Formation and isolation of Clu phospholipid particles
Patricia Yuste-Checa, F Ulrich Hartl, Andreas Bracher
Abstract
This protocol details how to efficiently make in vitro and isolate Clu-phospholipid particles using purified Clusterin from HEK293E cells (dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.bvvkn64w) and 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC).
Attachments
Steps
Formation of Clu-phospholipid particles
Prepare 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC) stock solution: 5-25 mg/ml DMPC in 3:1 Chloroform:Methanol and store it at -80°C.
Transfer the corresponding amount of DMPC solution to a glass vial and remove the solvent by evaporation through a constant stream of nitrogen gas until it dries out and becomes waxy.
Resuspend the lipids with 1x PBS 7.2 to obtain the desired concentration, vortex and sonicate in a Bioruptor sonication bath (Diagenode) (25 cycles of 5 seconds on – 5 seconds off), or similar. The resulting mixture is turbid and white.
Mix 10micromolar (µM) Clusterin with 10millimolar (mM) DMPC in a PCR tube for a Clusterin:DMPC ratio 1:1000. For example, 10µL Clusterin 20micromolar (µM) + 10µL DMPC 20millimolar (mM) in PCR tubes.
Incubate the sample through 3 cycles of 18°C for 15 minutes – 30°C for 15 minutes using a PCR thermocycler.
Incubate the sample at 18°C for 0h 15m 0s – 30°C for 0h 15m 0s using a PCR thermocycler (1/3).
Incubate the sample at 18°C for 0h 15m 0s – 30°C for 0h 15m 0s using a PCR thermocycler (2/3).
Incubate the sample at 18°C for 0h 15m 0s – 30°C for 0h 15m 0s using a PCR thermocycler (3/3).
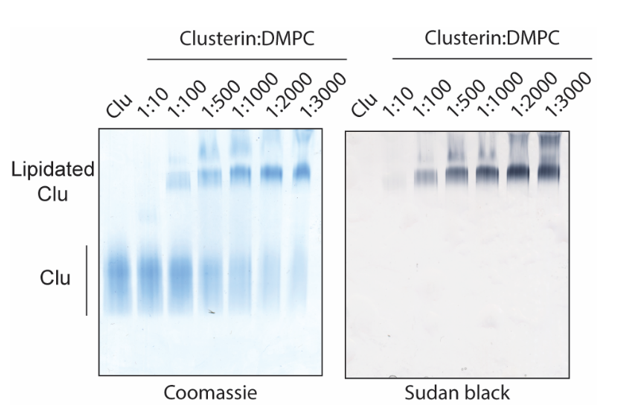
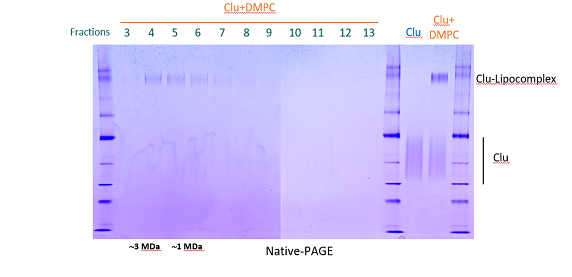
Analyze Clusterin lipidation by Native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (Native-PAGE). Mix the
samples with NativePAGE Sample Buffer (4X) (refer materials section), load them on a NativePAGE 3%–12% Bis-Tris SDS gel and run the gel in NativePAGE running buffer (refer materials section) at 140 V.
For protein staining, incubate the gel 0h 0m 30s with InstantBlue and de-stain next day with water.
Isolation of Clu-phospholipid nanodisc complexes
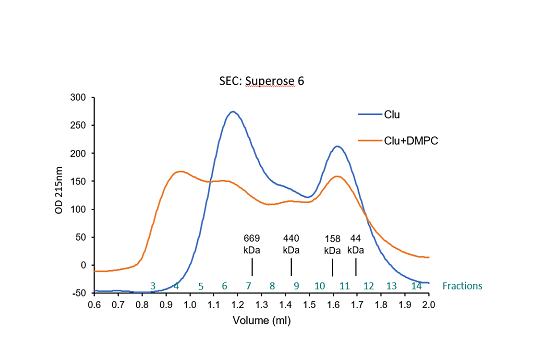
Centrifuge lipidated Clusterin using a table top centrifuge for 30 seconds to pellet big multi-lamellar lipid vesicles (white pellet).
Collect and concentrate the Clu-phospholipid complex containing fractions by ultrafiltration using
Vivaspin MWCO 10.000 (GE Healthcare).