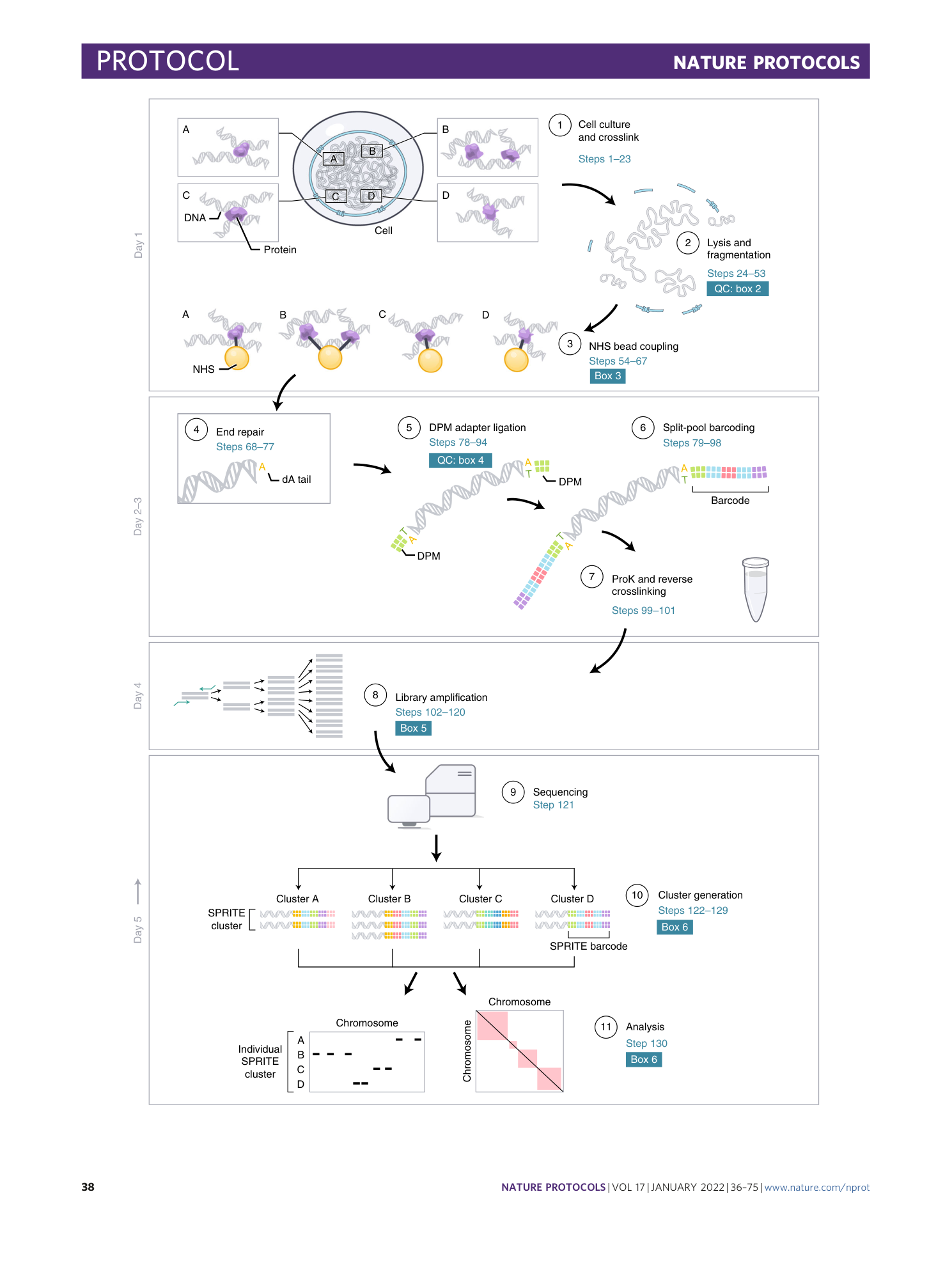
SPRITE: a genome-wide method for mapping higher-order 3D interactions in the nucleus using combinatorial split-and-pool barcoding
Sofia A. Quinodoz, Prashant Bhat, Peter Chovanec, Joanna W. Jachowicz, Noah Ollikainen, Elizabeth Detmar, Elizabeth Soehalim, Mitchell Guttman




























Extended
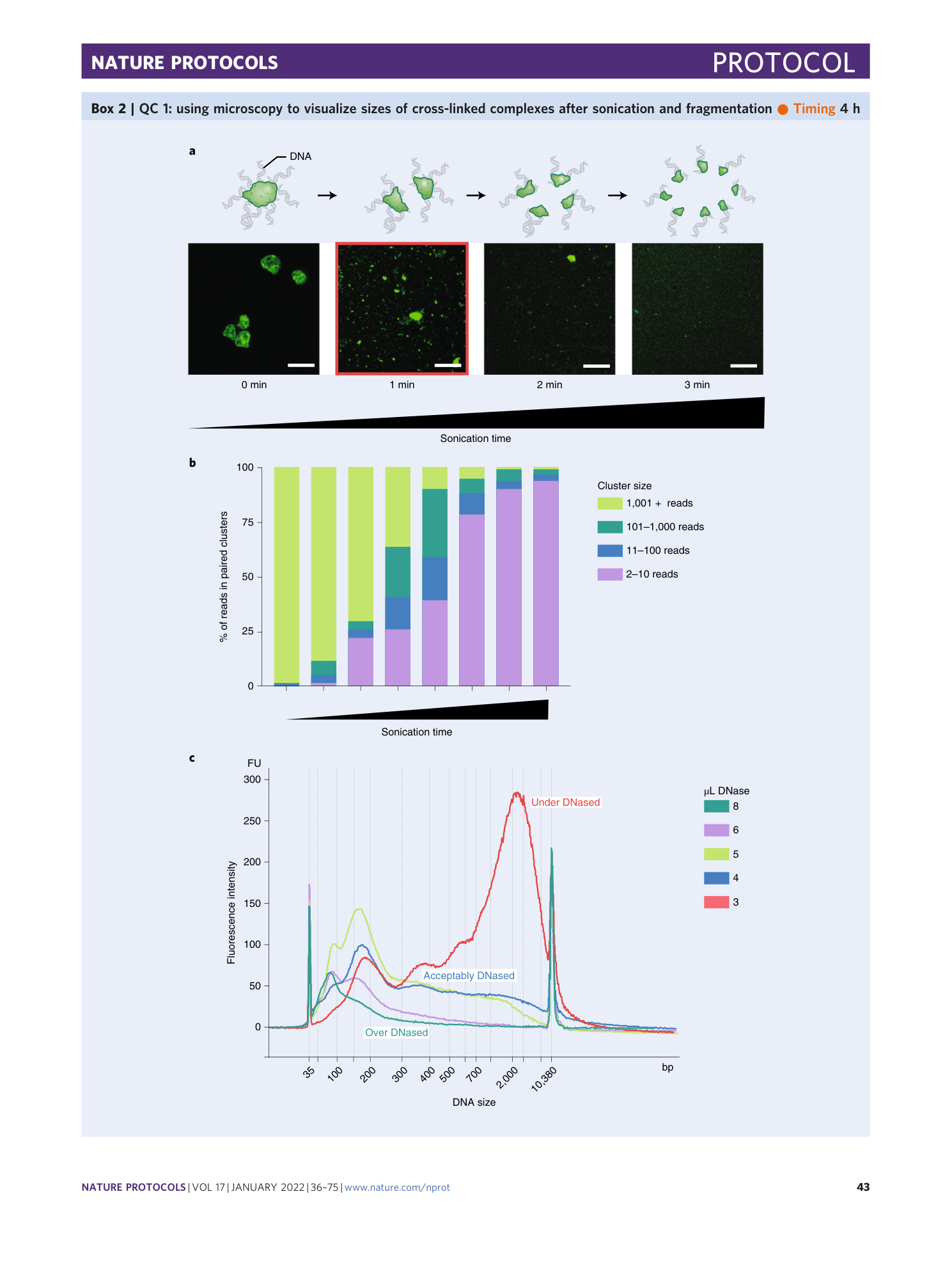
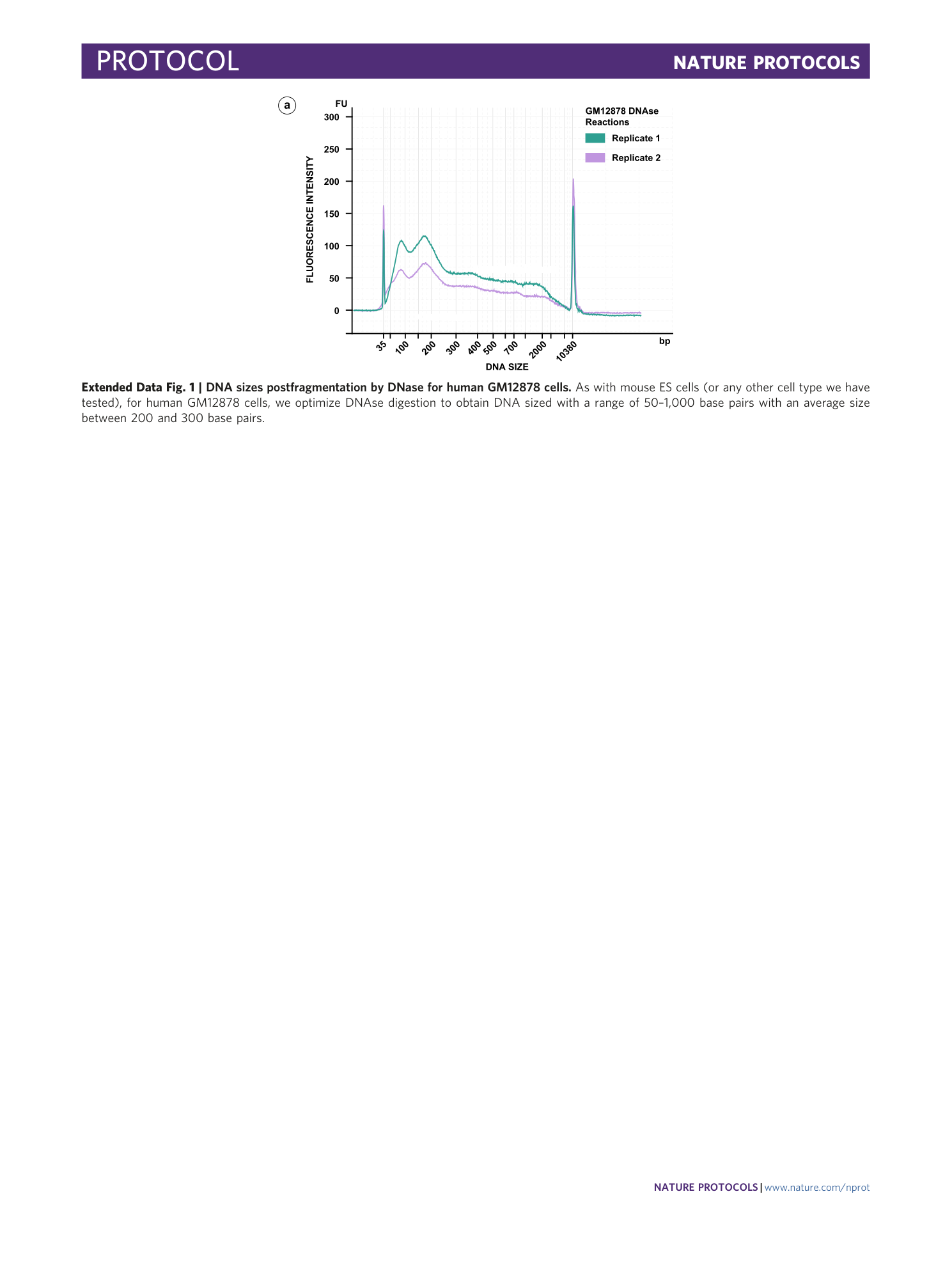
Extended Data Fig. 1 DNA sizes postfragmentation by DNase for human GM12878 cells.
As with mouse ES cells (or any other cell type we have tested), for human GM12878 cells, we optimize DNAse digestion to obtain DNA sized with a range of 50–1,000 base pairs with an average size between 200 and 300 base pairs.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Methods.
Supplementary Video 1
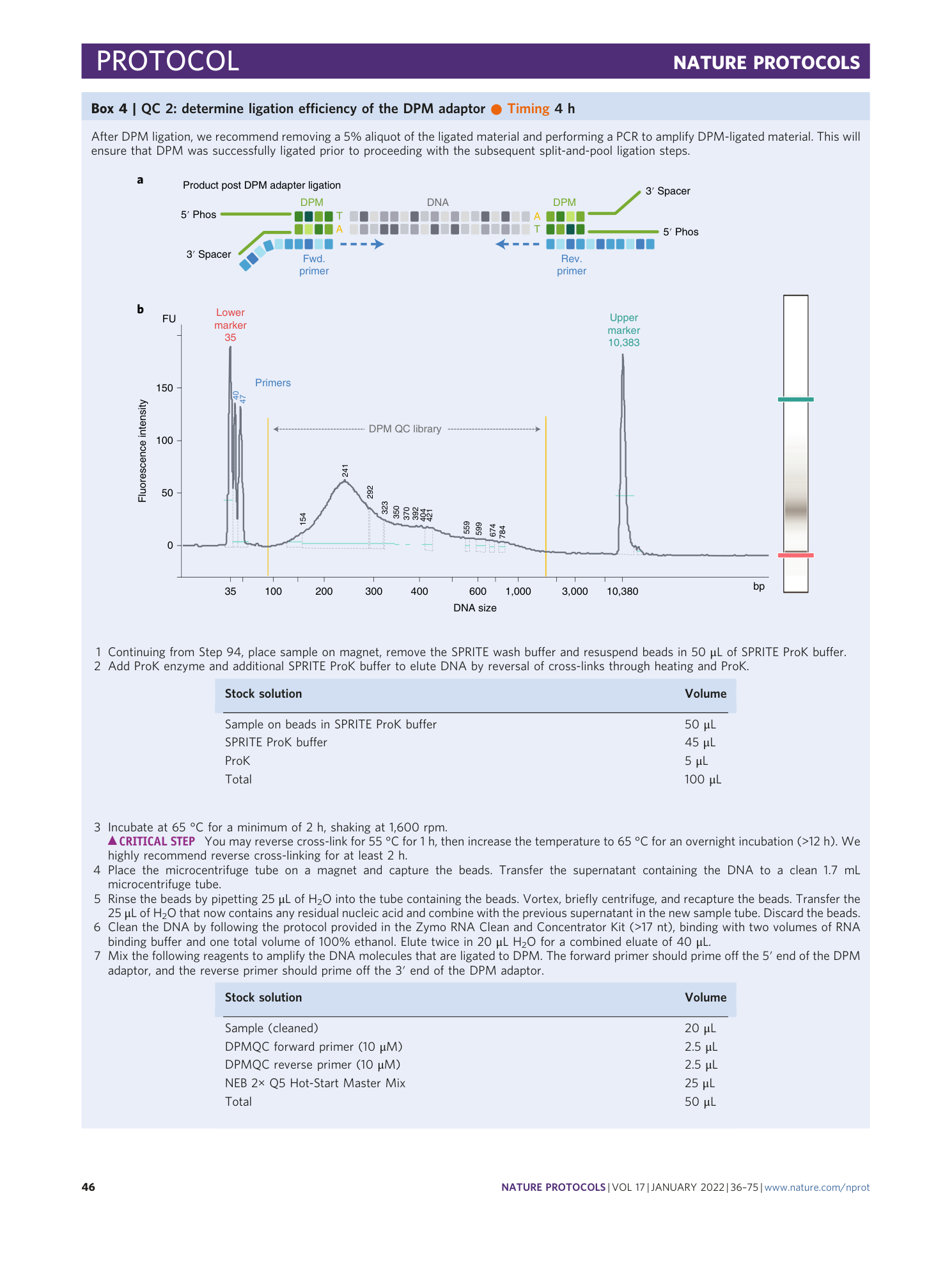
The main experimental steps of the SPRITE method are shown, including split-and-pool barcoding and pre-library amplification steps. A conceptual overview of the SPRITE method is also provided. Please see https://youtu.be/6SdWkBxQGlg for a higher resolution version of this video.
41596_2021_633_MOESM3_ESM.xlsx
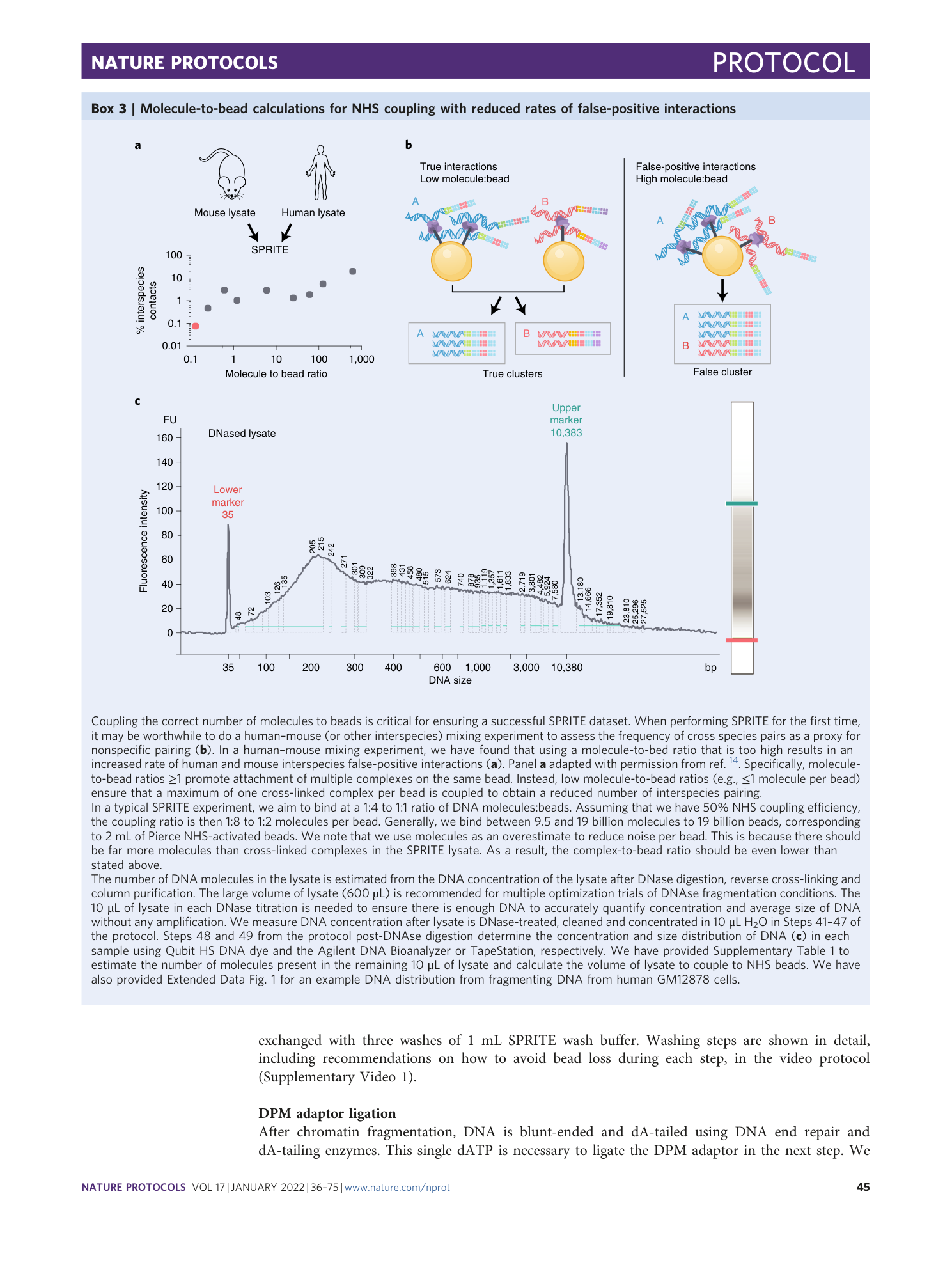
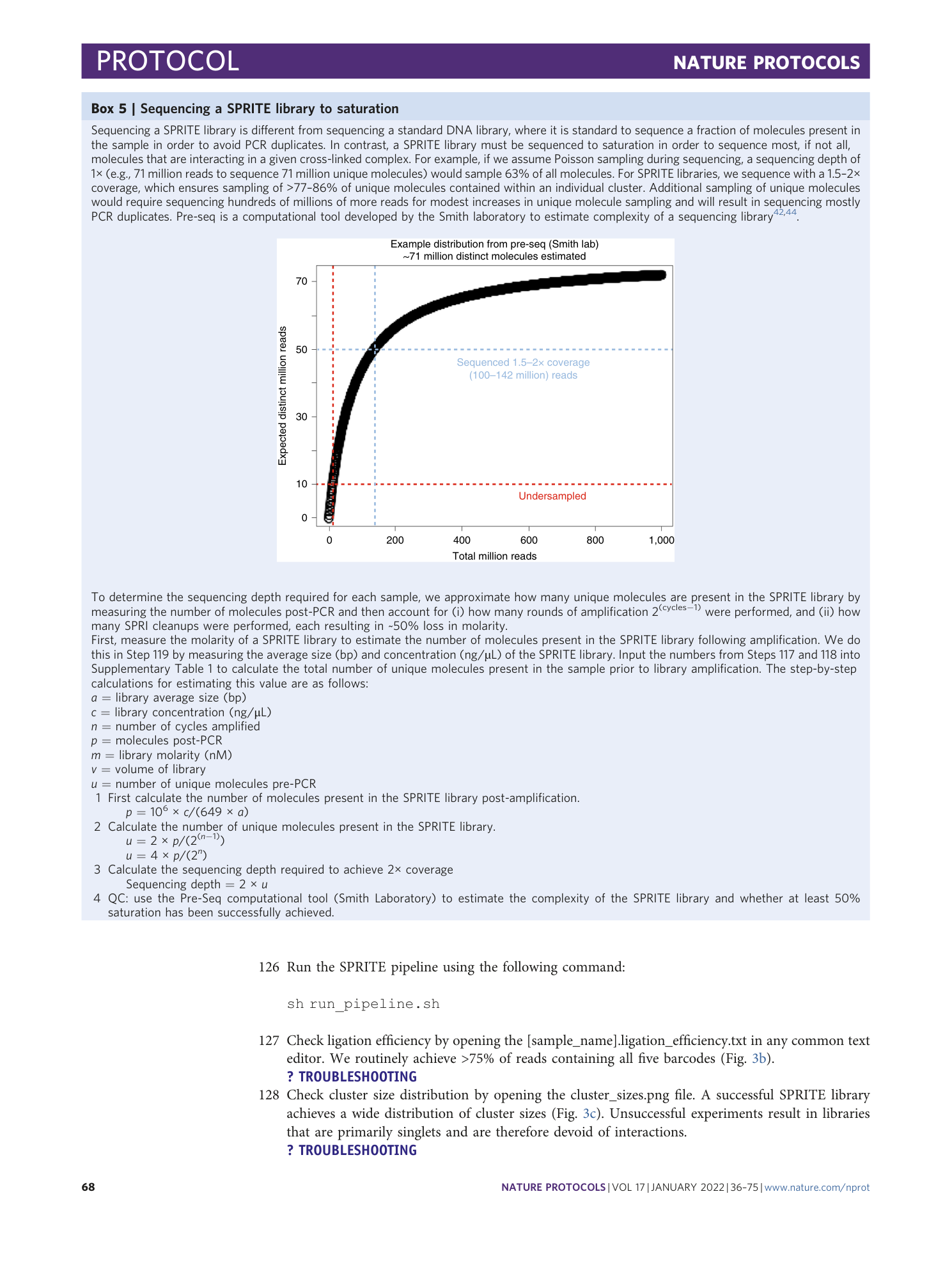
Supplementary Table 1 Calculate number of molecules for NHS coupling and the number of reads required to sequence each SPRITE library to saturation. (Sheet 1) To calculate the amount of lysate to couple to NHS-activated beads, enter the average size (bp) and concentration (ng/ul) of DNA in the DNAse digested lysate. This spreadsheet will calculate the number of DNA molecules in the DNAse digested lysate and determine the µL of lysate to couple. (Sheet 2) To determine the amount of reads required to sequence each SPRITE library aliquot to saturation, estimate the number of unique molecules pre-PCR from the final library concentrations using the library molarity and number of cycles.
41596_2021_633_MOESM4_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary Table 2 Sequences of the SPRITE barcodes . All sequences of SPRITE barcodes (DPM, Terminal, Odd, Even) and the indexed Illumina sequencing primers are provided.

