Install WSL and VSCode on Windows 10
Kenneth Schackart
Abstract
This protocol describes how to install Ubuntu, WSL, and connect to WSL with VS Code on Windows 10. By the end you should have a working version of Ubuntu and WSL. VS Code will be able to work with your Ubuntu installation. You will also have Python3 since Ubuntu comes packaged with it.
Most of the information presented here is given in the attached Microsoft Docs link.
Before start
To update to WSL 2, you must be running Windows 10.
- For x64 systems: Version 1903 or higher, with Build 18362 or higher.
- For ARM64 systems: Version 2004 or higher, with Build 19041 or higher.
- Builds lower than 18362 do not support WSL 2. Use the Windows Update Assistant to update your version of Windows. To check your version and build number, select Windows logo key + R , type winver , select OK . Update to the latest Windows version in the Settings menu.
Steps
Enable WSL
Open Windows Powershell as Administrator.
In Powershell, enter the following command to enable WSL:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart
In Powershell, enter the following to enable virtualization:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
Restart your machine to make the changes take effect.
Download the Linux kernel update package:
https://wslstorestorage.blob.core.windows.net/wslblob/wsl_update_x64.msi
Run the package.
Set WSL2 as Default
Open Powershell as administrator and run:
wsl --set-default-version 2
Install Ubuntu
Go to the Microsoft Store and install a version of Ubuntu.
Check Installation
Open Ubuntu by hitting the Windows key, and type "Ubuntu", and open it.
If an Ubuntu window opens but is quickly closed, continue to the next step.
If Ubuntu opens properly, go to step 13 to set up VS Code.
If WSL has failed to open by briefly flashing and then closing, it means your machine is still blocking virtualization. This must be resolved by entering BIOS. How to do this varies by laptop type. It will generally involve shutting the machine off, powering it on, and while it boots you need to hit a certain key to pause boot up.
Search the web for "How to enter BIOS
You will not be able to see this protocol in BIOS, so open this page on another device.
Once in BIOS, use the arrow keys to navigate the menus and search for any settings regarding "virtualization" and enable them.
This may be something like "Virtualization Technology".
Save the changes you have made to the BIOS settings and restart.
Check Installation Again
Try starting Ubuntu again.
If it still gets closed, hit the Windows key, type features, and select "Turn Windows features on or off". If there is the feature "Windows Hypervisor Platform", enable that. Also make sure that "Virtual Machine Platform" and "Windows Subsystem for Linux" are enabled.
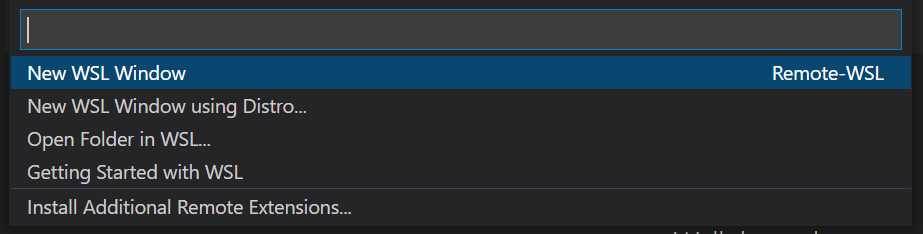
Set up VS Code
Update
From the top menu, select Terminal -> New Terminal
In the new terminal run the following to update
sudo apt-get update
You should now have a working version of WSL and access to it through VS Code.
Some things to keep in mind:
-
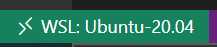
You can see if your current VS Code session is running in WSL by looking at the green rectangle at the bottom left corner
-
Since WSL has its own file system, if you plan to interact with GitHub using SSH keys, you will need to generate new ones using the WSL terminal, and add them to your GitHub
-
Whatever repositories you want to run in WSL should be cloned using the WSL terminal
-
WSL can be run without VS Code to have a nice linux terminal