Spotting-based differentiation of functional dopaminergic progenitors from human pluripotent stem cells
Jisun Kim, Jeha Jeon, Bin Song, Nayeon Lee, Sanghyeok Ko, Young Cha, Pierre Leblanc, Hyemyung Seo, Kwang-Soo Kim
Human pluripotent stem cells
Parkinson''s disease
Dopaminergic progenitors
Spotting-based differentiation
Cell therapy



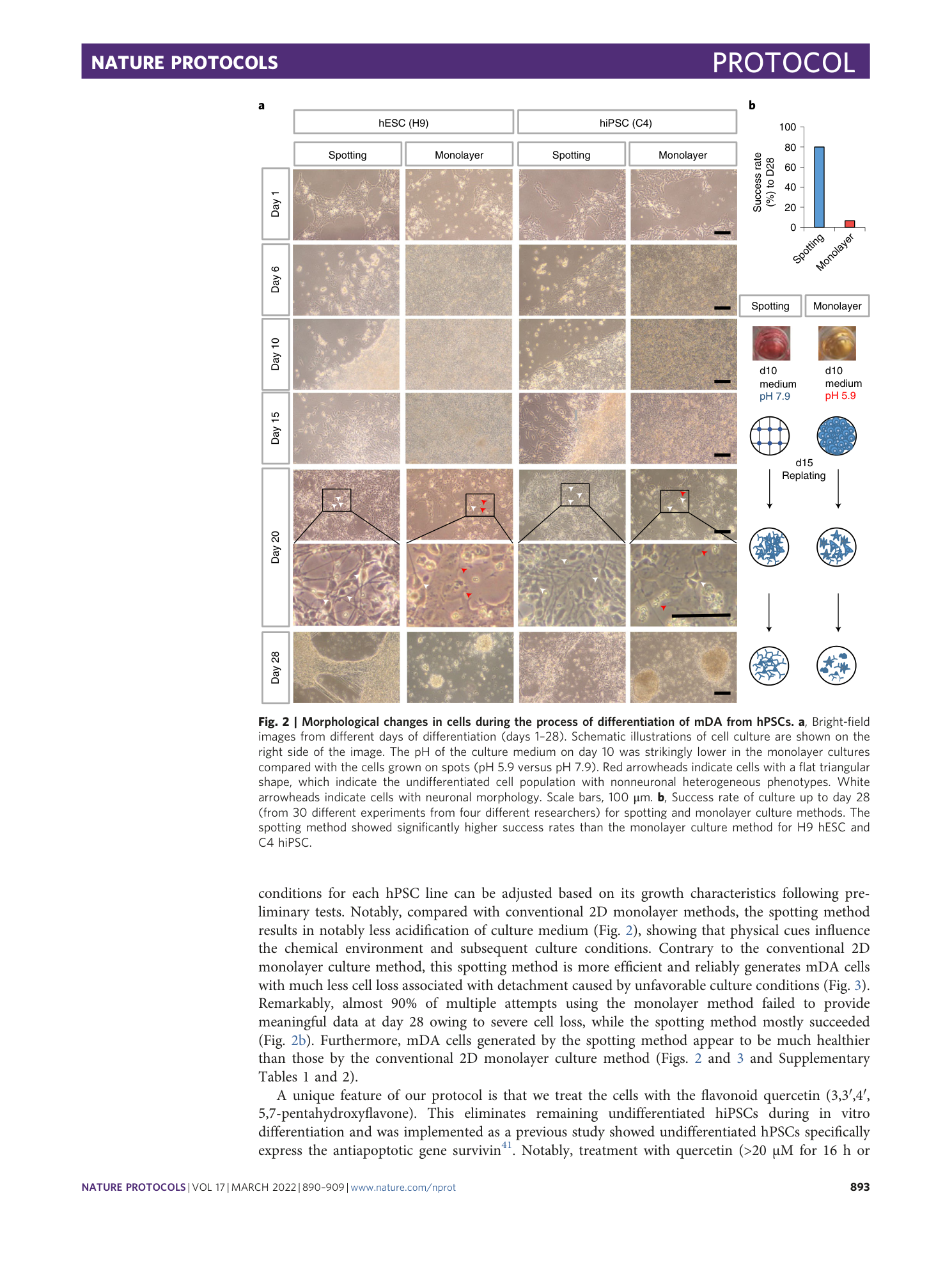
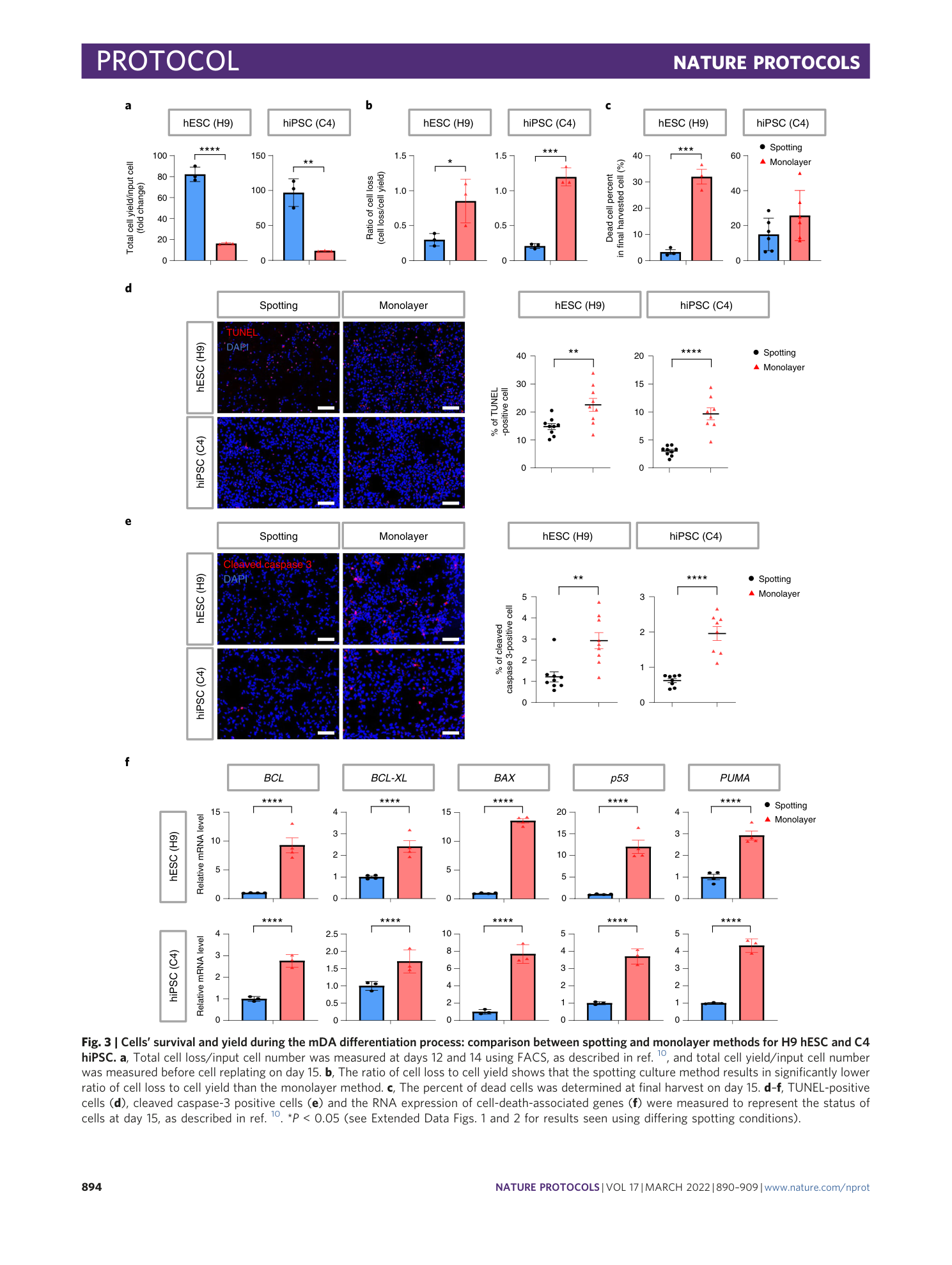

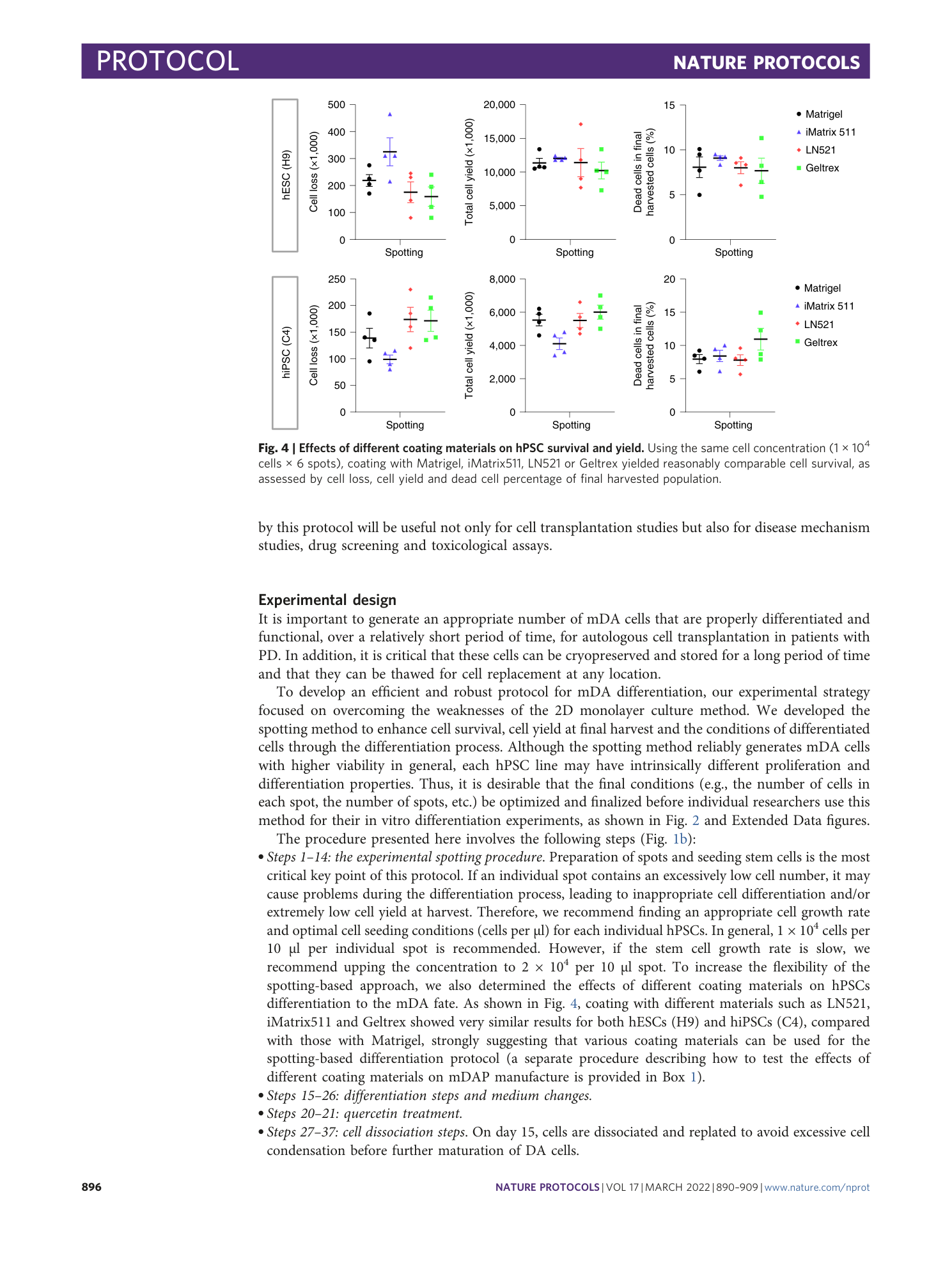

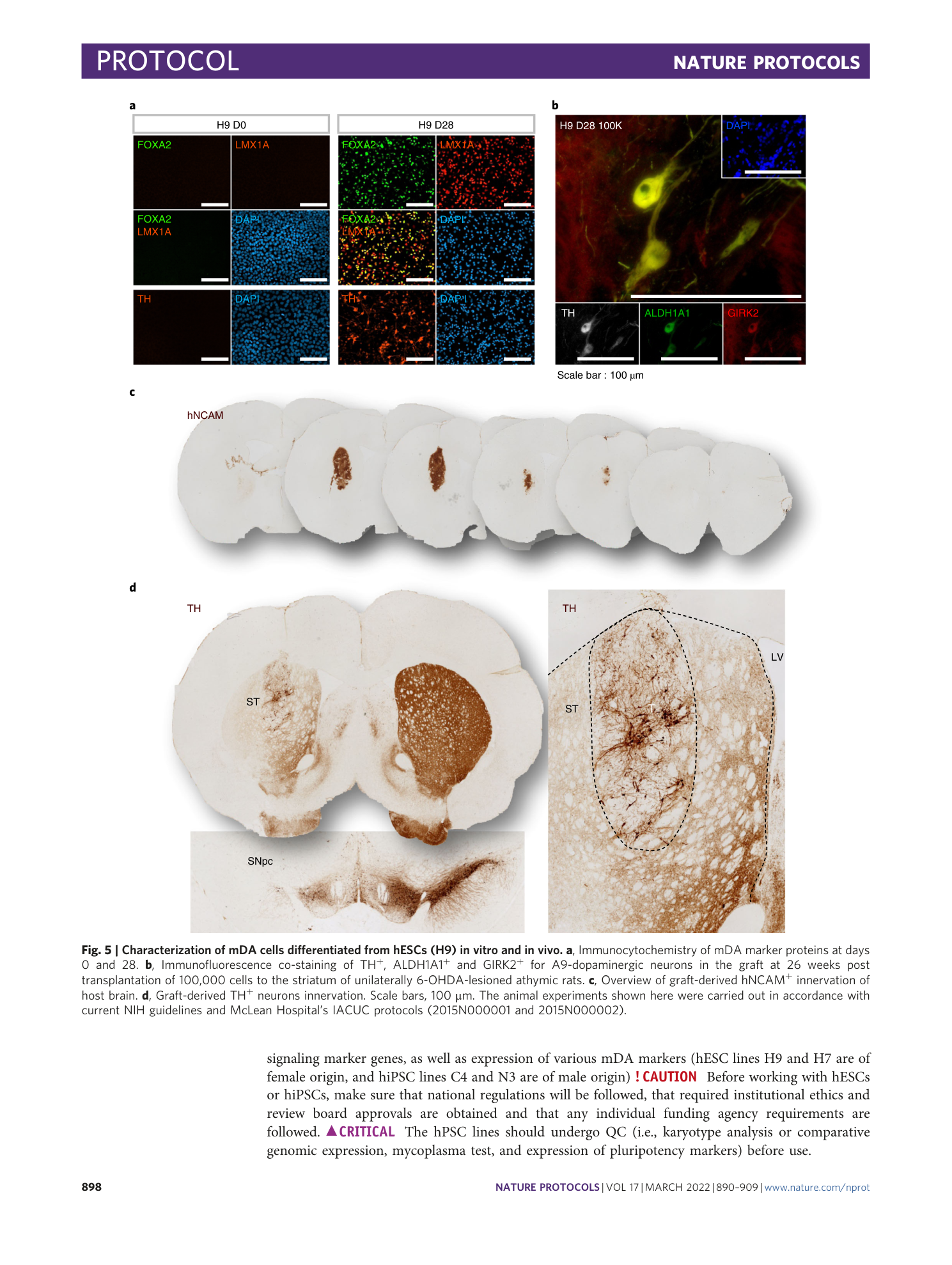







Extended
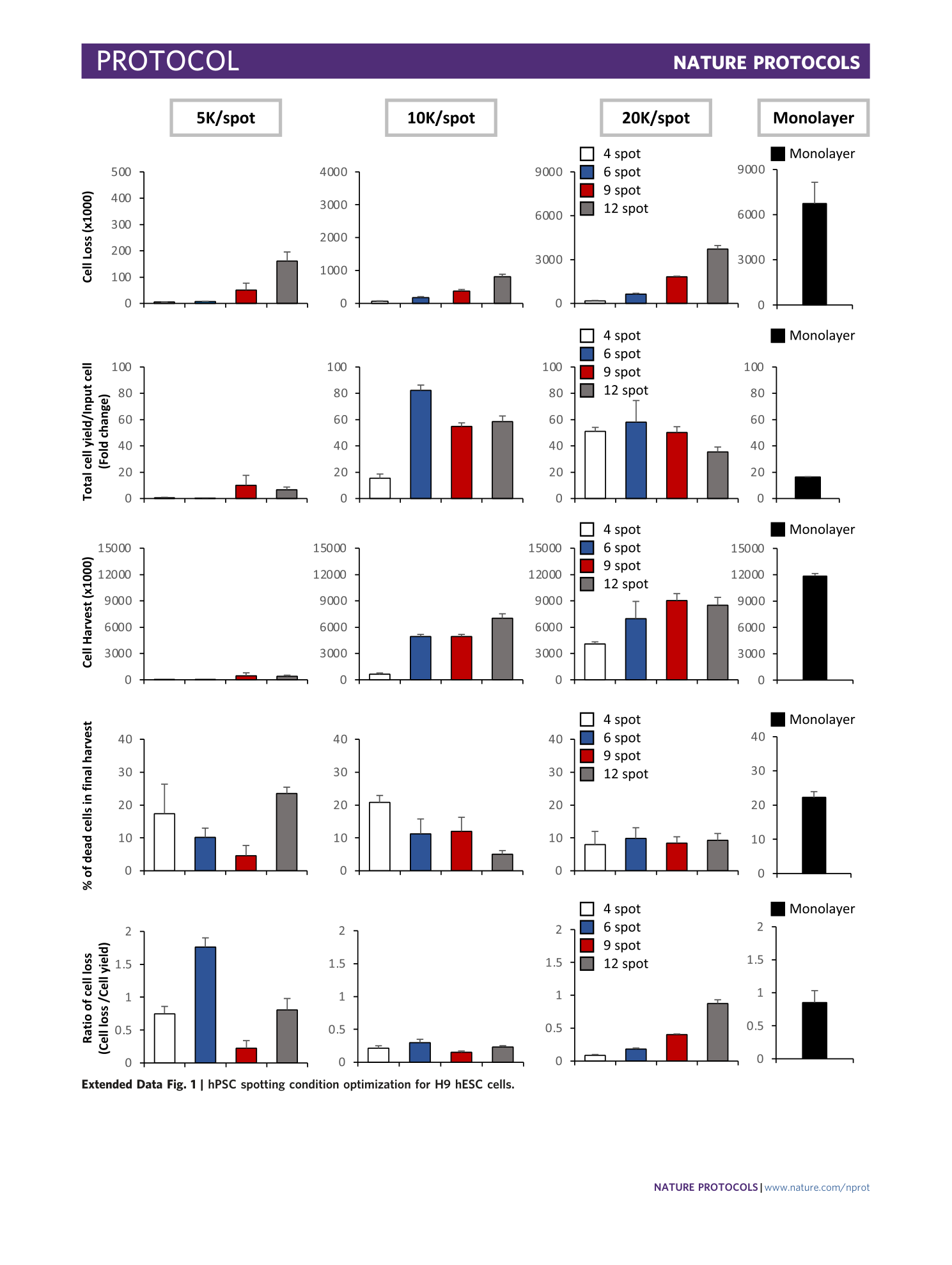
Extended Data Fig. 1 hPSC spotting condition optimization for H9 hESC cells.
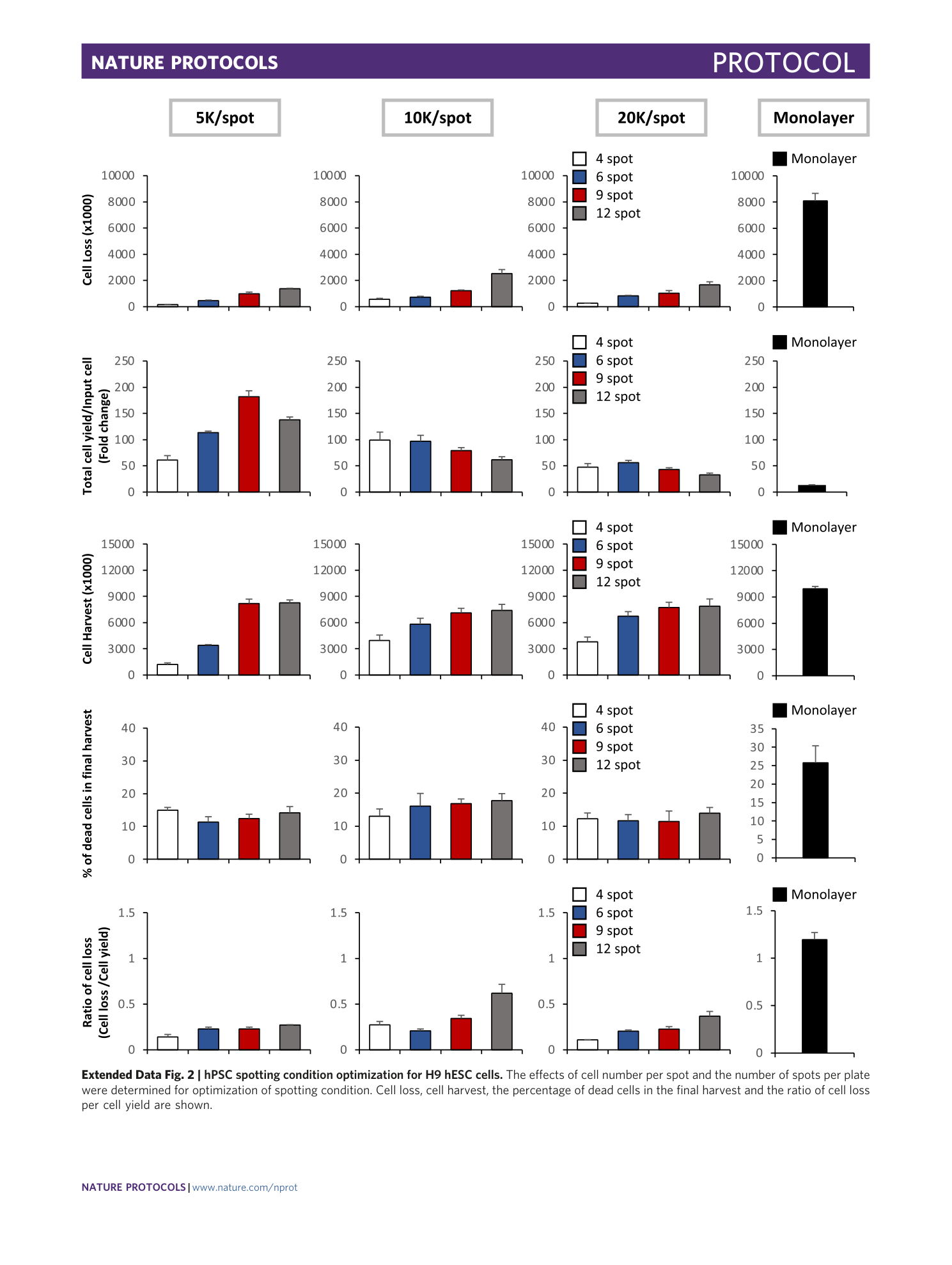
Extended Data Fig. 2 hPSC spotting condition optimization for H9 hESC cells.
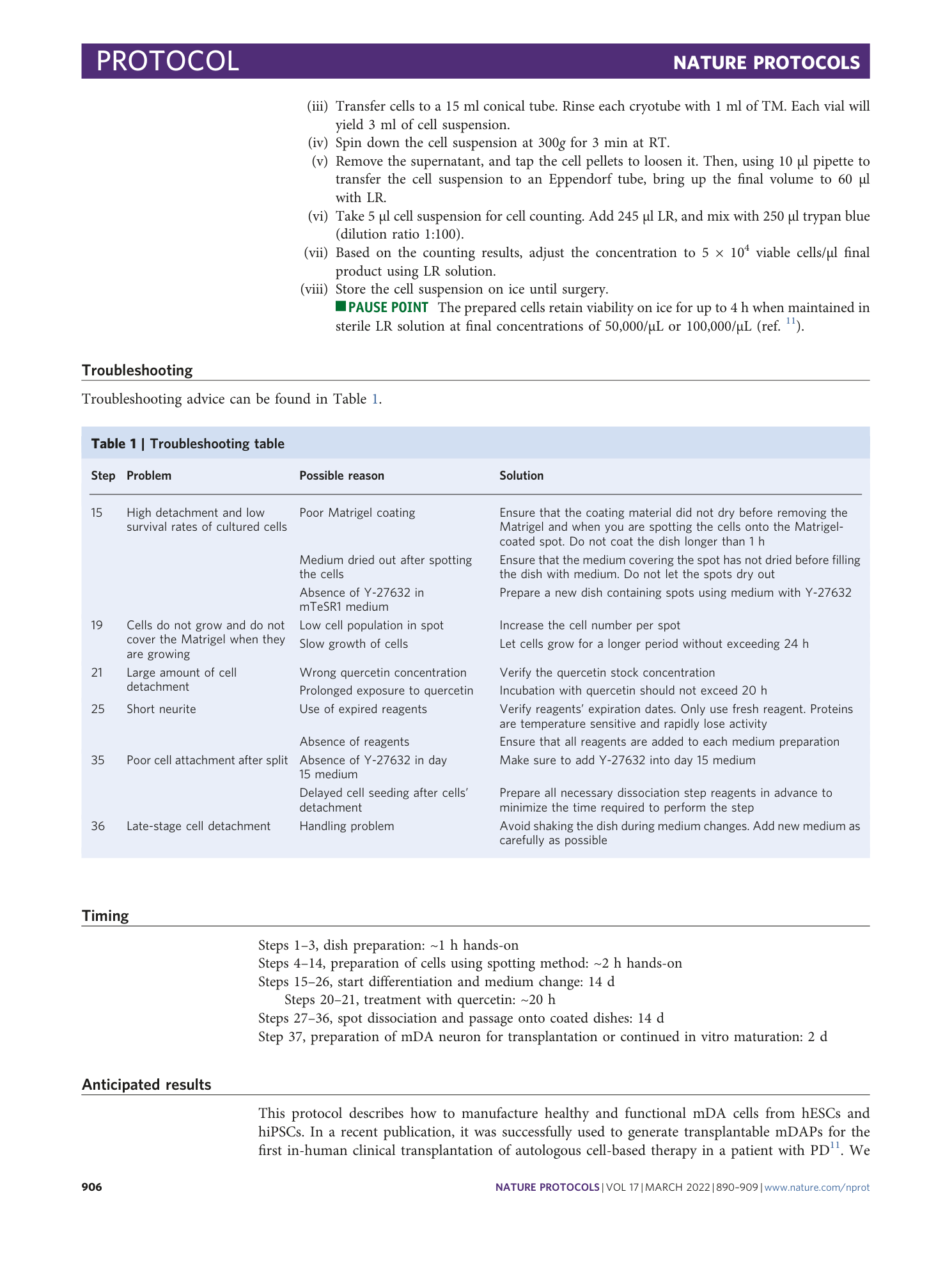
The effects of cell number per spot and the number of spots per plate were determined for optimization of spotting condition. Cell loss, cell harvest, the percentage of dead cells in the final harvest and the ratio of cell loss per cell yield are shown.
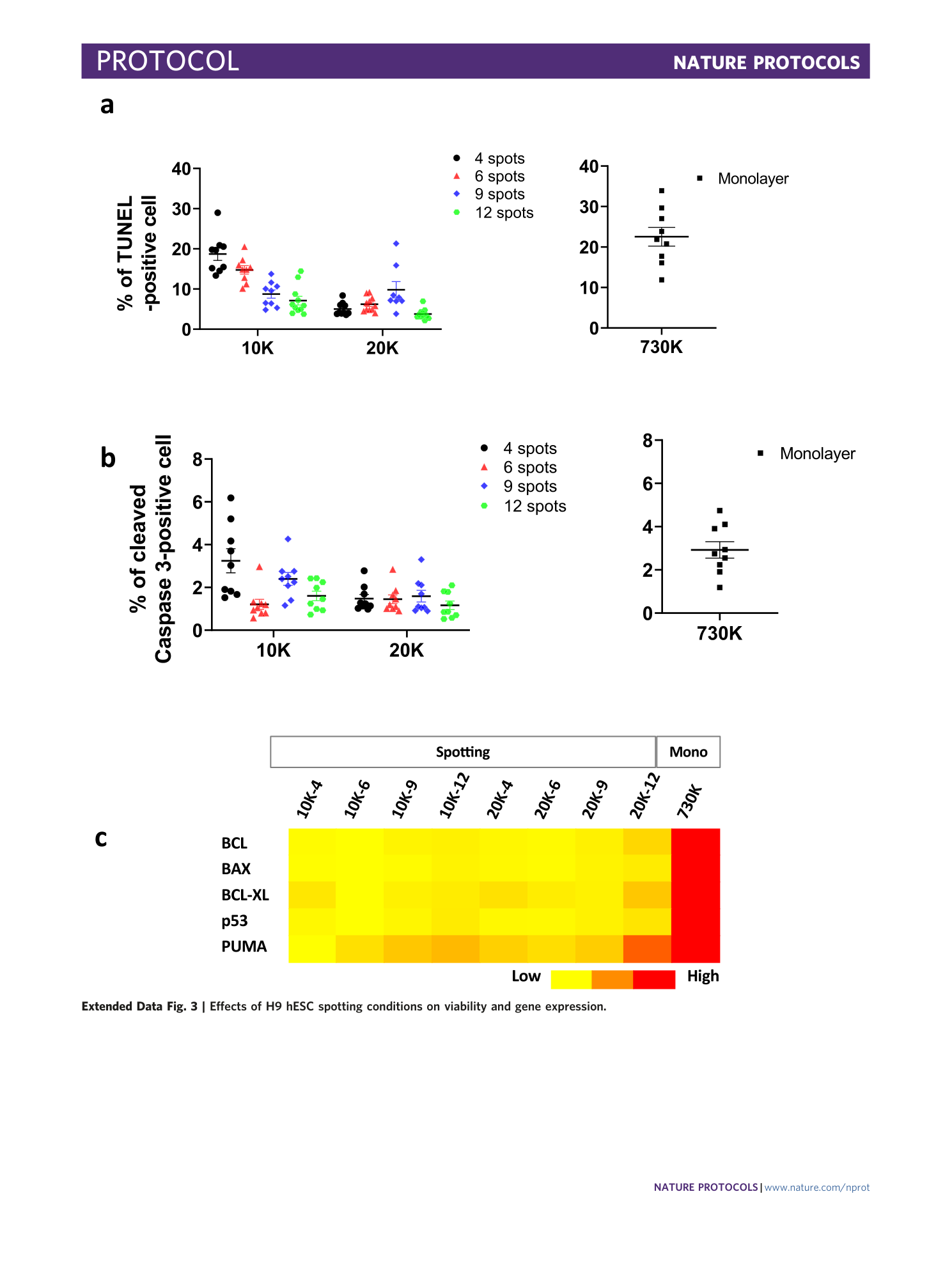
Extended Data Fig. 3 Effects of H9 hESC spotting conditions on viability and gene expression.
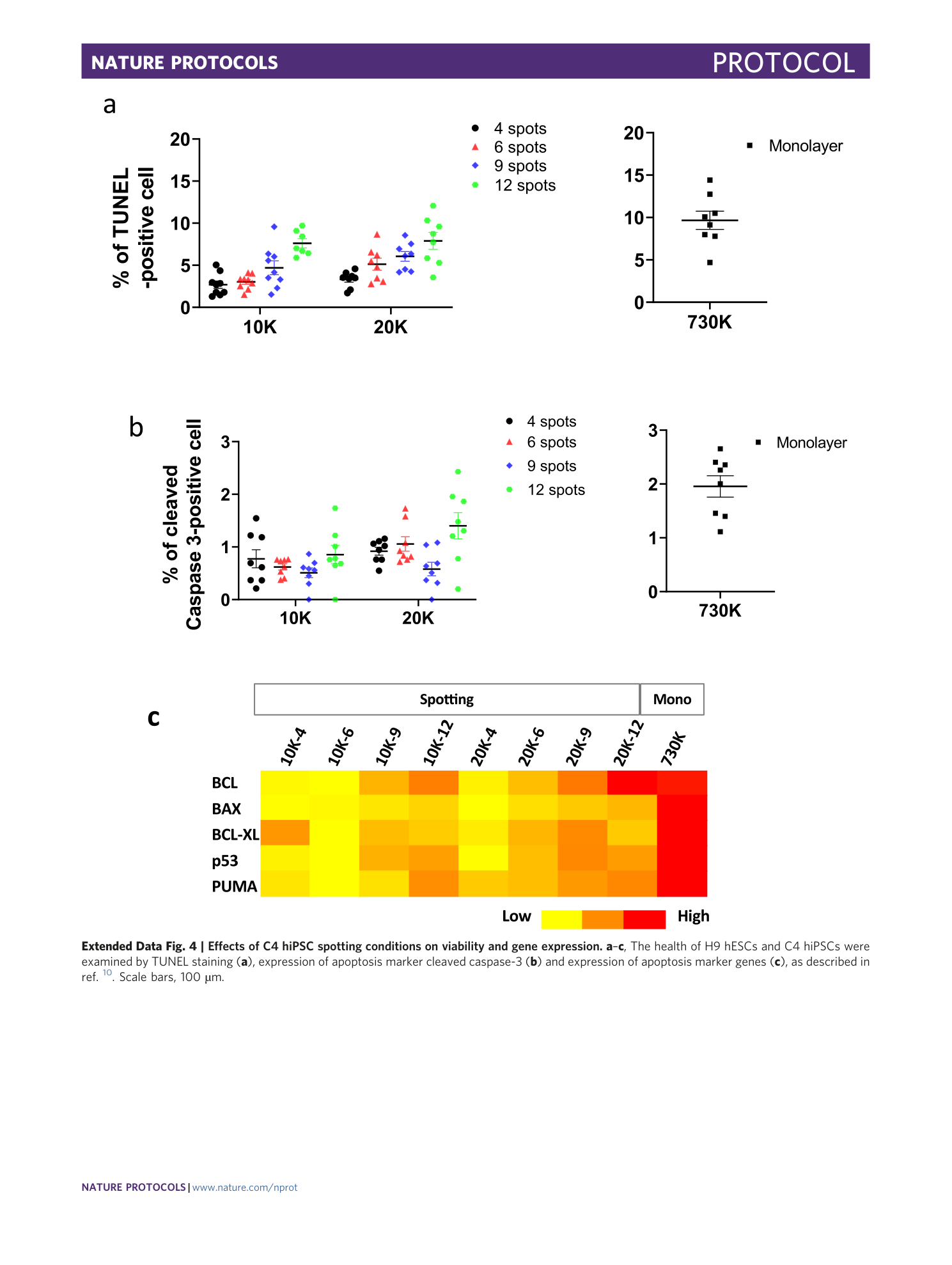
Extended Data Fig. 4 Effects of C4 hiPSC spotting conditions on viability and gene expression.
a – c , The health of H9 hESCs and C4 hiPSCs were examined by TUNEL staining ( a ), expression of apoptosis marker cleaved caspase-3 ( b ) and expression of apoptosis marker genes ( c ), as described in ref. 10 . Scale bars, 100 µm.
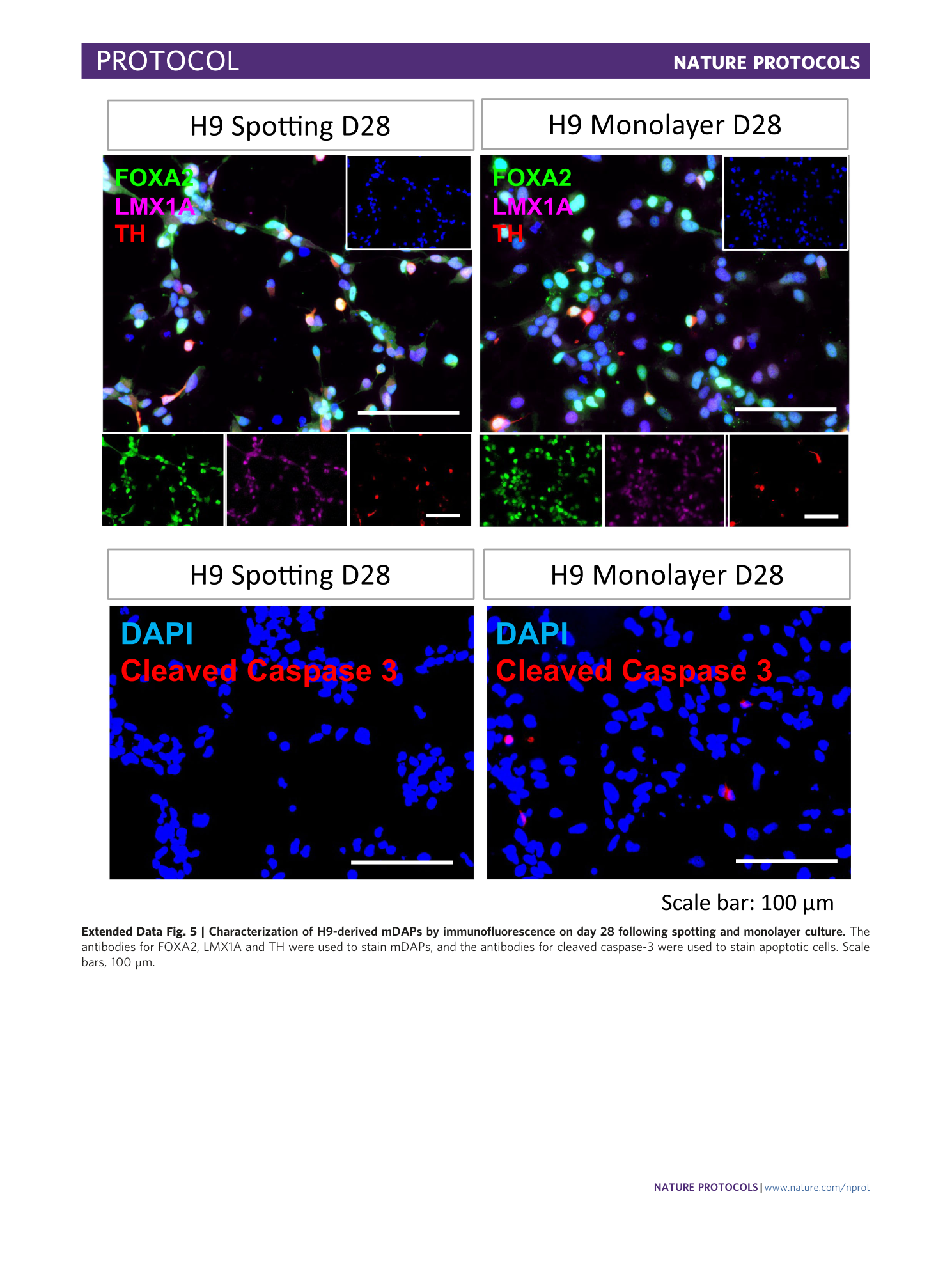
Extended Data Fig. 5 Characterization of H9-derived mDAPs by immunofluorescence on day 28 following spotting and monolayer culture.
The antibodies for FOXA2, LMX1A and TH were used to stain mDAPs, and the antibodies for cleaved caspase-3 were used to stain apoptotic cells. Scale bars, 100 µm.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Tables 1 and 2.

