Combining surface-accessible Ag and Au colloidal nanomaterials with SERS for in situ analysis of molecule–metal interactions in complex solution environments
Chunchun Li, Yingrui Zhang, Ziwei Ye, Steven E. J. Bell, Yikai Xu
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Nanoparticle colloids
Molecule-metal interactions
Plasmonic nanoparticles
Metal liquid-like films

























Extended
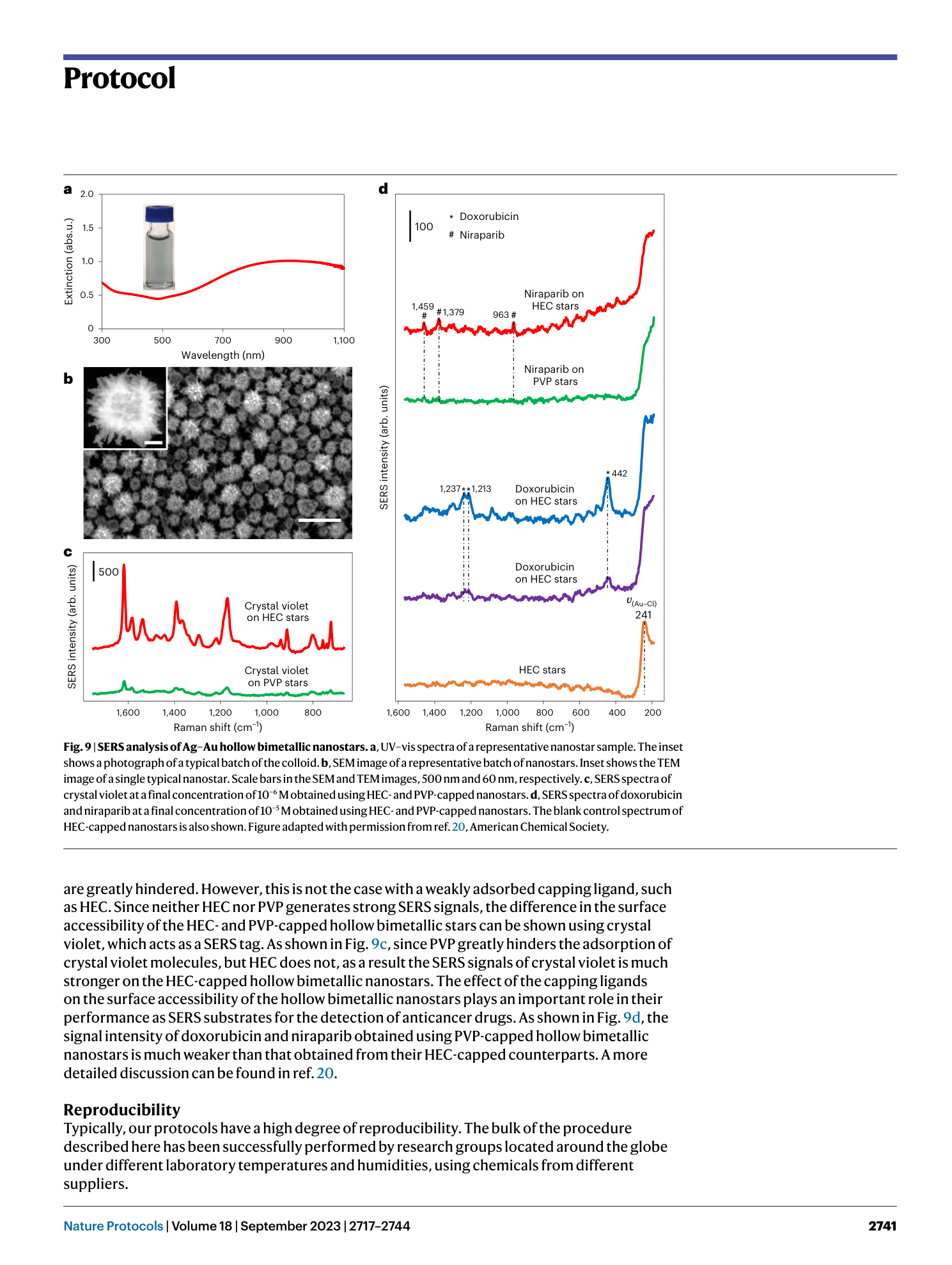
Extended Data Fig. 1 The aggregation kinetics of CRGC monitored by SERS.
( a ) Plot showing the intensity of the Au-Cl vibration band measured over time. ( b ) SERS spectra of aggregated CRGC obtained 30 seconds, 150 seconds, 300 seconds, 450 seconds, 600 seconds, 750 seconds and 900 seconds after adding in the aggregating agent.
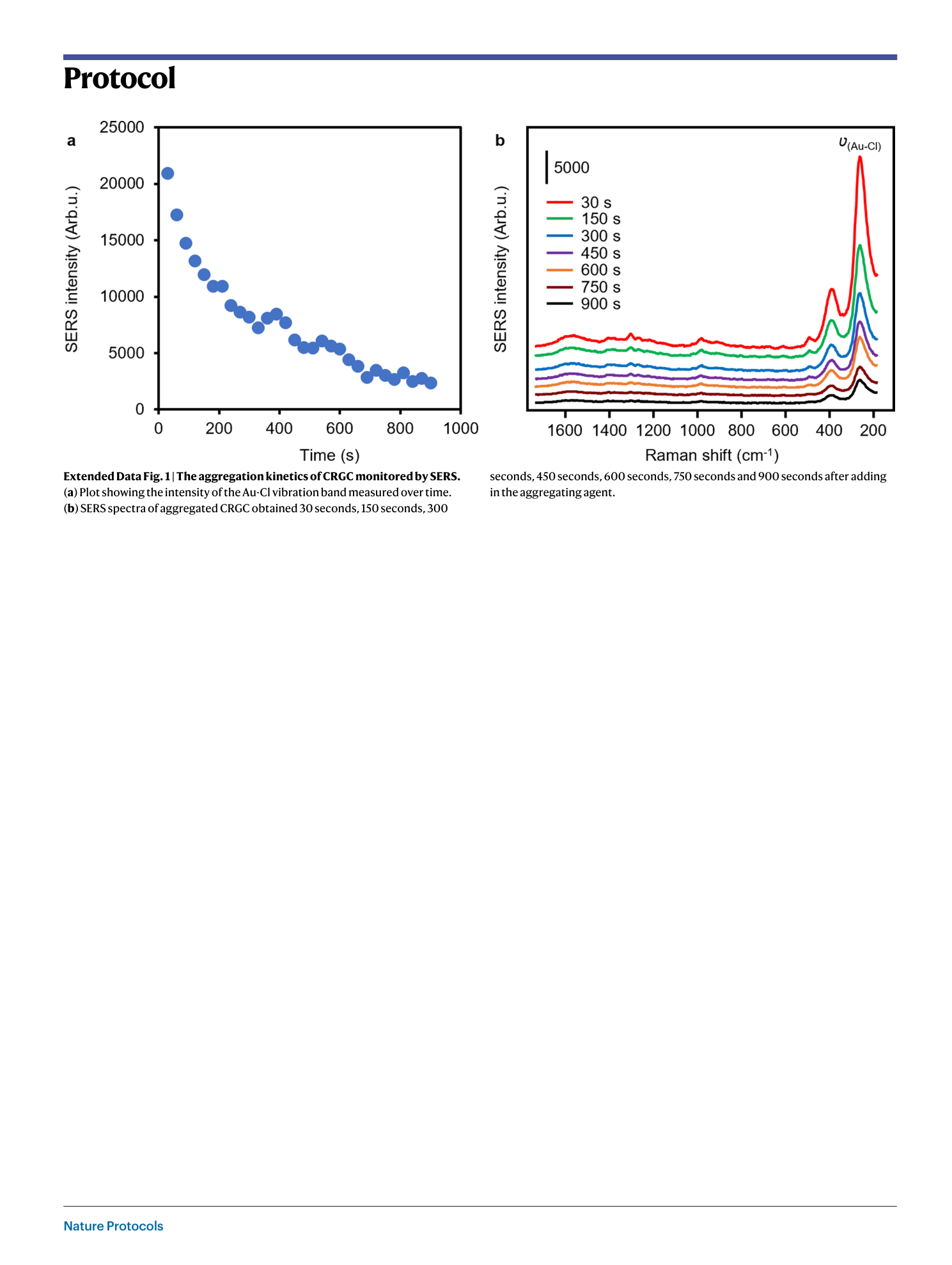
Extended Data Fig. 2 SERS reproducibility data using aggregated colloid.
SERS data obtained from five independent samples of aggregated CRSC.
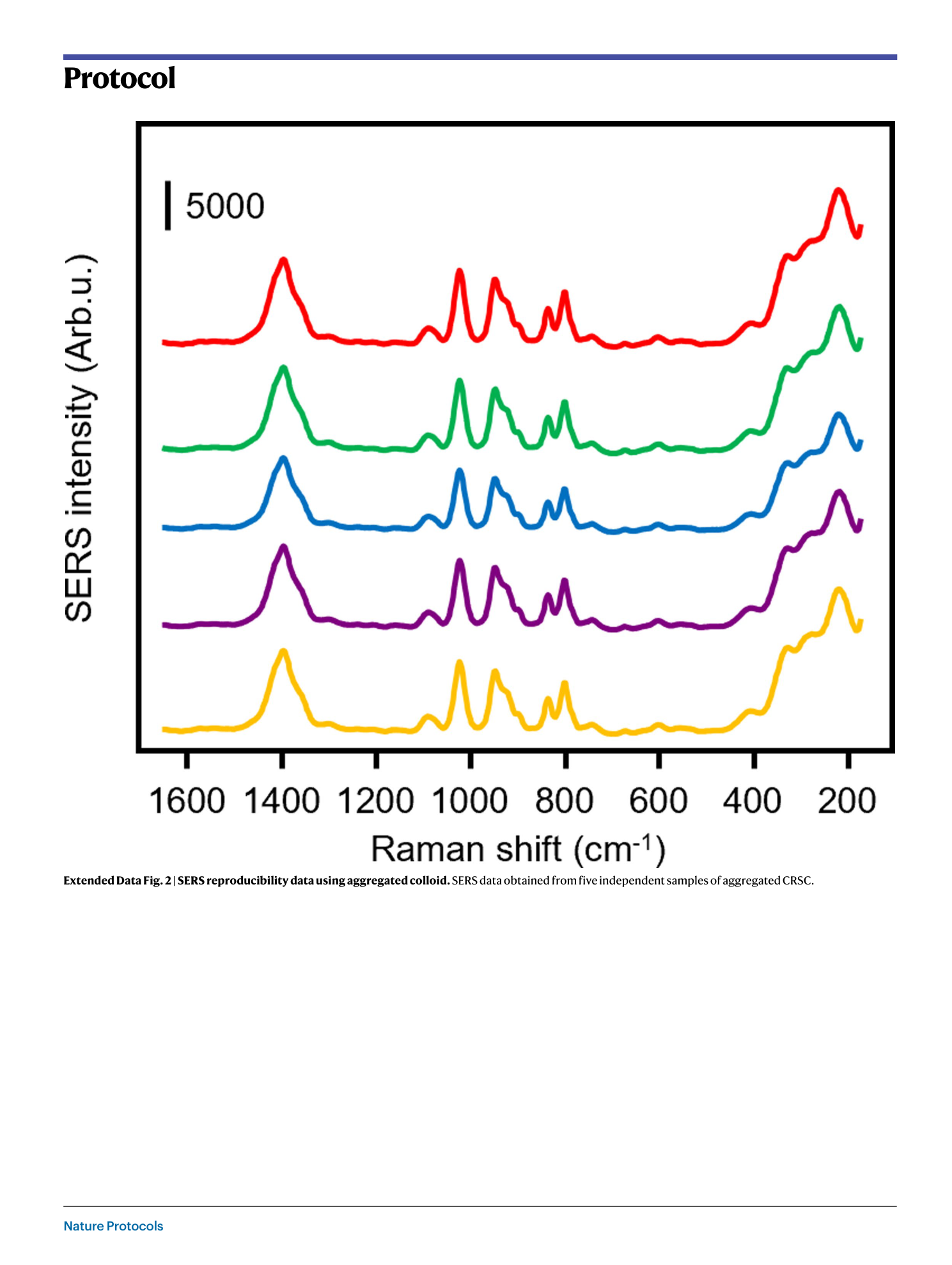
Extended Data Fig. 3 SEM images of nanoparticle-polymer films formed with incorrect particle concentrations.
( a ) A typical CRGC nanoparticle-polymer film formed with low concentrations of particles leading to a loosely packed particle layer. ( b ) A typical CRGC nanoparticle-polymer film formed with high concentrations of particles leading to the formation of wrinkles in the particle layer. Scale bars, 500 nm.
Extended Data Fig. 4 Optical microscopy image showing a MeLLF sample before and after being damaged by laser irradiation.
( a ) A CRSC MeLLF observed with a confocal Raman microscope. ( b ) The same area of the MeLLF after being damaged with laser irradiation. Scale bars, 100 µm.

