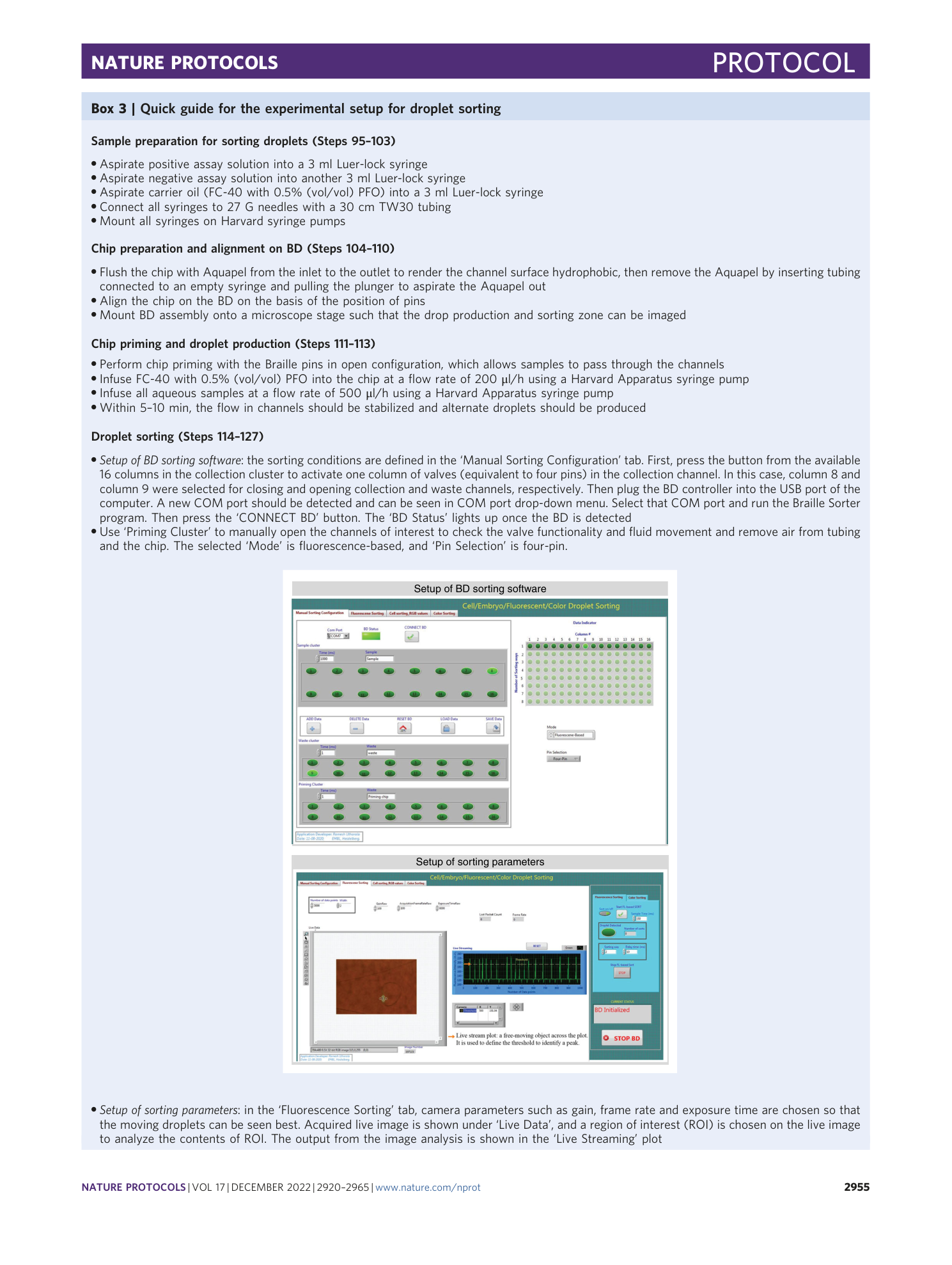
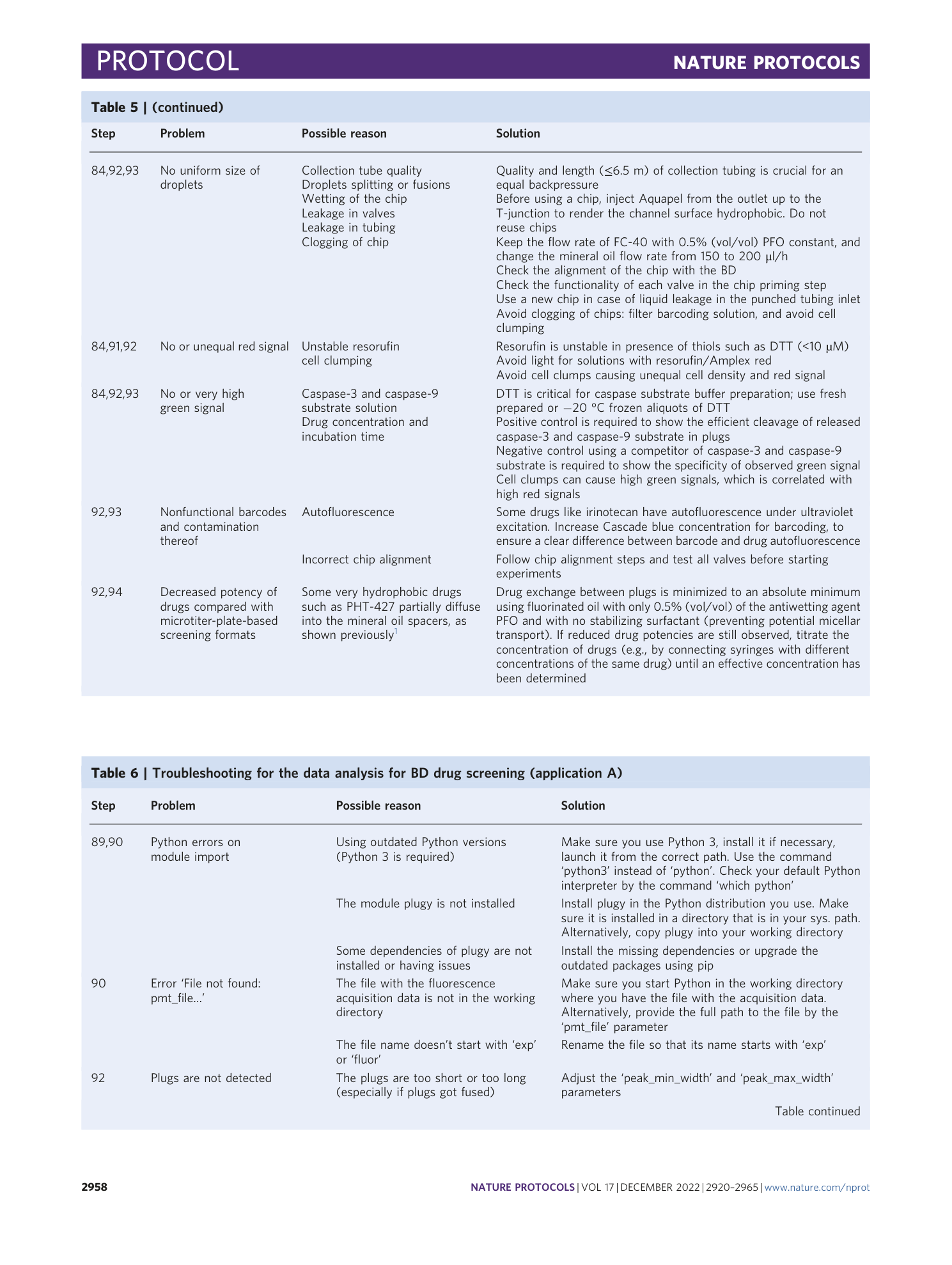
A microfluidic Braille valve platform for on-demand production, combinatorial screening and sorting of chemically distinct droplets
Julio Saez-Rodriguez, Ramesh Utharala, Anna Grab, Vida Vafaizadeh, Nicolas Peschke, Martine Ballinger, Denes Turei, Nadine Tuechler, Wenwei Ma, Olga Ivanova, Alejandro Gil Ortiz, Christoph A. Merten

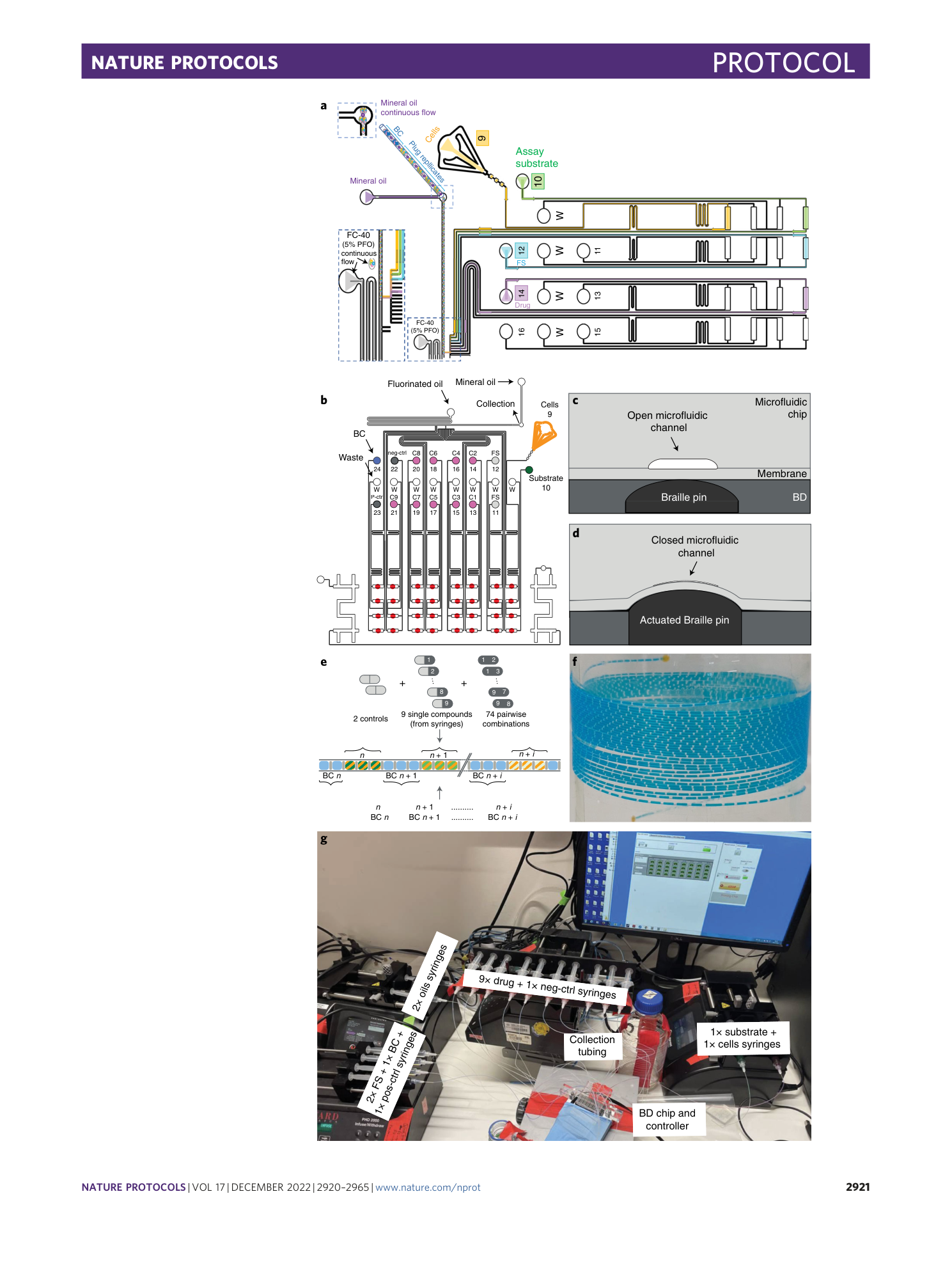







































Extended
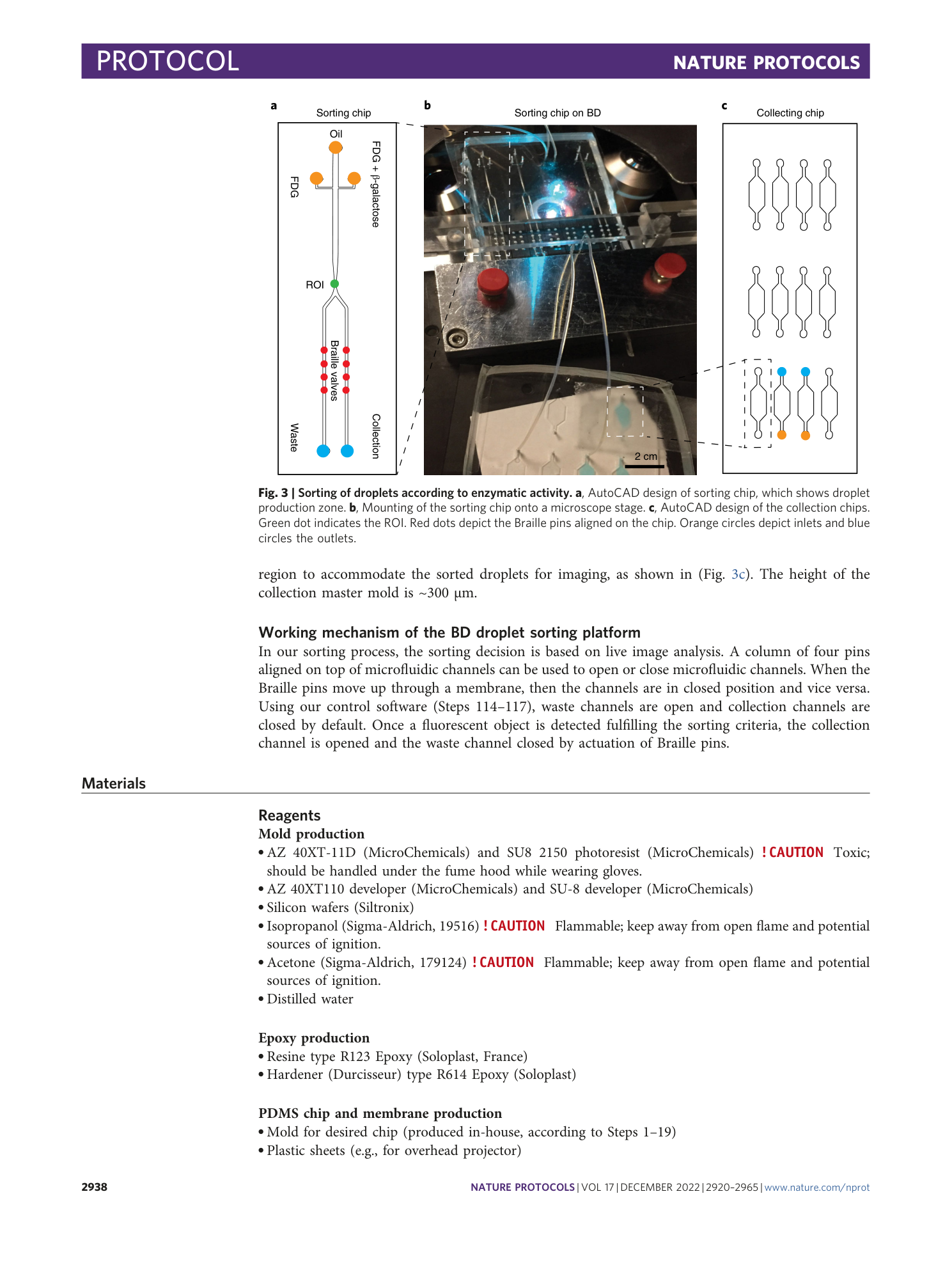
Extended Data Fig. 1 Equipment used for the BD drug screening platform.
a , The main equipment used for drug screening: (1) BD, (2) Luer-lock syringes, (3) needles, (4) syringe tubing, (5) waste tubing and container, (6) cell syringe tubing, (7) PDMS chip, (8) Aquapel syringe, (9) blue color syringe, (10) WiFI microscope camera, (11) collection tube prefilled with plugs, (12) tweezers, (13) scissors, (14) wax melter and (15) wax. b , BD and custom-made BD controller. The BD is built into an aluminum frame, and a plexiglas with spring-loaded bolts holds the chip in place. c , The electronic part of BD should be protected from liquids, e.g., by covering with a rubber glove. Take care not to let it heat up excessively.
Extended Data Fig. 2 Steps for preparation of the cell syringe with tubing directly attached to the syringe without a needle.
a , Preparation based on a needle: a 23 G needle is used and the metal part is heated so that it can be removed from the plastic part. In the top of the plastic part, a hole is punched using a 0.75 mm puncher, then the cell tubing is inserted and fixed by UV glue. Finally, the syringe is autoclaved. b , Alternative method for syringe preparation based on PDMS: PDMS is mixed using elastomer and curing agent in a ratio of 1:10 in a plastic beaker, and syringes are inserted into the PDMS. The PDMS is degassed in a desiccator and cured overnight at 65 °C. Syringes are separated using a scalpel, and the cell tubing is inserted into the PDMS, so that the end of the tubing is outside the PDMS. The tube is fixed with UV glue and autoclaved. c , Setup for stirring cells: ice pack and a magnetic stirrer are placed on top of the cell syringe to ensure cooling and agitation of cells (here we used a VP710 magnetic tumble stirrer as also used in DropSeq 1 , but more conventional stirrers turned upside down can be used as well).
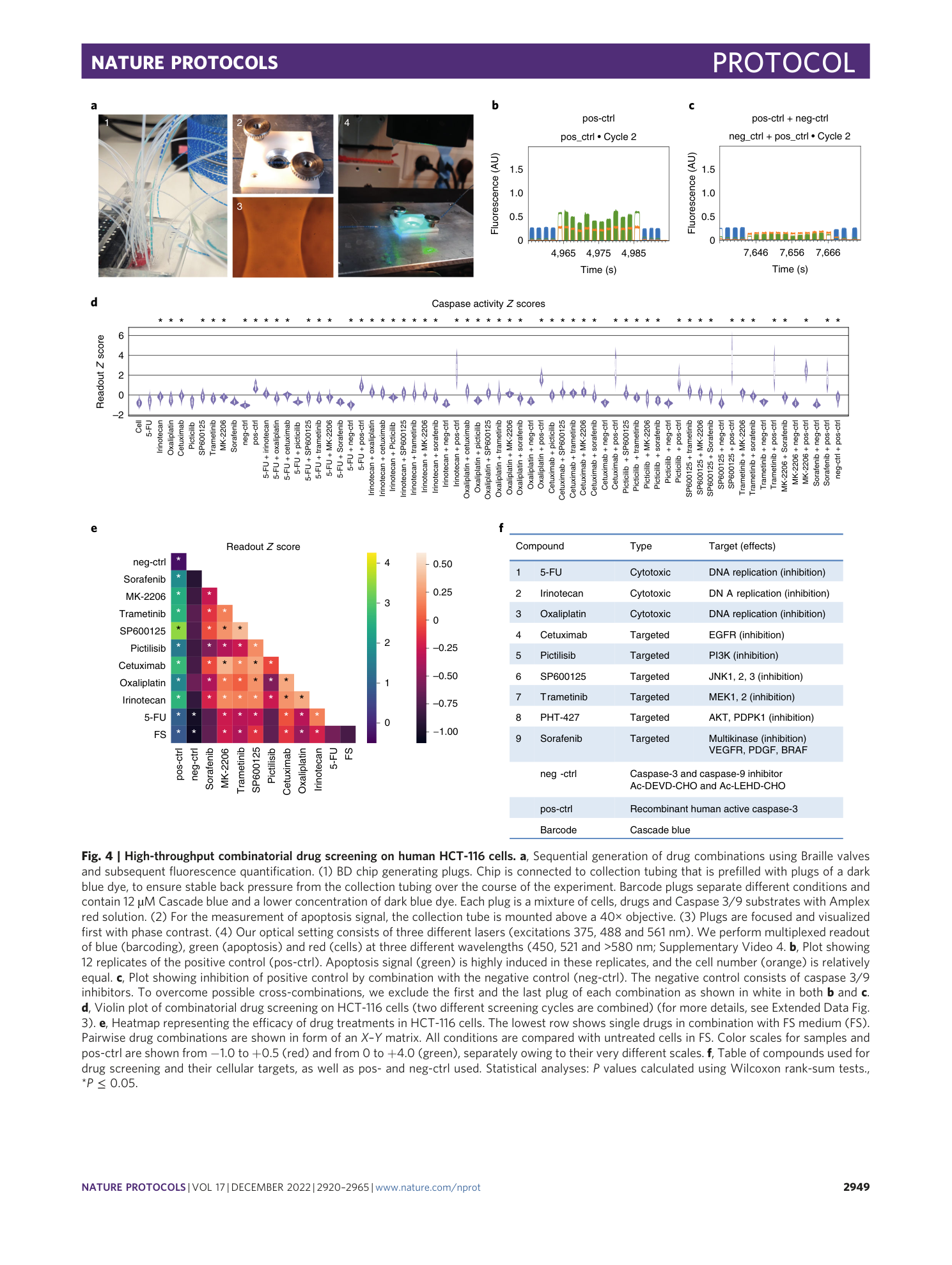
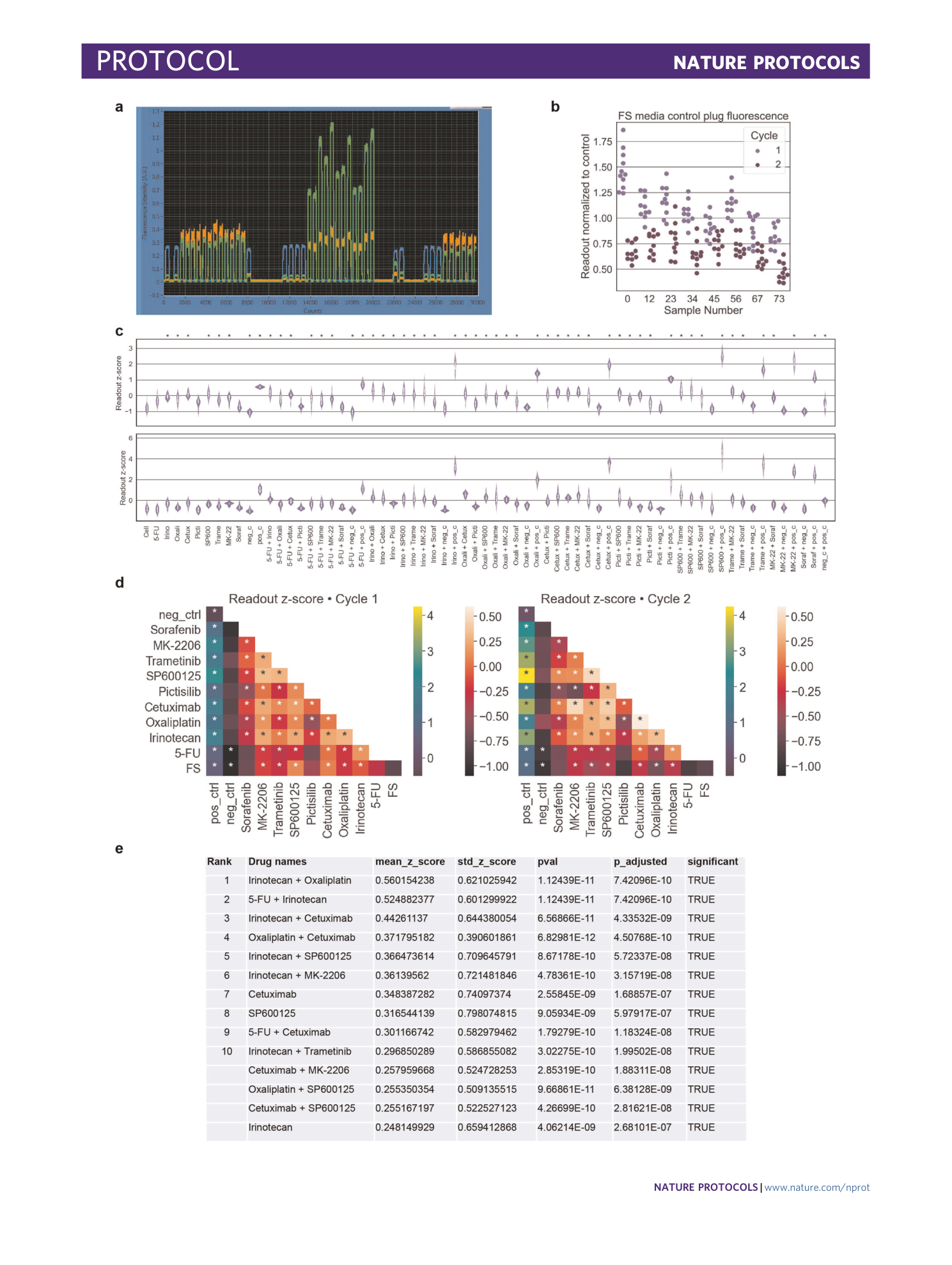
Extended Data Fig. 3 High-throughput combinatorial drug screening on human HCT-116 cells.
The experiment is exhibited in two cycles, while each combination was repeated in 12 plugs and separated from the next sample by five barcode (BC) plugs. a , Screenshot shows 12 replicates of a highly efficient drug combination (middle) compared with two low efficiency drug combinations (left and right), which are separated by 5 BCs. Caspase 3/9 signal (green) is strongly induced in highly efficient drug combinations samples, and cell number (orange) is relatively equal for all three conditions. b , Quality-control plot for the normalized caspase activity of cells in the FS controls during cycle 1 and cycle 2. c , Overview of the caspase signal normalized to the cell number for cycles 1 and 2. Each violin corresponds to one sample condition and shows the distribution of the normalized caspase signal for the 12 sample replicates. d , Heatmap representing the drug efficacy (single or in combination) in HCT-116 cells for cycle 1 and cycle 2. All conditions are normalized to a regression curve through the caspase activity of untreated cells in FS medium. The Z m value for cycle 1 = 0.49 and for cycle 2 = 0.42 (average for both cycles 0.45). e , Drug hits from both screening cycles with a mean Z score above 0.2 are listed in the table (top ten are indicated). These are single or combinatorial drugs, which significantly induced apoptosis compared with FS control medium. Positive controls are not shown, and their mean Z scores is above that of all other drugs. The complete list is available as Extended Data Table 2.
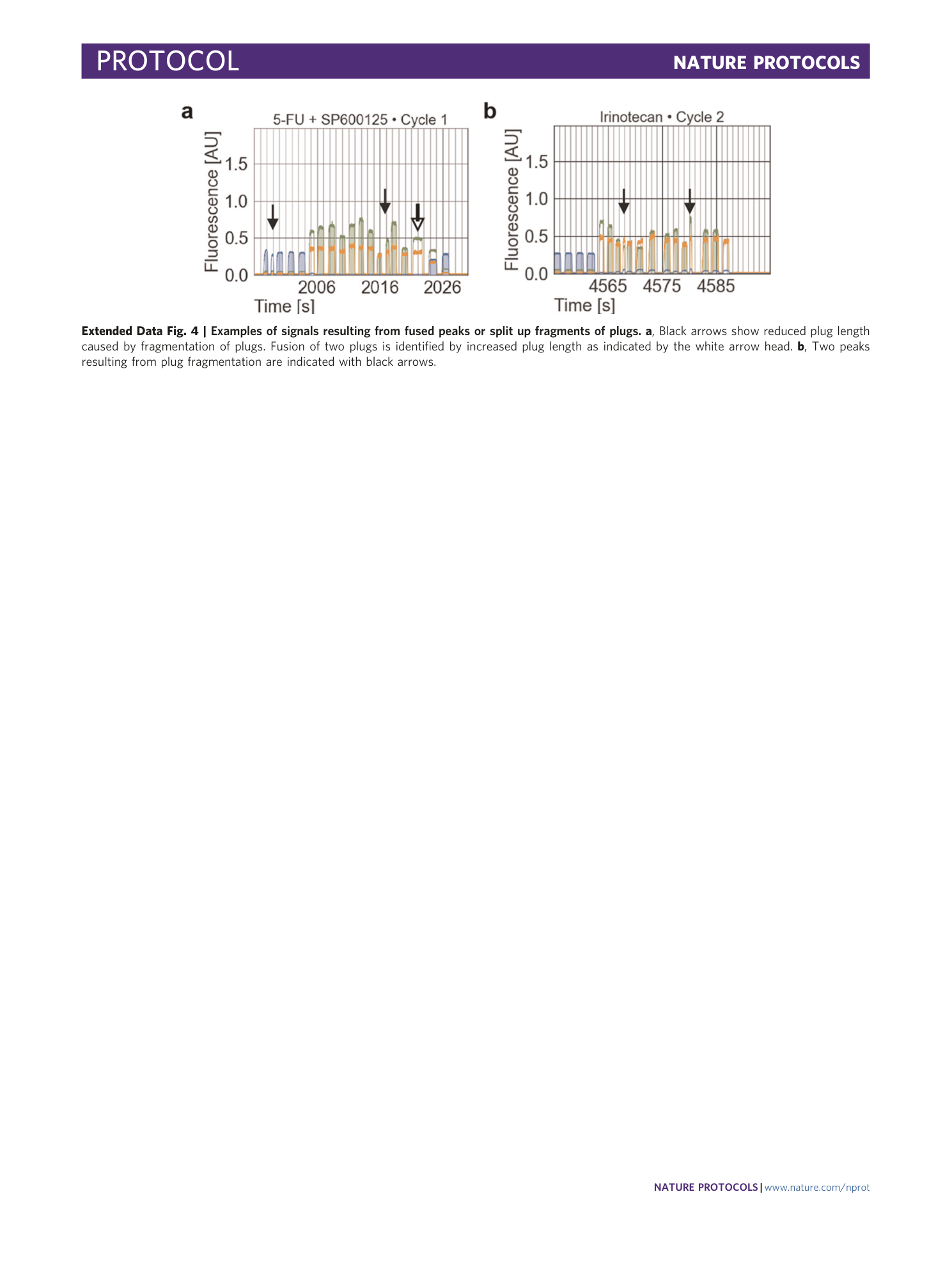
Extended Data Fig. 4 Examples of signals resulting from fused peaks or split up fragments of plugs.
a , Black arrows show reduced plug length caused by fragmentation of plugs. Fusion of two plugs is identified by increased plug length as indicated by the white arrow head. b , Two peaks resulting from plug fragmentation are indicated with black arrows.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Protocols 1–5, Fig. 1–7 and Tables 1–3.
Supplementary Video 1
Working principle of generating plugs using the BD valve system.
Supplementary Video 2
Testing Braille pin movements.
Supplementary Video 3
Alignment of screening chip on braille valves.
Supplementary Video 4
Collection, incubation and fluorescence readout of plugs.
Supplementary Software 1
All SolidWorks 3D designs of the inhouse parts for the BD platform. The easm file extension is an eDrawings Assembly file, which is a type of CAD file format in SolidWorks software.
Supplementary Software 2
Code for the Braille control board, using the BASCOM-AVR software.
Supplementary Software 3
All CAD designs of the microfluidic chips used in this protocol.
Supplementary Software 4
Plugy input data.
Supplementary Software 5
All files for manufacturing and running the PCB.
Supplementary Software 6
All LabVIEW files used in this protocol.
Supplementary Software 7
All Python files for data analysis.
Supplementary Software 8
File specifying a sequence of Braille pin actuations, used for sample barcoding. Barcoding was used to keep track of the combinations that are being generated. Each series of 12 replicates of a treatment condition is followed by 5 barcode plugs (Cascade blue- a blue fluorescent dye).
Supplementary Software 9
File specifying which drug is connected to which inlet of the Braille valve chip (needed for data analysis).
Supplementary Software 10
File specifying a sequence of Braille pin actuations, used for chip testing. The column contains the opening time of the valve, the number of repeats, sample name and 4 numbers of valves, which are opened at the same time.
Supplementary Software 11
File specifying a sequence of Braille pin actuation, used for priming the setup prior to a drug screen. (For more details please see Box 1.).
Supplementary Software 12
File specifying a sequence of Braille pin actuations, used for drug screening. It contains information on which pins are actuated and also the exact timing.

