a python script for an Opentrons 2 robot and an excel file containing the required variables to set the number of samples, volumes of transfer, type of plates, etc...
In our laboratory, this protocol has been used to perform plasmids using the Golden Standard modular cloning of levels 1 and level 2
This protocol is a set of instructions or description of the LAP repository entry LAP-MoCloAssembly-OT2-1.0.1
Before start
Being a one-pot reaction in this protocol only 1 restriction enzyme is used so one type of level, in the case of the golden standard database, can be produced in only 1 run
Steps
Files Preparation
Preparing Customized Template
Preparing the template (a .xlsx) with the specific variables for each experiment.
Here there is attached a template of the variable file with several sheets and a PDF file explaining each variable:
- GeneralVariables: variables related mainly to the labware that is going to be used
- PerPlateVariables: variables related to the specifications of each source plate
- PipetteVariables: variables related to the pipettes that are going to be used
- ReactionVariables: variables that will determine the final mix of the wells
- ModuleVariables: variables related to the modules used in the protocol, the thermocycler and the heater-shaker
- Combinations: set of combinations that are going to be created in the final wells, one combination per row and one DNA part per cell
- Map DNA Parts Sheet(s): sheet(s) with the names of each DNA part that can be used to create final assemblies denoted in the combinations sheet. The sheet(s) need to have also dthe name of the rows and columns of the plate and the wells that does not have any sample need to be left empty --> not included in the template but needed to be included and have the same names as established in the variable Name Map DNA Parts from the PerPlateVariables Sheet Name Map DNA Parts from the PerPlateVariables Sheet
- TemperatureProfile (Optional): a profile that will be performed in the thermocycler if set as True in the ModuleVariables sheet
Fill the template with the corresponding values
Store it with the name VariablesMoCloAssembly.xlsx
Transferring file to Robot
Transfer the VariablesMoCloAssembly.xlsx to the directory /data/user_storage of the OT robot
that we are going to use to perform the protocol.
Here, we present a summary of how to transfer the files in 3 Operative Systems: Windows, MacOS and Linux
MacOS/Linux
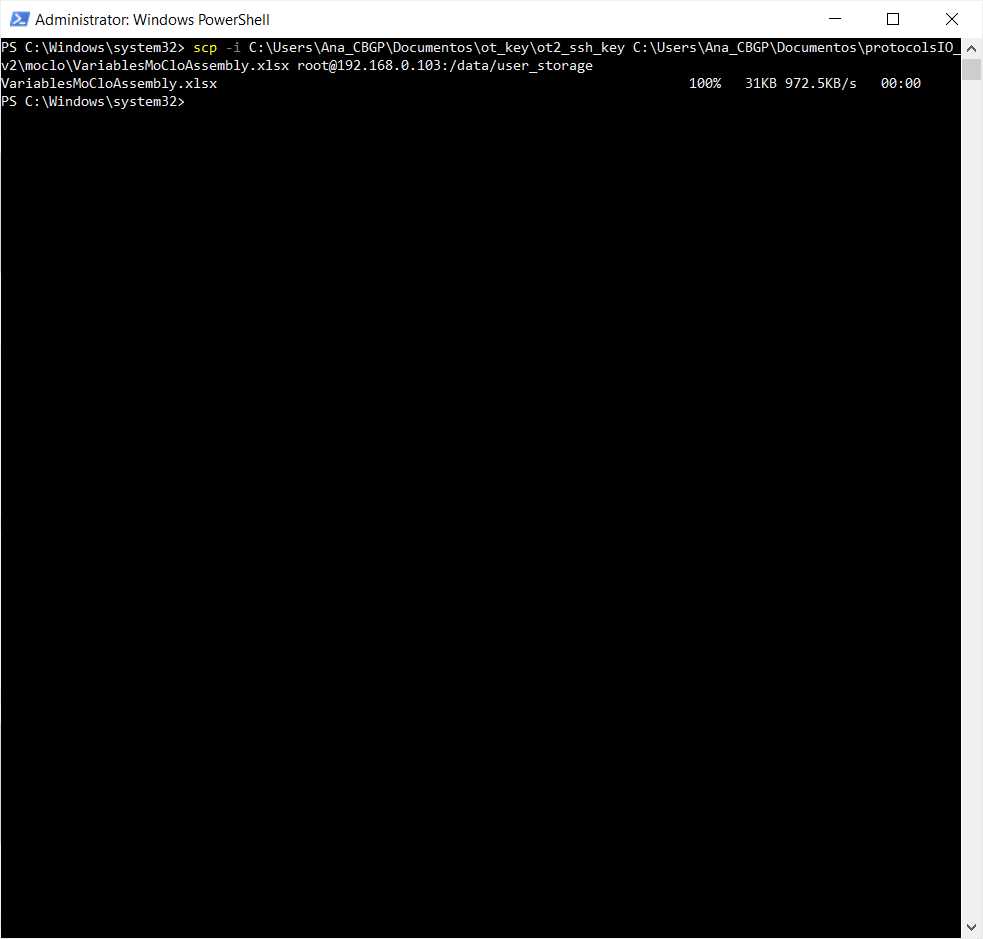
We will use the command line with scp to transfer the file VariablesMoCloAssembly.xlsx to the OT system.
We need to perform the following command
#Passing Files to OT
scp -i [ot_key] [file] root@[IP_OT]:/data/user_storage
#Transferring files to OT (MacOS 13 and 14)scp -Oi [ot_keypath] [file path] root@[OP_robot]:/data/user_storageWindows
There are several ways to send files from a Windows to a Linux (for example, with a virtual machine or Windows Powershell in the latest versions of Windows).
Here, we will use FileZilla (https://filezilla-project.org/download.php?type=client).
Go to File -> Site Manager -> New Site -> Change Protocol to SFTP . Then, introduce in Host the OT IP, change the Logon Type to key file, change User to root and give the directory where the ot key is. It should look something like this
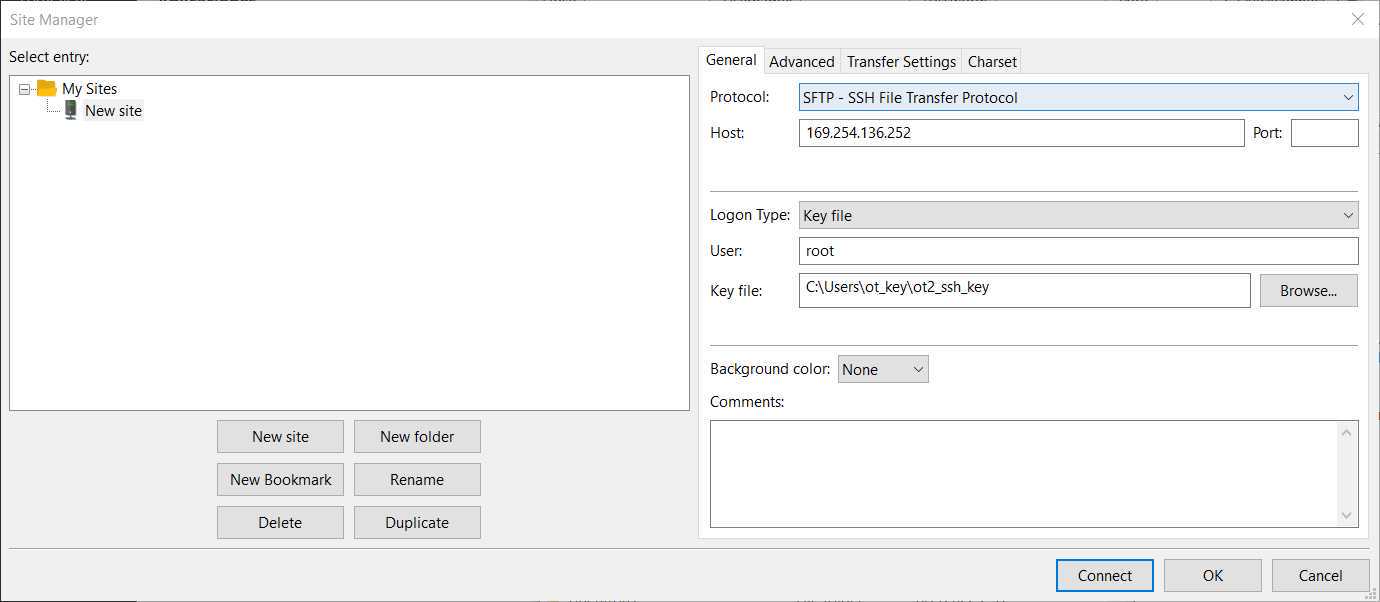
Then press Connect , and we will have a connection between our computer and the robot.
After this connection, we should be able to move the file VariablesMoCloAssembly.xlsx (in our computer) to the directory /data/user_storage in the robot.
This method can be used as well in some Linux and MacOS
Adding the custom labware
There is only a need to do this step when the labware that you are using is not OT official or is not included in the OT app
Creation of .json file
The description file can be obtained by describing the labware dimensions at https://labware.opentrons.com/create/
Uploading files to the OT App
In the OT app, we need to perform the following route: Labware -> Import -> Choose File -> Select file we have created in step 3.1
Transfer labware files to the robot
If you are using the entry LAP-MoCloAssembly-OT2-1.0.0 or LAP-MoCloAssembly-OT2-1.0.1 with custom labware, an additional step is needed, which is transferring a folder with the custom labware
We need to create for our custom labware a folder with the API name containing the description file (.json) called 1.json and then transfer that folder to the robot's folder /data/labware/v2/custom_definitions/custom_beta in a similar way as in the Step 2 but with the difference that is a directory that needs to be transferred and not a file.
#Transferring the custom labware to OT (Linux)
scp -i [ot_key] -r [directory_custom_labware] root@[IP_OT]:/data/labware/v2/custom_definitions/custom_beta
Prepare RobotOS
Install needed packages
This script needs the package openpyxl , which is not installed by default in the OT-2 robots
Connect to the robot
to find the IP of the robot in which you want to run the script
To connect to the robot, you can do it via ssh with the following command
#Connect to Linux based OT via ssh
ssh -i [path ot_key] root@[Robot_IP]
```In Windows you can do this command in Windows Powershell
<Note title="Citation" type="success" ><span>If the connection has been successful you should obtain a screen similar to the following image</span><img src="https://static.yanyin.tech/literature_test/protocol_io_true/protocols.io.5jyl8p82rg2w/pi66bxsu77.jpg" alt="Drawing obtained when entering an OT-2 system" loading="lazy" title="Drawing obtained when entering an OT-2 system"/></Note>
Install the package
Once inside the robot's system, you need to run the following command
#Install openpyxl package (Linux 4.14.74-v7)
pip install openpyxl
Running Protocol
Load script in OT-App
Now that we have transferred the variable files to the robot, we can load the script and run it in the selected robot
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| Opentrons App | NAME |
| Windows >=10, Mac >=10 | OS_NAME |
| , Ubuntu >=12.04 | OS_VERSION |
| https://opentrons.com/ot-app/ | REPOSITORY |
| Opentrons | DEVELOPER |
Load the script in the App
Protocols -> Import -> Drag Python script
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| LAP Repository | NAME |
| www.laprepo.com | REPOSITORY |
| https://biocomputationlab.com/ | DEVELOPER |
Select Robot to Perform Script
Click in the protocol -> Start setup -> Choose the OT where the file VariablesMoCloAssembly.xlsx is -> Proceed To Setup
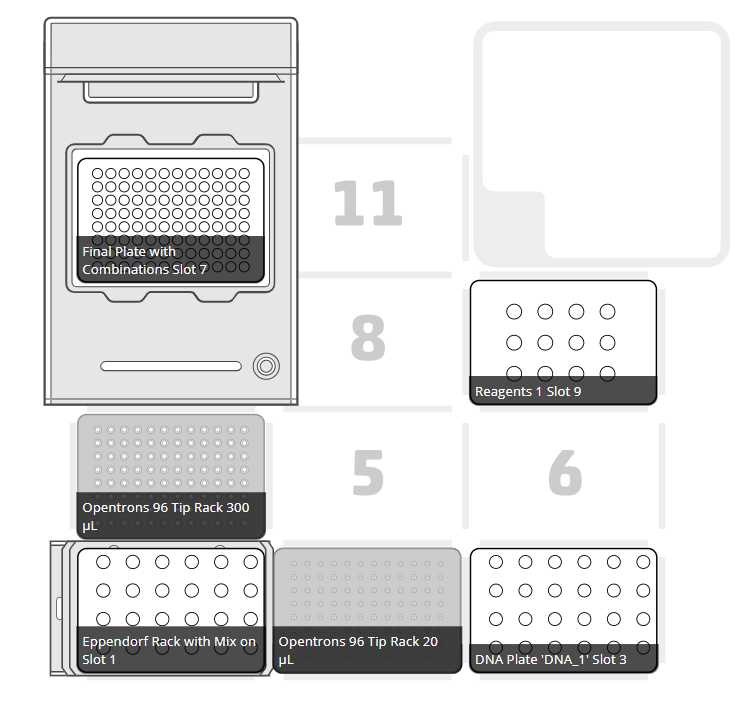
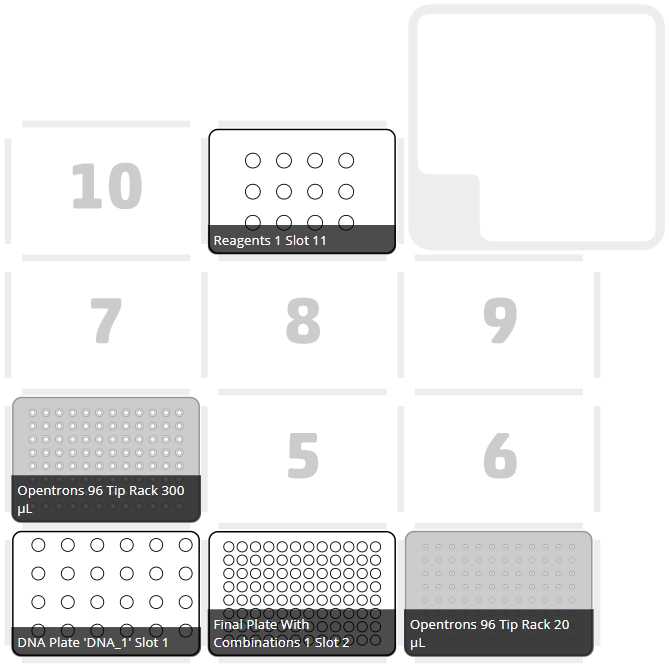
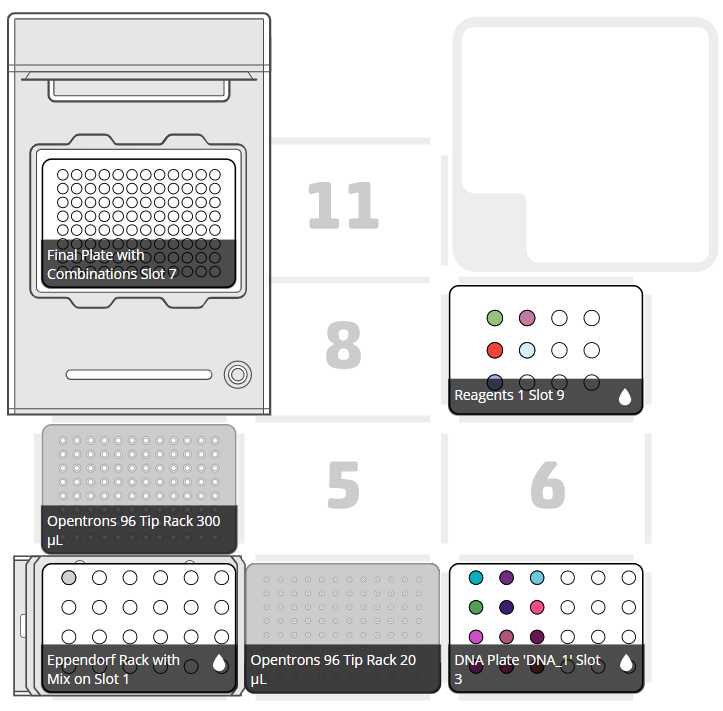
After clicking on Proceed to Setup, you should obtain, if there is no error, the positions of the labware in the Labware tab and the reagents, with their corresponding volume in the Liquids tab.
In case the protocol with the set variables cannot run, an error will be raised by the app. Many errors are contemplated already and have a specific message that will give the user a hint of what could have gone wrong.

Run Protocol in OT
Make sure the needed calibrations are done
Pipettes, tip racks and tip length calibrations need to be done for the items used in this run
Labware position check is performed (if needed)
Clean the surface of the robot with 70% ethanol to clean and disinfect the surfaces
Set the labware and reagents as shown in the OT-App
Start Run
The procedure that the robot is going to do is mainly divided into 9 parts:
- (Optional) The block temperature from the thermocycler reaches a temperature set by the user in case that variable is not empty
- Distribute the needed water to each final well (the volume of water is calculated by the OT-2 according to the volume set in the variable Volume Final Each Reaction (uL) taking in account the volume of the other reagents and the number of DNA parts that is going to that specific well)
- Creation of mix(es) transferring ligases, buffer, serum and restriction enzyme to new tube(s)
- Mixing with either a pipette or heater-shaker
- Distribute mix to final plate(s)
- Distribute DNA parts to the corresponding wells (as many transferrings as set in the combinations sheet)
- Generate identity maps to be exported
- (Optional) Pause the program for user to put lids on the plate located in the thermocycler (if in the input variable)
- (Optional) Temperature profile with thermocycler module
- (Optional) Block of thermocycler stay to the set temperature
After-Running
Retrieve labware from the OT
Importing map from robot
To retrieve the file we can and reproduce it by transferring the files to the computer.
They will be in the directory /data/user_storage . It will be a file with an extension .xlsx and have the name provided in the input variable file
#Transferring files from OT to computer (Linux, macOS)
scp -i [path_ot_key] root@[IP_robot]:/data/user_storage/[name_map].xlsx [final_path_computer]
Example
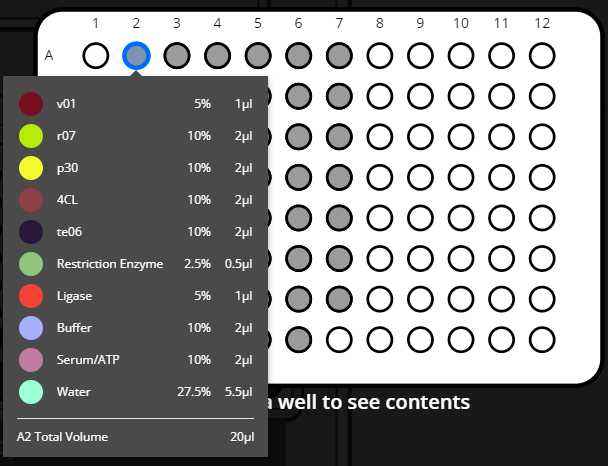
We want to make 47 constructs that are all level 1 from 38 parts, some created in the lab, some from the golden standard database.
We are going to use the heater-shaker module to mix the assembly mix (enzyme, ligase, serum and buffer) and use a thermocycler module to perform the construct assembly with a provided temperature program.
Prepare variable file
Excel temple filled and saved with the name VariablesMoCloAssembly.xlsx
Retrieve labwares from the OT
Retrieve the final map(s) file from the robot where we run the protocol. In this case, they will be called final_construct_map-example.xlsx (name that is stated in the variable file in the variable Name File Final Constructs located in the GeneralVariablesSheet )
Upload custom labware to app
We are using a custom labware called 3dprinted_opentrons_shaker_1.5mleppendorf that has been created with a 3D printer and its file with the labware creator that opentrons offers (https://labware.opentrons.com/create/)
3dprinted_opentrons_shaker_1.5mleppendorf.json
Upload it to the opentrons app and make sure it is loaded in it
Because we are using version 1.0.1 of the script in this example, we will transfer the directory of the labware as well (here we have attached a zip, but it is the folder that must be transferred, not the zip)
3dprinted_opentrons_shaker_1.5mleppendorf.zip
#Transferring the used custom labware to OT (Linux)
scp -i [ot_key] -r 3dprinted_opentrons_shaker_1.5mleppendorf root@[IP_OT]:/data/labware/v2/custom_definitions/custom_beta
Run the protocol in the robot that we have transferred the Excel file
Example-MoClo.py Example-MoClo.py -> Start setup -> Select robot in which we are going to run the protocol
If we do not have any errors, the output should look similar to the following pictures
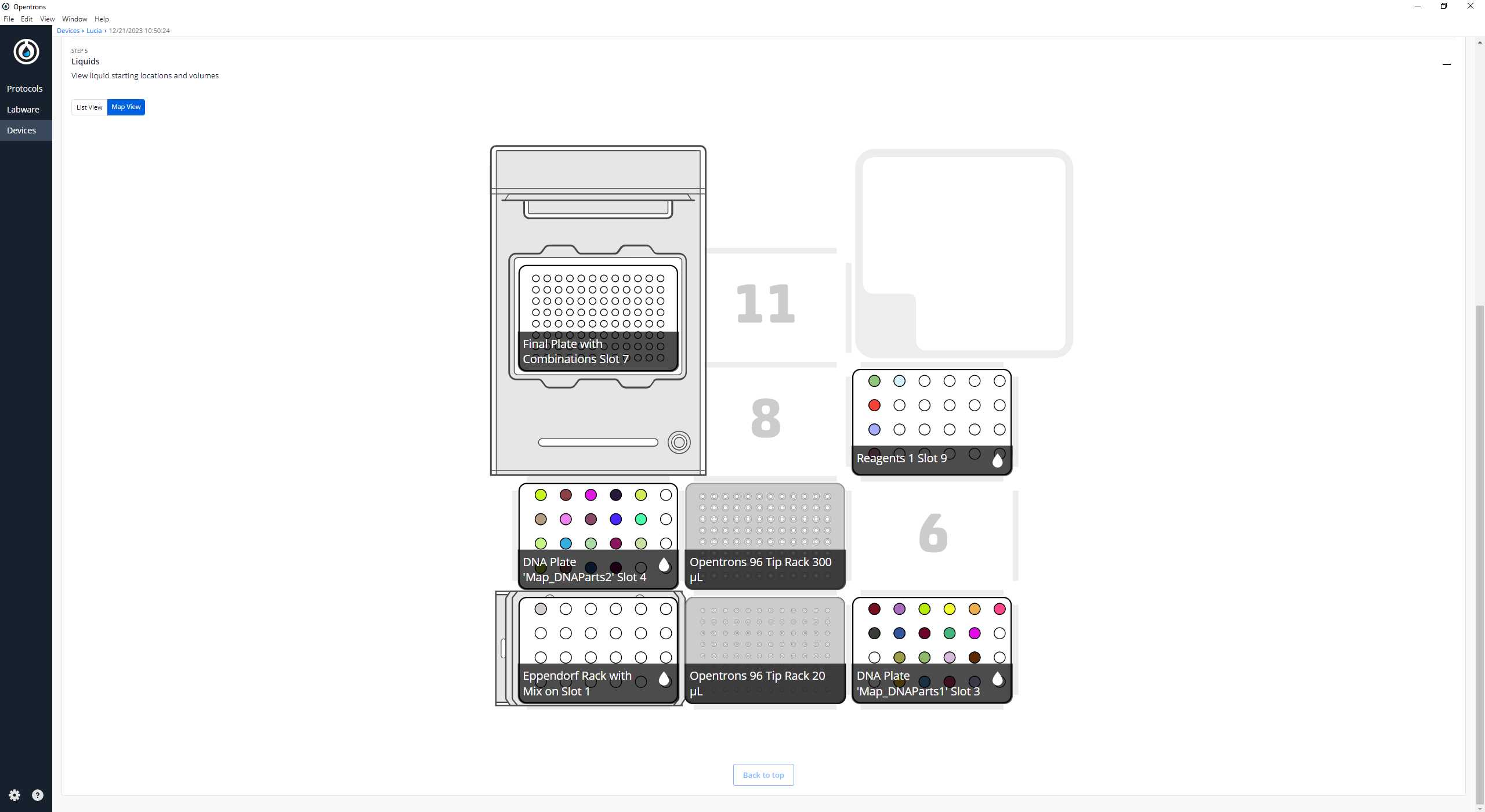
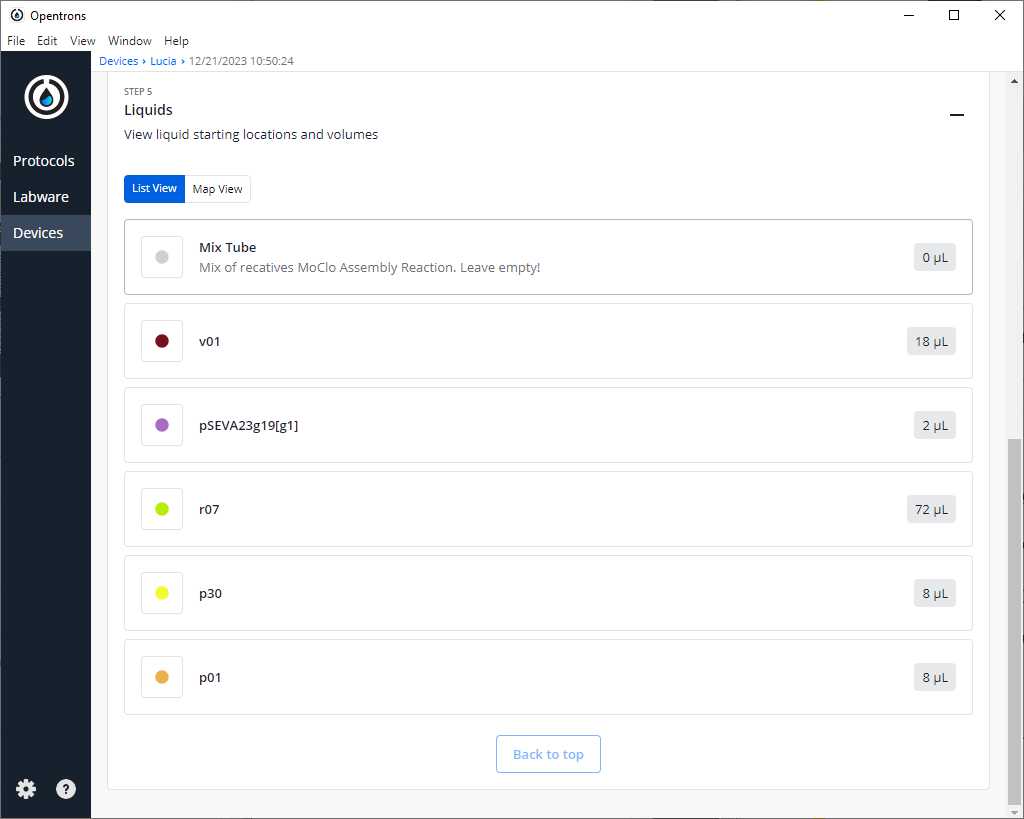
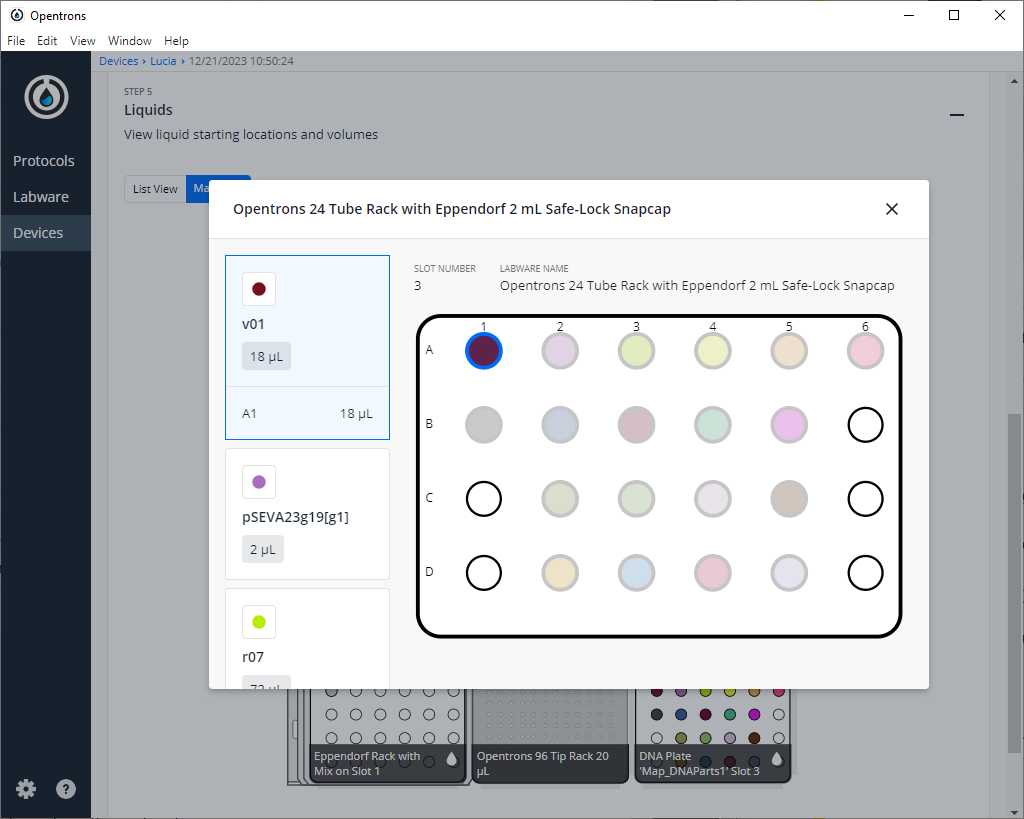
Clean the platform of the robot that we are going to perform the protocol
Prepare all reagents and labware in the places as the App is showing taking into account the notes in step
Start run