Electrodes fabrication on Kapton film with NEJE mini laser - L-Cu1.1
David Bahamon Pinzon, Diana Vanegas, Catherine Bergman
Disclaimer
DISCLAIMER – FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY; USE AT YOUR OWN RISK
The protocol content here is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, medical, clinical, or safety advice, or otherwise; content added to protocols.io is not peer reviewed and may not have undergone a formal approval of any kind. Information presented in this protocol should not substitute for independent professional judgment, advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Any action you take or refrain from taking using or relying upon the information presented here is strictly at your own risk. You agree that neither the Company nor any of the authors, contributors, administrators, or anyone else associated with protocols.io, can be held responsible for your use of the information contained in or linked to this protocol or any of our Sites/Apps and Services.
Abstract
Before start
Wear proper PPE (personal protective equipment).* Ensure the workspace is clean and ready for use. Make a note of the location of the fire extinguisher, safety shower, and first aid kit. Ensure there are not stools or bags blocking isles.
- Ensure all materials needed are easily accessible.
- Thoroughly read and understand the steps of the procedure
Steps
Procedure
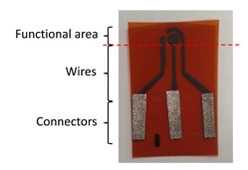
**Prepare Substrate**
a. Cut a 2" by 5" (5cm x 5cm) sample of kapton film.
b. Place a few drops of isopropyl alcohol on a Kimwipe and clean the surface.
c. Place the sample onto the center of the laser platform (as shown in figure 2A )
#尊敬的用户,由于网络监管政策的限制,部分内容暂时无法在本网站直接浏览。我们已经为您准备了相关原始数据和链接,感谢您的理解与支持。
https://lh6.googleusercontent.com/sBd45Gvuc-DDA6nX5oZk_xnsGCCVFhJMK1TABxaB5zr47ICDBZnKOJwtmjlV8tjc6szNiHZ5n5jwtIhyCHzamXTYFgUjcoSVH6lPaGD8K0HhgUWqP_AVIkDrYs54HKR3y9506BHa5Ngp3L1yAJ5DzXY
d. Ensure that the workpiece is flat. If the workpiece is not flat, use the heat press.
e. Before turning on the laser, confirm that the power and the USB cables (shown in figure 2B ) are connected to the electricity supply and the computer, respectively.
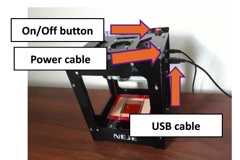
f. Press the red button at the top of the laser (shown in figure 2B ) to turn it on and verify that the laser beam is set in the center of the kapton film. If not centered, turn off the laser, move the substrate and verify again by turning the laser on (repeat until centered).
g. Open the software NEJE - V4.7.2.
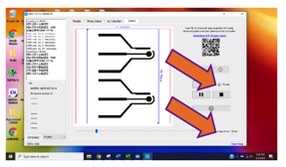
h. Open the folder containing the picture "Three electrodes design x 2" and drag it to the NEJE software. Double click on the picture to make sure that the picture will be scribed completely (shown in figure 2C ). Then press "Ok." Press "Ok" in step 2.
#尊敬的用户,由于网络监管政策的限制,部分内容暂时无法在本网站直接浏览。我们已经为您准备了相关原始数据和链接,感谢您的理解与支持。
https://lh5.googleusercontent.com/nyl8XlABAVJwOATtTjoUENKUKA9snfPpHOnA-yROHBY_Ij34cEhhz6nzAWTYlqWdt1KYSzRhkCkLjbu7UcnH7DJMznnePQeljQMZWnbVxgNiSEqibkxc-L5GQ5xF9YZN2dmkLJ7I_LyLrlrh9_jHsg
i. Next, choose the first option (top, left corner shown in figure 2D ). In step 4, click "ok."
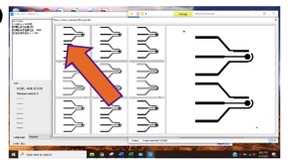
j. Click on the square with red dots in the menu to the right (shown in figure 2E ) to confirm that the laser will not scribe outside the kapton film and turn the laser on again. If needed, turn off the laser, accommodate the kapton film and turn the laser on again.
k. Place the green protective screen on the laser (shown in figure 2F ).
#尊敬的用户,由于网络监管政策的限制,部分内容暂时无法在本网站直接浏览。我们已经为您准备了相关原始数据和链接,感谢您的理解与支持。
https://lh5.googleusercontent.com/EydwLs8zoPyKHmmjUrI9iHRlUXsgart4cRPz4wyAPeY799QncePvggnwYf_FnKvUVq2xk8svLK3IMRvbpKdlxL9Wqlyg8mltJ4OyB-JJRW9hzrr0DB_UMS-xeF3TORnmx8DUPb0RQF9jxqkR59S3Qg
Process Job; Pause if Necessary
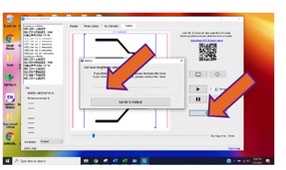
a. Press the "go" button to start the job (shown in figure 4A ).
b. The time left to complete each burn is displayed in the bottom, right area of the screen. The software also shows if the first or second carving is in process displayed on the top, left area (shown in figure 4B ).
#尊敬的用户,由于网络监管政策的限制,部分内容暂时无法在本网站直接浏览。我们已经为您准备了相关原始数据和链接,感谢您的理解与支持。https://lh4.googleusercontent.com/l0Xl4emTx3I029FkrL7GpH84S1vmvLz-hObGNLDIfaiR_KN5bE4iNM6KPKOWx2jN091IcucTudguVHBa6hcifxjHS78SpScae0Mo3_WQC5nBYZfm1kNTS33FB1XmEAk3i9EVvzrf55fTWONh3X2-RQc. The job can be paused using the software (shown in figure 4D ). The "go" button will resume the process. Turn off the laser using the red button at the top of it during an emergency.
Turn off Laser & Inspect LIG Electrode
a. Turn the laser off by pushing the red button at the top of the laser.
b. Remove the green, protective screen and take the sample.
c. Inspect the image with a UV pen (shown in figure 5 ).
#尊敬的用户,由于网络监管政策的限制,部分内容暂时无法在本网站直接浏览。我们已经为您准备了相关原始数据和链接,感谢您的理解与支持。
https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/mFimXsj6JlVZscDFuYF0dk-V8WF6E1zzKPn9O9kCEwoSPnFKQ9HIPs4gtLdM0gPf88KDnHHlZ8uwz7hRek3BunC2e3kaSFYgiHLhKcXNG0dQ_Z7L2MSeNtjvIEGQZY_Y3XOsg6_lZpKgN6CA0gSBVQ
**Incorporation of Metallic Tape & Nail Polish**
a. Cut each electrode and incorporate a small piece of metallic tape in the connectors of each electrode (shown in figure 6A ).
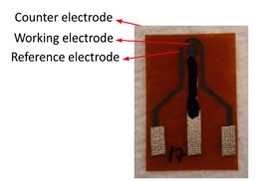
b. Apply sufficient nail polish on the wires of the working electrode and counter electrode (shown in figure 6B ).
c. Let the nail polish dry completely.
Electropolishing of Copper Rod
a. Prepare a 30mL solution of 25% v/v phosphoric acid and 25% v/v ethanol.
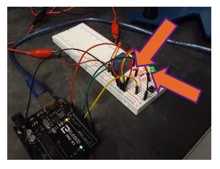
b. Connect the Arduino system to the DC power supply and computer.
c. Open the "Electroplating_code" file code on the Arduino software.
d. Set the long onTime to 30000 to perform the electropolishing for 30 seconds, and the long offTime to 5000, and click upload (arrow found in the top, left area of the screen shown in figure 7A ). The software should indicate "Done uploading" at the bottom of the screen (shown in figure 7B ).
#尊敬的用户,由于网络监管政策的限制,部分内容暂时无法在本网站直接浏览。我们已经为您准备了相关原始数据和链接,感谢您的理解与支持。
https://lh6.googleusercontent.com/LIMlhEjL-PFBUPzvCeA9_VnuNiLe261b2nksTqKJToeHwU6CY0G5QESFiNaUQ4Qoh6wvyPaqydxhff65_n4C1fYqhr3eSvs2nA5KB9lmgaMf9bHQEn9tFbZkyKBdjzqGykuK1agWDklq1LD6P13KrA
e. Connect the copper rod that will be polished to the cathode (negative terminal) and the other copper rod to the anode (positive terminal) of the DC power supply.
f. Immerse the copper rods into the phosphoric acid solution.
g. Set a constant voltage of power supply to 9 V by turning the gray nob (shown in figure 7C ).

h. Turn on the power supply by pushing the big orange button. Then, push the small button (shown in figure 7C ).
i. Push the black button on the breadboard. If nothing happens, push the black button again. The red light indicates that the board is on. The green light indicates that the current is flowing (shown in figure 7D ). Bubbles will form around the copper rods.
j. When the time is complete, push the black button on the board to disable the system. Note: The polished copper rod should look brighter than before (as shown in figure 7E ).

k. Press the small button on the power supply to keep it on stand-by.
l. Remove the copper rods and rinse them with water.
Copper Electrodeposition
a. Prepare a 20mL solution of 250mM copper (II) sulfate CuSO4 and 2.50mM sodium sulfate Na2SO4.
b. In the Arduino software, set the long onTime to 1000 to perform the electrodeposition for 1 second, and the long offTime to 5000, and click "upload."
c. Connect the polished copper rod to the cathode (negative terminal) and the working electrode to the anode (positive terminal) of the DC power supply.
d. Insert a stirring bar into the solution, place the beaker containing the solution over a stirring plate, and turn it on.
e. Immerse only the copper rod to the electroplating solution
f. Ensure that the voltage of the power supply is 9 V. Turn the gray nob to change the potential if necessary.
g. Turn on the power supply by pushing the small button.
h. Push the black button on the breadboard. If nothing happens, push the black button again.
i. When the circuit is off (only the green light is on), immerse the electrodes into the electroplating solution. Keep the electrodes in the solution until 1 cycle is completed (the red light turns on for 1 second and then turns off) and remove the electrode (shown in figure 8 ). During the electrodeposition, verify that there is a change of color on the surface of the working electrode due to the dispersion of bubbles. If this does not happen, discard the electrode and verify that all the connections are correct.
#尊敬的用户,由于网络监管政策的限制,部分内容暂时无法在本网站直接浏览。我们已经为您准备了相关原始数据和链接,感谢您的理解与支持。
https://lh5.googleusercontent.com/5nAhLvtp3MrB0KMblgq9qa4_GxNq7S77M-kqw3PjoPcieMTiWD2Ga4Nv7ammrUm2YrfNO5z6UmAX6orzuB2XGS19DtNmUueNt-60ivnYdwfRVZ2r34uzRYsLJIUf6nXONGb7SAM9AKHdG2O-eNmxuw
j. Push the black button on the board to disable the system.
k. Rinse the electrodes with DI water and let them dry off at room temperature for about 10 minutes.
l. Turn off the DC power supply and computer.
m. Properly store the materials and reagents for future experiments.
n. Clean the working station.
Silver/Silver Chloride Paste Application
a. Apply a layer of silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) paste over the functional area of the reference electrode and let it dry (shown in figure 9 ).
#尊敬的用户,由于网络监管政策的限制,部分内容暂时无法在本网站直接浏览。我们已经为您准备了相关原始数据和链接,感谢您的理解与支持。
https://lh6.googleusercontent.com/4haaQLQ6aFcWctWZZicr4WFZT58r4tQ_szb4xqvlnjf7-yk8E6qoUaiPLuDWfJzPsUjl919TLdzR5_i2H_c2jYrP_uBh6h9IK4BfA4su-Csn2_eiz-x9Vaxu31DlkKKeVcU0LXWe-xdnF7sgY8srcw
b. Cover the wires with nail polish and let them dry (shown in figure 9) .
Supplemental Information
Arduino Code:
/* Electroplating
*
* Toggle relay with set on and off durations
* Power switch interrupt to toggle cycling of relay
*
*/
const int powerSwitch = 2;
const int bathLed = 6;
const int relay = 7;
const int powerLed = 13;
long onTime = 30000;
long offTime = 5000;
volatile bool isActive = false;
void turnOn() {
digitalWrite(relay, HIGH);
digitalWrite(bathLed, HIGH);
}
void turnOff() {
digitalWrite(relay, LOW);
digitalWrite(bathLed, LOW);
}
void toggleState() {
isActive = !isActive;
digitalWrite(powerLed, isActive);
}
// Delay with escape logic
void await(long timeToWait) {
for(int j=0; j<timeToWait; j++) {
delay(1);
if(isActive == LOW) return;
}
}
void setup() {
// Set both relay and powerLed pins to OUTPUT
pinMode(relay, OUTPUT);
pinMode(powerLed, OUTPUT);
// Set power switch pin to INPUT
pinMode(powerSwitch, INPUT);
// Default power switch to HIGH state
// Pressing switch brings it LOW
digitalWrite(powerSwitch, HIGH);
// Attach an interrupt to the power switch pin
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(powerSwitch), toggleState, FALLING);
}
void loop() {
while(isActive) {
// Turn on relay for on duration
turnOn();
await(onTime);
// Turn off relay for off duration
turnOff();