Collection – Staining– Analysis of vaginal smears
Roberta Marongiu
Abstract
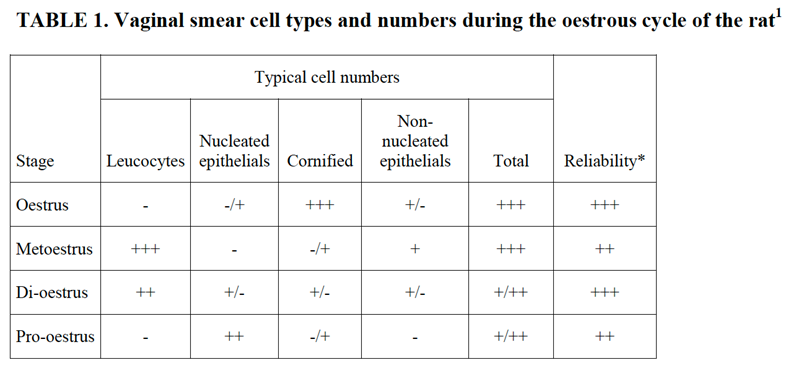
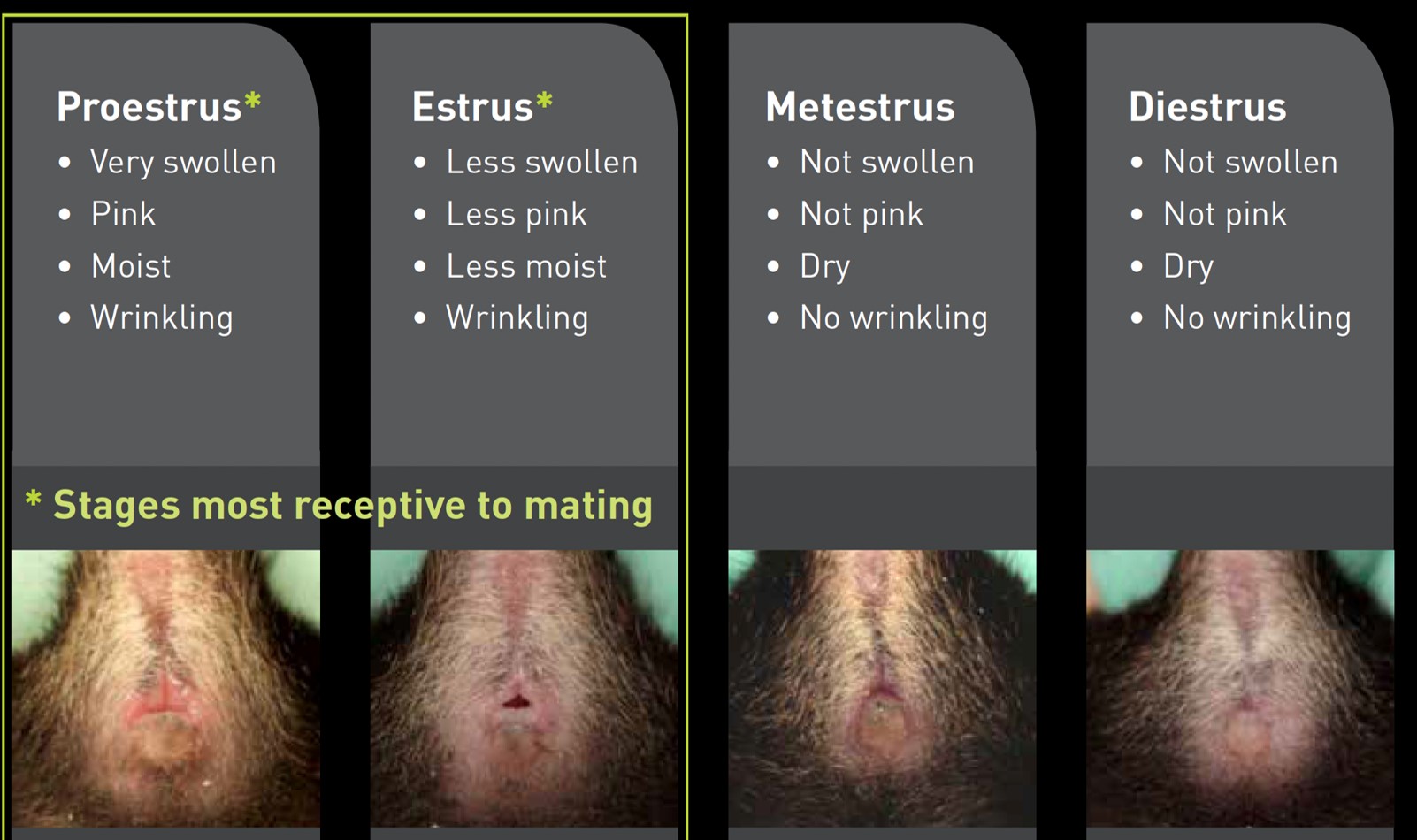
The 4 stages of the rodent’s female cycle are:
- Metestrous – M
- Diestrous -D
- Proestrous -P
- Estrous – E
Transitional stages, i.e. showing characteristics of two consecutive stages e.g. M-D or D-P, are not uncommon, particularly if smears are taken very early or late in the day.
The most commonly used smearing techniques (methods of obtaining vaginal cell samples) are:
a) Lavage or washing with saline or water from a pipette.
b) Swab or cotton bud (moistened with saline or water).
The standard swabbing method consists of inserting a moistened cotton bud swab into vagina, gently removing the cells from the vaginal lumen and walls and transferring the cells to a glass slide. It is the quickest method of smearing and the smears retain their original appearance indefinitely. However, because there is a risk of causing pseudopregnancy if the cervix is stimulated during estrus, we collect samples without inserting the cotton swab into the vagina.
Steps
Sample collection
Pre-label slides with study number, animal numbers, date and time of collection, using a permanent marker, and place them on a suitable tray. Slides can be set up on a date basis, with one set of slides for all females each day.
Hold the mouse by the base of the tail, lifting the back a little.
Moisten the cotton wool tip slightly by dipping into a jar of saline or distilled water and sharply flick off any surplus.
Collect sample with a rotating action of the swab and at an angle of about 45o to the animal’s body. The rotating action of the swab stick is continued, in the same direction.
With the swab held almost horizontally, to ensure cells from the full length of the vagina are transferred, the tip is rolled gently onto a clean, pre-labelled glass slide, below the relevant animal number.
It is important to avoid getting too much fluid on the slide (usually resulting from too much pressure being applied when rolling the swab onto the slide) and to avoid urine contamination as these factors can mask the cells and make reading very difficult.
The swab stick is discarded, a new one being used for each animal.
Let the slides dry completely (it should take 5-10 minutes) on a horizontal position before proceeding with staining.
Staining
Transfer each solution into a Coplin jar.
Dip dry smear/slide 5-10x for one second each in Hema 3 Fixative Solution.
Cover Fixative when not in use to avoid MethOH evaporation.
Allow excess to drain/blot slides.
Dip slide 5-10x for one second each in Hema 3 Solution I.
Allow excess to drain/blot slides.
Dip slide 5-10x for one second each in Hema 3 Solution II.
Allow excess to drain/blot slides.
Rinse slide with DI water.
- Allow excess to drain.
- Allow to dry.
NOTE
Staining intensity may be varied by increasing or decreasing the number of dips in Solutions I and II:
Eosinophilic staining may be intensified by increasing dips in Solution I.
Basophilic staining may be intensified by increasing dips in Solution II.
Analysis
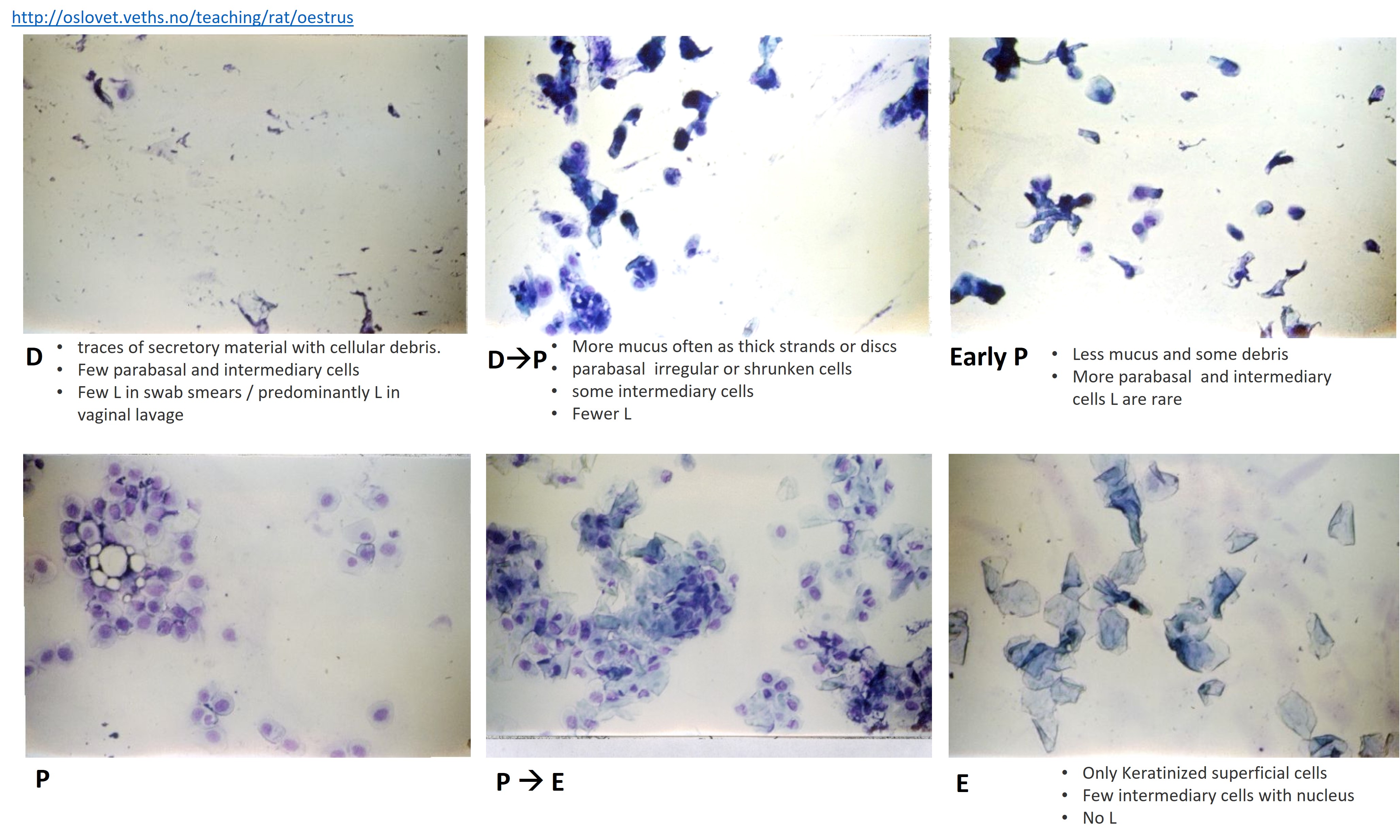
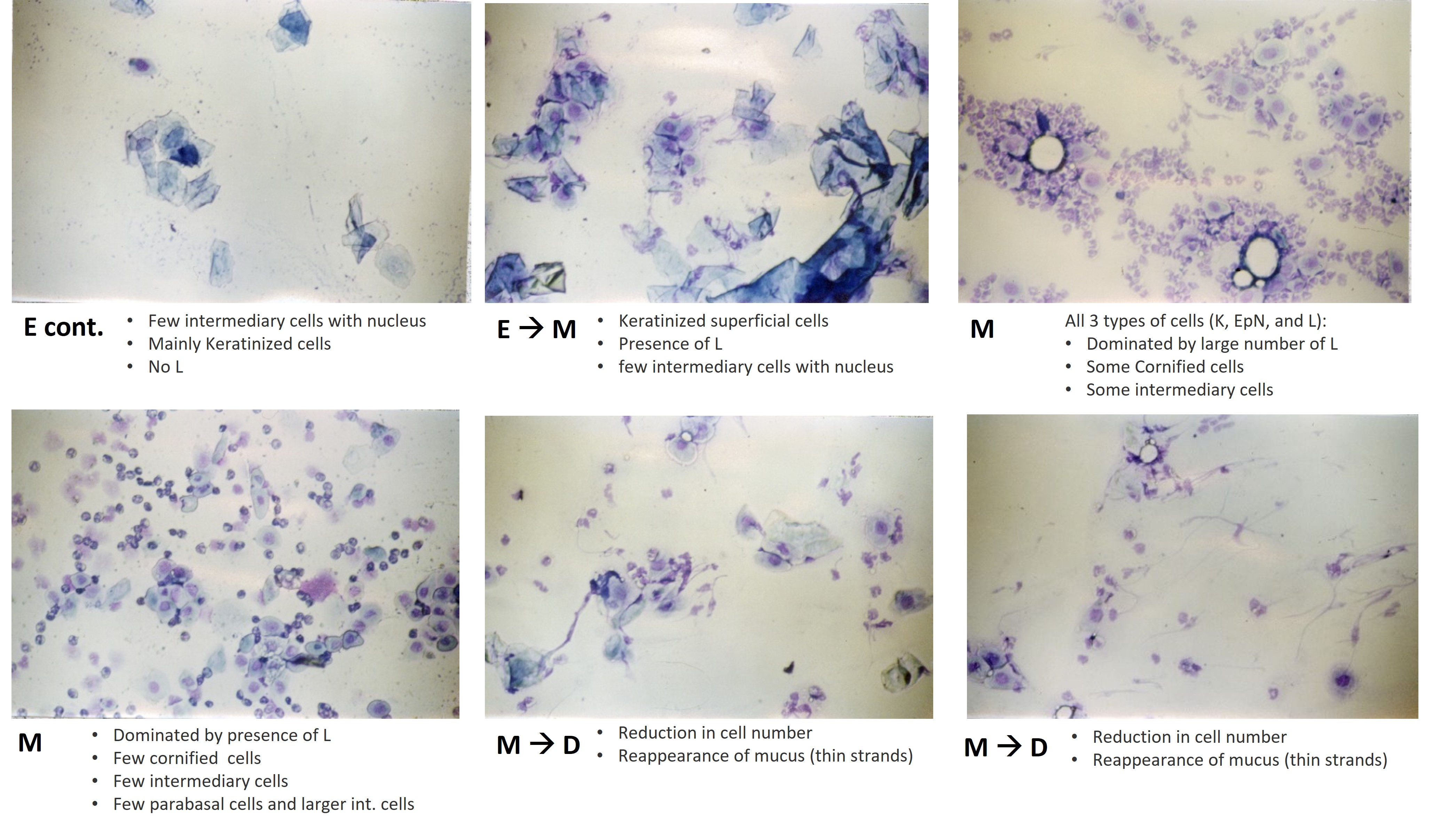
The normal 4-5-day cycle will be in the sequence M, D, P, E, M, D, P, E etc…
- Single stage (E, M, D or P) - if within the normal range of appearance.
- Transitional stage (e.g. MD or DP) - if characteristic of both stages.
These stages of the estrous cycle can be recognized by the presence, absence or proportional numbers of epithelial cells (two types), cornified (keratinized) cells and leucocytes. It is the balance of proportions between these cell types that permits the classification of the stage of the cycle between successive ovulations. Occasionally mucus is also seen, especially in acyclic females.