Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP) with BioRad Software
Olivia E Todd, Eric L Patterson
Abstract
A short guide to primer design with HEX/FAM tags and a basic KASP protocol using LGC Genomics KASP master mix and BioRad analyzation software.
Attachments
Steps
Primer Design
Design regular primers over the mutation you wish to test.
Copy and paste the FAM and HEX tags to your wild type and mutant alleles. Pay attention to which tag is which.
FAM tag: GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCT
HEX tag: GAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATT
Example: IAA16 GG to RR mutation Primers in Bassia scoparia
Thaw primers; one reverse primer, two forward primers, each specific to a SNP and corresponding fluorophore.
Make primer mix:
| A | B |
|---|---|
| EACH forward primer | 18 μl |
| Reverse primer | 45 μl |
| H2O | 69 μl |
| Total primer mix | 150 |
Add 12µL of primer mix to the 2x KASP tube, this now the KASP master mix.
Add 4µL of KASP master mix to each sample well of a 96 well plate.
Add 4µL of template DNA @ 5ng/μl-20ng/μl.
Include 3 NTCs, as well as appropriate controls.
Bio-Rad machine and software
Set up thermocycling conditions according to the protocol:
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| Step | Temperature | Length |
| 1 | 94 C | 15 minutes |
| 2 | 94 C | 20 seconds |
| 3 | 61 C | 1 min |
| 4 | Go to step 2 | 10x |
| 5 | 94 C | 20 seconds |
| 6 | 55 C | 1 min |
| 7 | 30 C | 10 seconds |
| 8 | Go to 5 | 35x (take read each cycle) |
Make sure that each well of the plate has both FAM and HEX fluorophores selected.
Click Start Run.
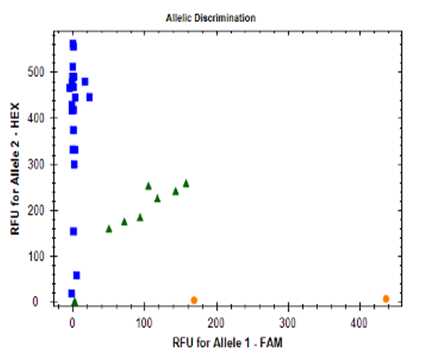
Analysis
On the “Allelic Discrimination” tab the relative florescence units (RFU) for FAM and HEX are displayed, these are used to make a call on the SNP(s) present in each sample.