L-Leucine based supramolecular gelator
Raviraj Kusanur, Trilokchandran B, G Vijaya Kumar, M R Padmini, Sushma C, Namrata Patil, Rajalaxmi.S
Abstract
Gels are basically made up of polymers which, are either cross-linked or entangled in order to form a solid-like network. A new class of gels known as the supramolecular gels was formulated when small molecules self-assemble through various non-covalent interactions. These weak non-covalent interactions help in preventing the supramolecular gels from time-varying changes in their material properties. They self-assemble in order to form a micro-scale or nano-scale fibrillar network which, helps in immobilizing a large volume of solvents. This particular L-Leucine-based supramolecular gelator is composed of three main components that is, a hydrophobic tail, gluconic acid, and L-Leucine amino acid. It was tested for it's gelation properties using various solvents. Based on the observations made, we have concluded that liquid paraffin when used as a solvent for gelation had shown the best gelation properties by being stable and firm.
Steps
ESTERIFICATION
L-Leucine (C6H13NO2) 2.62g (0.02 mol) and Cetyl alcohol (C16H34O) 4.85g (0.02mol) were dissolved in toluene (75 ml). P-toluene sulphonic acid monohydrate (C7H8O3S.H2O) 7.60g (0.04mol) was added.
The reaction mixture was refluxed at 95℃ for 10 hours.
The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC (15% ethyl acetate in Hexane).
After completion of the reaction, toluene was removed using rotary evaporator and allowed to cool to room temperature.
The residue obtained was dissolved in dichloromethane (75ml) and washed with 10% sodium carbonate solution (70ml, twice), water (50ml, twice) and brine solution (50 ml).
The organic layer was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulphate. The dichloromethane was removed using rotary evaporator.
The amino ester obtained was purified by converting the amino ester hydrochloride salt by dissolving in acetone 100ml and Conc. Hydrochloric acid 25ml.
The solution was kept in refrigerator at 5℃ for 16 hours. The hydrochloride salt obtained was dissolved in DCM (75 ml) and washed with 10% sodium carbonate solution (50ml, twice), water (50ml, twice) and brine solution (50 ml). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulphate.




COUPLING
The crude oily liquid obtained from first step (6.6g, 0.18 mmol) was dissolved in ethyl alcohol 75ml and Glucono delta lactone (C6H10O6) 3.6g (0.02mol) was added.
The mixture was refluxed for 8 hours.
The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC.
After completion of the reaction, ethyl alcohol was removed by using rotary evaporator.
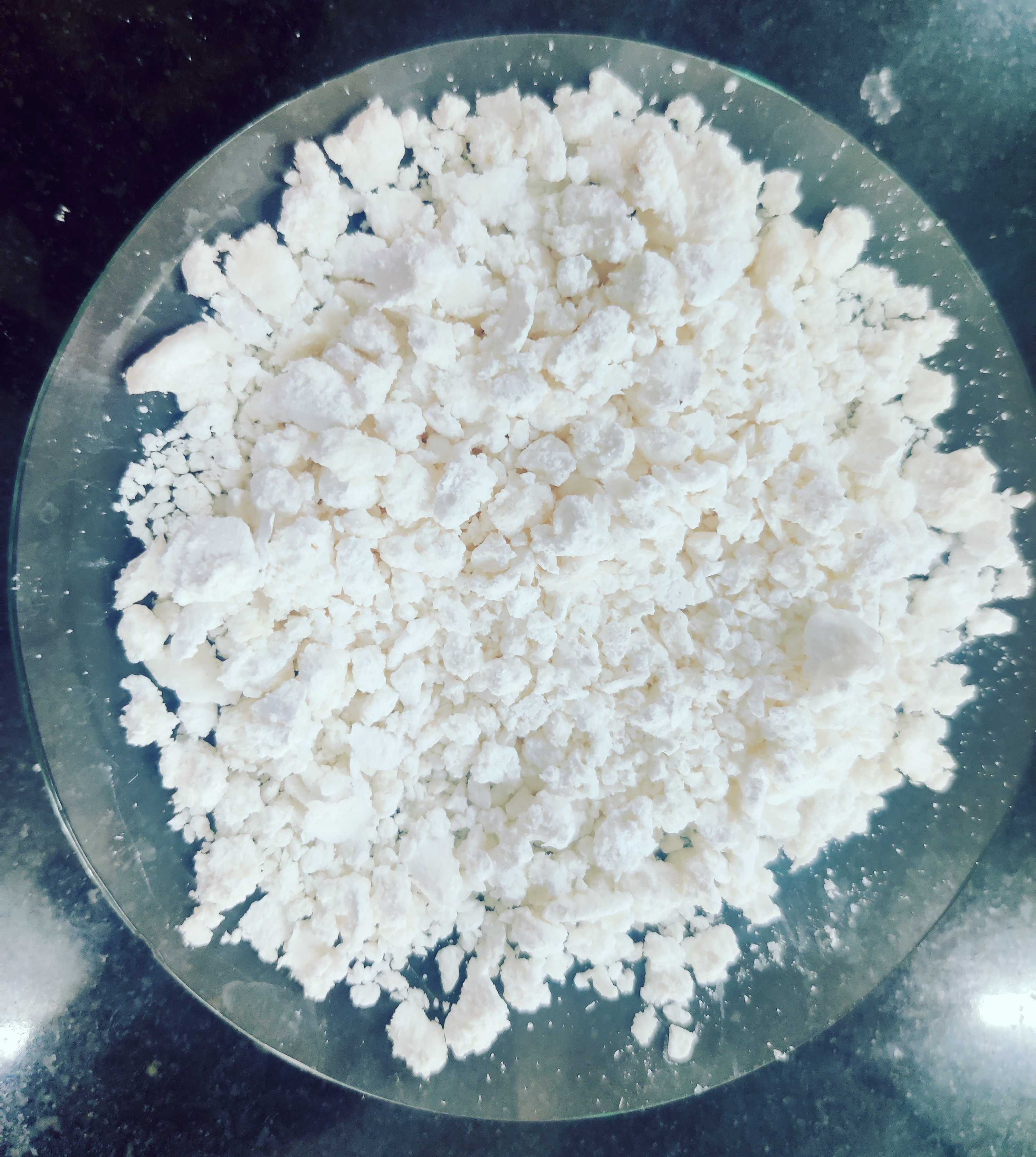
The crude compound was dissolved in THF and filtered hot.
The THF was removed to get colourless powder.
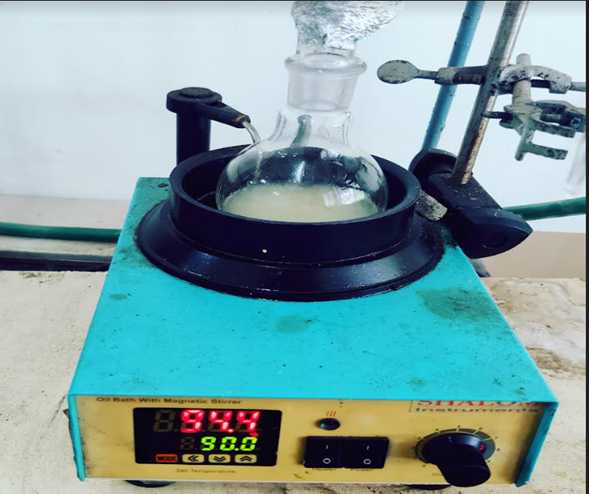
GELATION
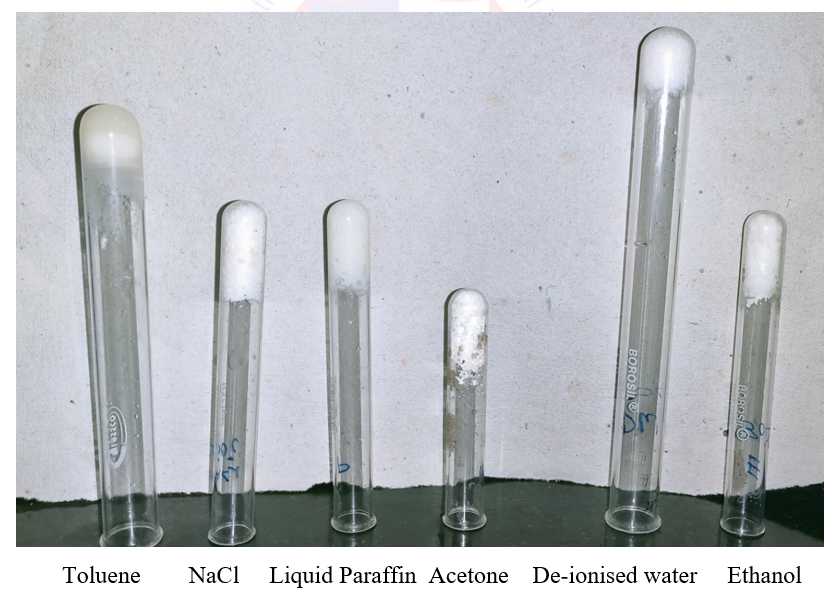
The dry gelator obtained after the process of recrystallization was weighed.The gelation properties were tested through the tube inversion test which, was done by dissolving the gelator using various solvents
The gelator was uniformly dissolved in liquid paraffin using a sonicator for 20 minutes at 60 ℃ which, which was very firm and stable even after 48 hours.
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| Weight of gelator (mg) | Solvent (ml) | Inference |
| 500 | De-ionised water -1.5 ml | The gelator was partially soluble in distilled water and the gel had become dry and brittle after 24 hours |
| 500 | NaCl (20mM) -1.5 ml | The gelator was partially soluble in NaCl solution and the gel had become dry brittle after 24 hours |
| 500 | Acetone-1.5 ml | The gelator had completely dissolved in acetone but the solvent had evaporated and the gel had become very dry and brittle after 24 hours. |
| 500 | Toluene-1.5 ml | The gelator had completely dissolved in toluene. The gel was stable for 24 hours but the solvent had evaporated completely and the gel had become dry and brittle after 48 hours. |
| 500 | Paraffin- 1.5 ml | The gelator had completely dissolved in liquid paraffin and was very firm and stable for more than 48 hours. |
| 500 | Ethanol-1.5 ml | The gelator had completely dissolved in ethanol and the gel was stable but started developing cracks after 48 hours. |
Observations made after 48 hours of tube inversion test




