Collect and Extract Biomass Cyanobacteria (English)
Ricardo M. Borges, Fernanda Chagas
Abstract
It is crucial to pay meticulous attention to high-quality materials, including HPLC-grade solvents, pristine microtubes, and never-before-used Eppendorf Quality tips. Stringent quality controls encompass the 'Cultivation Blank' (culture medium without cyanobacterial inoculation), 'Extraction Blank' (extraction sample container without biomass), 'Combined Quality Control (QC-pool)' (containing aliquots from different cultures), and 'External Quality Control' (strain CCRM0280 cultured simultaneously).
These are defined as follows:
- Cultivation Blank: culture medium devoid of cyanobacterial inoculation, subjected to the same procedures as the samples with cultivated cyanobacteria.
- Extraction Blank: sample vial for extraction (2 mL microtube with screw cap) devoid of dry biomass, subjected to the same extraction procedures.
- Combined Quality Control (QC-pool): a representative sample of the study that faithfully represents an average of all extracted metabolites. It can also be used for optimization of technical analysis parameters.
- External Quality Control (QCExt): The sample containing strain CCRM0280 cultured in parallel will serve as a reference for comparative studies. After drying, the new CCRM0280 sample obtained in the current cultivation will be combined with the CCRM0280-QCExt stock for equitable distribution of inter-batch Quality Control. This protocol is described in a separate document.
Before start
Important
- Before starting the procedure, it is imperative that the entire protocol be thoroughly read and understood. Additionally, a conversation with the responsible party is essential to clarify any doubts before proceeding with the steps. This will ensure that the procedure is conducted accurately and reliably."
Steps
Material
2 mL screw-cap microtubes (e.g., SSIbio) for FastPrep, new (never used)* 2 mL Eppendorf-type microtubes (Eppendorf Quality, Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany), new (never used)
- P1000 pipette tips (Eppendorf Quality, Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany), new (never used)
- 1 mm Zirconia beads (e.g., BioSpec), new (never used)
Tip: Use a "ruler" to measure a single, consistent volume of beads for each sample.

-
HPLC grade Methanol (Tedia, Fairfield, OH, USA | Honeywell, Charlotte, NC, USA)*
-
HPLC grade Dichloromethane (Tedia, Fairfield, OH, USA | Honeywell, Charlotte, NC, USA)*
-
Ultrapure water (e.g., Milli-Q) *or another of comparable quality.
-
FastPrep (FastPrep-24, MP Biomedicals LLC., Santa Ana, CA, USA) at Platform for Expression, Purification, and Analysis of Biomolecules (PEPAB) - Biofícia - UFRJ
-
Ultrasonic Bath (Cristofoli, Brazil)
-
Vortex (model 772, Fisatom)
-
Refrigerated Benchtop Centrifuge (Hettich Model 320R, Tuttlingen, Germany)
-
Automatic P1000 pipette (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany)
-
SpeedVac (Christ model RVC 2-25, Osterode am Harz, Germany) at LabMeta - Chemistry Institute - UFRJ

Biomass Collection
After 28 days, extract ~80-90% of biomass from each Erlenmeyer flask (quantity determined visually only)
-
Allow the specimens to grow until a good amount of biomass is formed, with a tentative empirical limit of four months per specimen.
-
Each specimen will be allowed to continue growing until it becomes necessary to interrupt the cultivation for some reason (excess biomass, cell death, etc.).
-
Initially, a limit of four months will be established for each specimen.
Transfer the culture medium from each Erlenmeyer flask with the biomass to a 50 mL Falcon-type conical centrifuge tube, properly labeled (corresponding to the reference code in the sample list).1. Centrifuge: 3011 xg (4500 rpm) at 4°C for 15 minutes.
- Discard the supernatant.
- Continue transferring the contents of each Erlenmeyer flask, centrifuging and discarding the supernatant until all aqueous content is completely eliminated.
- Record the volume of biomass obtained (photo for file).
- If possible, filter and dry the previously obtained biomass.
This may not be feasible in some cases.
- Subject each properly identified sample to a lyophilization process until dry.
-
Each sample should be separately identified in clean, semi-screwed Falcon tubes (to prevent cross-contamination of the samples).
-
Insert pertinent details and observations in the Metadata.
-
Always store in a freezer at -20°C.
Prepare the material for the extraction step.
Verify the codes on the labels and the list of dried biomass samples.* Organize the microtubes for the addition of dried biomass (2 mL screw-cap microtubes) and for the storage of extracts (2 mL Eppendorf-type microtubes - Eppendorf Quality).
- Label all of them appropriately according to the sample table. All materials (Eppendorf microtubes, Eppendorf tips, vials, etc.) must be new. Never reuse these materials for this purpose.
Extraction of Biomass - for obtaining low to medium-polarity metabolites.
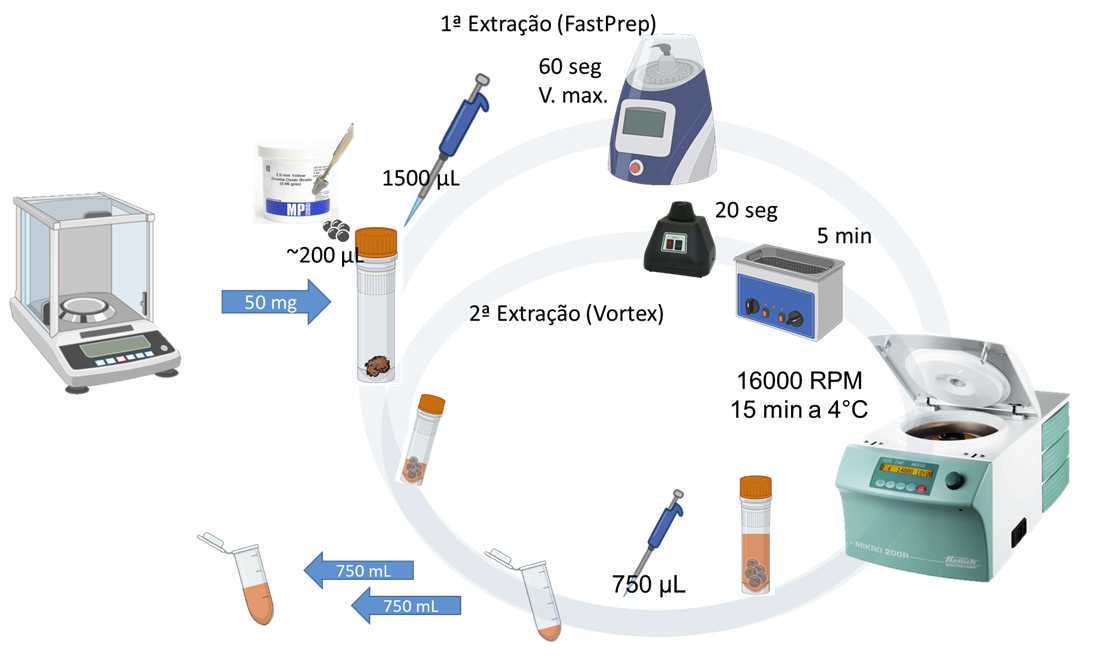
- Weigh 50 mg of dried biomass and transfer it to a 2 mL screw-cap microtube.
- Include Extraction Blanks: empty vials added at the beginning and end of the sample sequence, and at intervals of 10 samples.
- Add approximately 200 µL of Zirconia Beads to each biomass sample contained in the 2 mL screw-cap microtubes (use the template for transferring beads mentioned above).
- Always treat the analytical blanks as if they were real samples.
- Add 1.5 mL of the chosen extraction solvent (in this case: dichloromethane-methanol, in a 2:1, v/v ratio) to all screw-cap microtubes.
- Homogenize all samples for 60 seconds at the highest speed (6 m/s) of the FastPrep homogenizer.
- Centrifuge all samples at 24900 xg (16000 rpm) for 15 minutes at 4°C.
- Collect 750 µL (0.750 mL) of the supernatant from all samples in new 2 mL Eppendorf-type microtubes (Eppendorf Quality), properly labeled.
REPEAT EXTRACTION:
- Add an additional 750 µL (0.750 mL) of the same chosen extraction solvent (in this case: dichloromethane-methanol, 2:1, v/v) to all the vials.
- Homogenize the samples for 20 seconds on a Vortex-type shaker, followed by an ultrasonic bath for 5 minutes.
- Centrifuge all samples at 24900 xg (16000 rpm) for 15 minutes at 4°C.
- Completely evaporate all samples using the SpeedVac until dry.
- Store all samples in a freezer at -80°C until they are prepared for analysis.
Extraction of Biomass - for obtaining high polarity metabolites
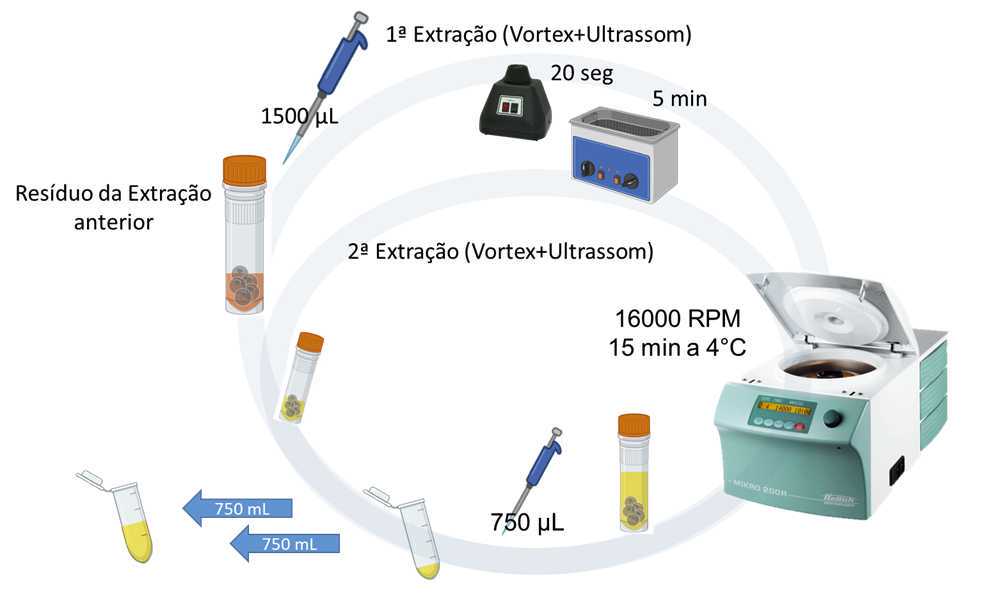
- Add 1.5 mL of the more polar extraction solvent chosen (in this case: methanol-water, 1:1, v/v) to all screw-capped microtubes containing the previously extracted biomass residue.
- Homogenize the samples for 20 seconds on a Vortex shaker, followed by an ultrasonic bath for 5 minutes.
- Centrifuge all samples at 24900 xg (16000 rpm) for 15 minutes at 4°C.
- Collect 750 µL (0.750 mL) of the supernatant from all samples into new 2 mL Eppendorf-type microtubes, properly labeled with tags.
Repeat the extraction:
- Add another 750 µL (0.750 mL) of the same more polar extraction solvent chosen (in this case: methanol-water, 1:1, v/v) to all the vials.
- Homogenize the samples for 20 seconds on a vortex shaker, followed by an ultrasonic bath for 5 minutes.
- Centrifuge all samples at 24900 xg (16000 rpm) for 15 minutes at 4°C.
- Completely evaporate all samples using the SpeedVac until dry.
- Store all samples in a freezer at -80°C until they are ready for analysis.
Pooled quality control sample
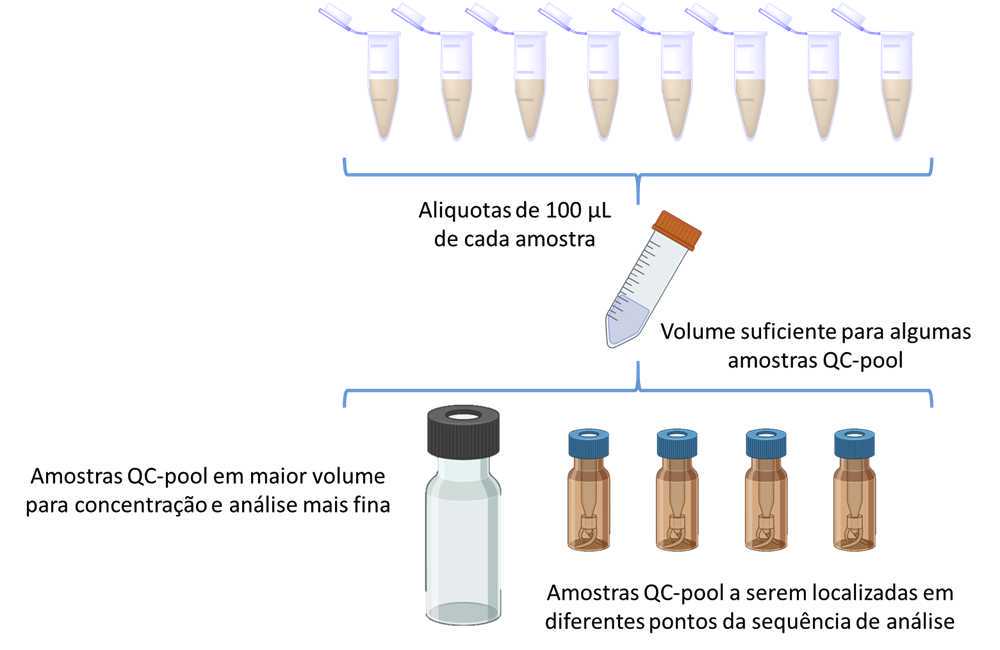
- To prepare the combined Quality Control (QC-pool) samples from approximately 10% of the volume (50 µL) of each sample, follow these steps:
- Take an aliquot of 50 µL from each individual sample.
- Transfer these aliquots into a new 20 mL flask
- Aliquote this pooled quality control sample into four new labeled analytical vials.
Make sure to label the QC-pool samples accurately for identification. Store the remaining quantity for future evaluation or analysis, such as 2D NMR analysis.
Expected Results
At the end of the protocol, it is expected to obtain extracts of low to medium polarity and high polarity for each produced sample, in addition to the Quality Control samples (Extraction Blank and QC-pool), allowing for a comprehensive and comparative analysis of the metabolites being produced by different cyanobacteria, with inter-batch quality control.