IBEX: an iterative immunolabeling and chemical bleaching method for high-content imaging of diverse tissues
Anita Gola, Andrea J. Radtke, Colin J. Chu, Ziv Yaniv, Li Yao, James Marr, Rebecca T. Beuschel, Hiroshi Ichise, Juraj Kabat, Bradley Lowekamp, Emily Speranza, Joshua Croteau, Nishant Thakur, Danny Jonigk, Jeremy L. Davis, Jonathan M. Hernandez, Ronald N. Germain





















Extended
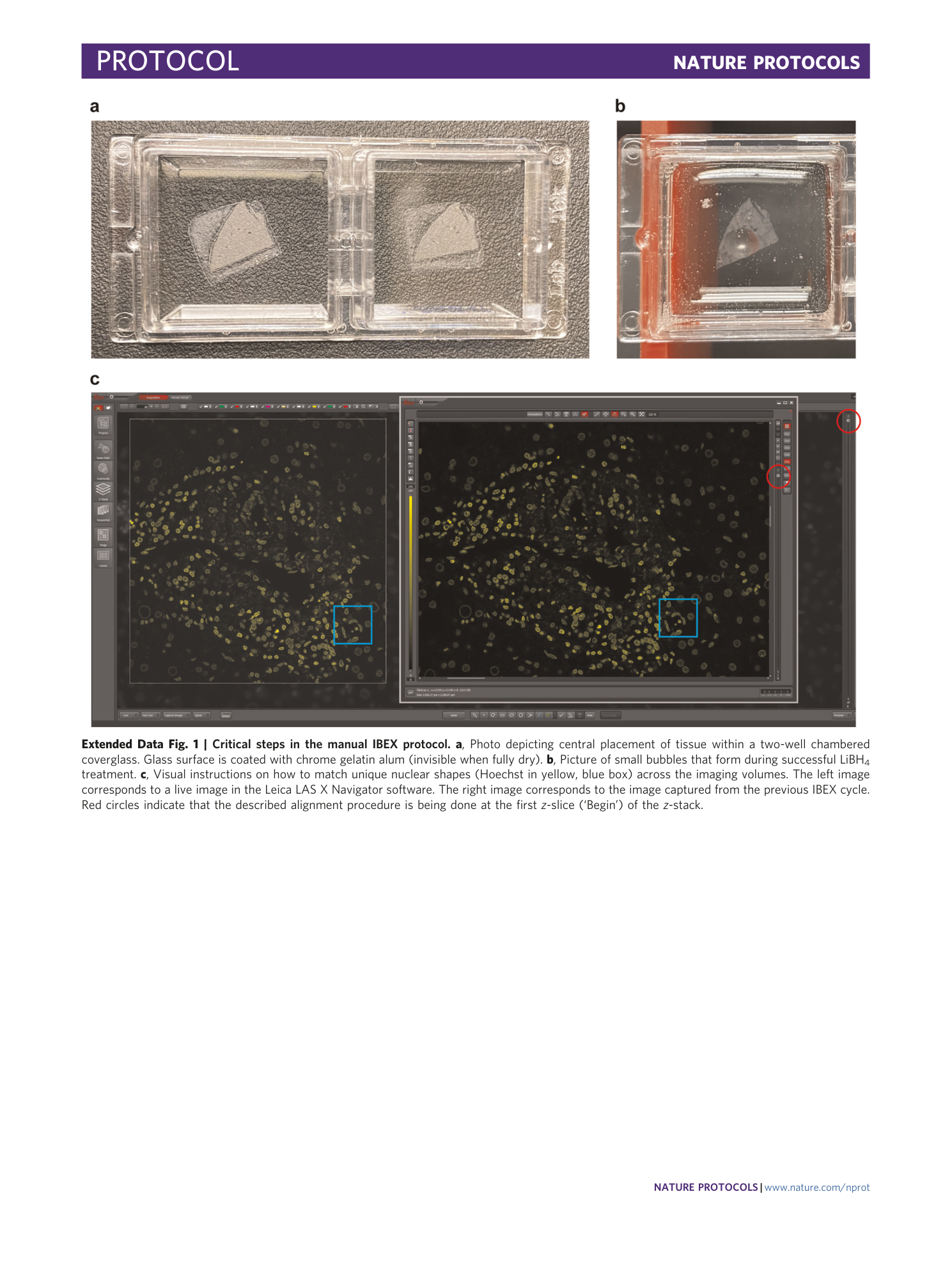
Extended Data Fig. 1 Critical steps in the manual IBEX protocol.
a , Photo depicting central placement of tissue within a two-well chambered coverglass. Glass surface is coated with chrome gelatin alum (invisible when fully dry). b , Picture of small bubbles that form during successful LiBH 4 treatment. c , Visual instructions on how to match unique nuclear shapes (Hoechst in yellow, blue box) across the imaging volumes. The left image corresponds to a live image in the Leica LAS X Navigator software. The right image corresponds to the image captured from the previous IBEX cycle. Red circles indicate that the described alignment procedure is being done at the first z -slice (‘Begin’) of the z -stack.
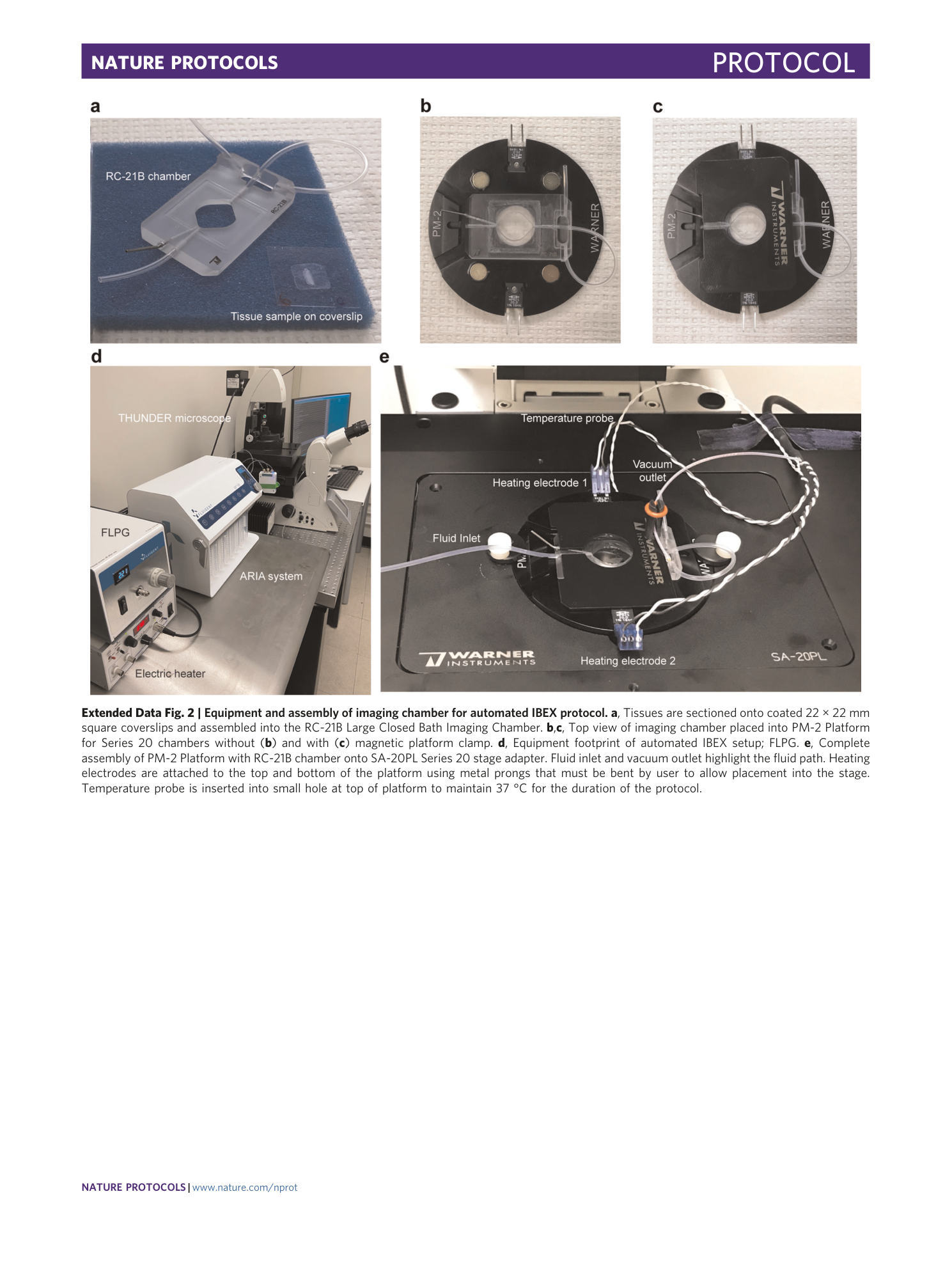
Extended Data Fig. 2 Equipment and assembly of imaging chamber for automated IBEX protocol.
a , Tissues are sectioned onto coated 22 × 22 mm square coverslips and assembled into the RC-21B Large Closed Bath Imaging Chamber. b , c , Top view of imaging chamber placed into PM-2 Platform for Series 20 chambers without ( b ) and with ( c ) magnetic platform clamp. d , Equipment footprint of automated IBEX setup; FLPG. e , Complete assembly of PM-2 Platform with RC-21B chamber onto SA-20PL Series 20 stage adapter. Fluid inlet and vacuum outlet highlight the fluid path. Heating electrodes are attached to the top and bottom of the platform using metal prongs that must be bent by user to allow placement into the stage. Temperature probe is inserted into small hole at top of platform to maintain 37 °C for the duration of the protocol.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Tables 1–4 and legends for Supplementary Videos 1–7.
Reporting Summary
Supplementary Video 1
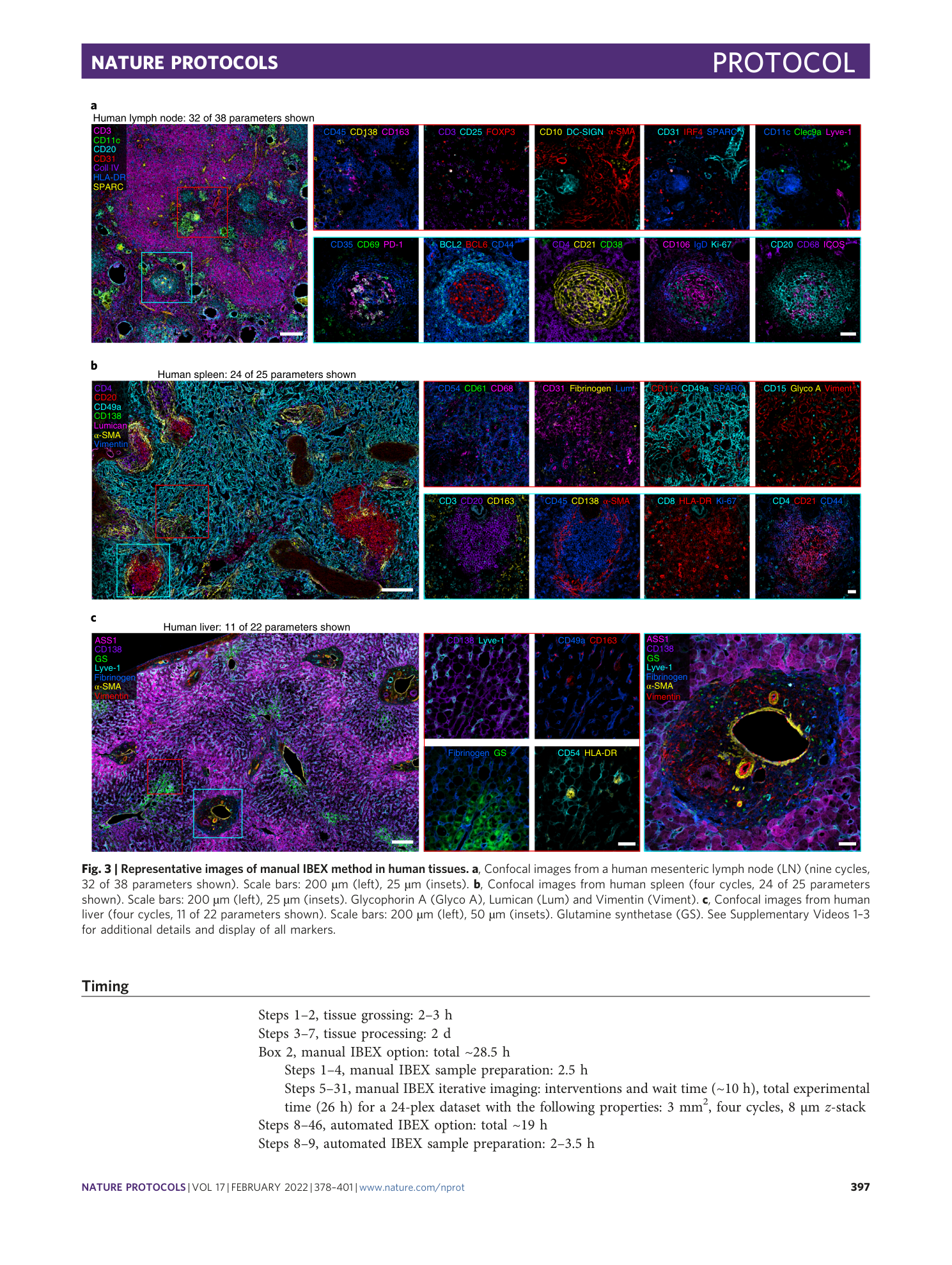
High dimensional imaging of human lymph node using manual IBEX method. Confocal images of human mesenteric lymph node from a 9 cycle 38 parameter IBEX experiment with Hoechst serving as a fiducial.
Supplementary Video 2
High dimensional imaging of human spleen using manual IBEX method. Confocal images of human spleen from a 4 cycle 25 parameter IBEX experiment with Hoechst serving as a fiducial.
Supplementary Video 3
High dimensional imaging of human liver using manual IBEX method. Confocal images of human liver from a 4 cycle 22 parameter IBEX experiment with Hoechst serving as a fiducial.
Supplementary Video 4
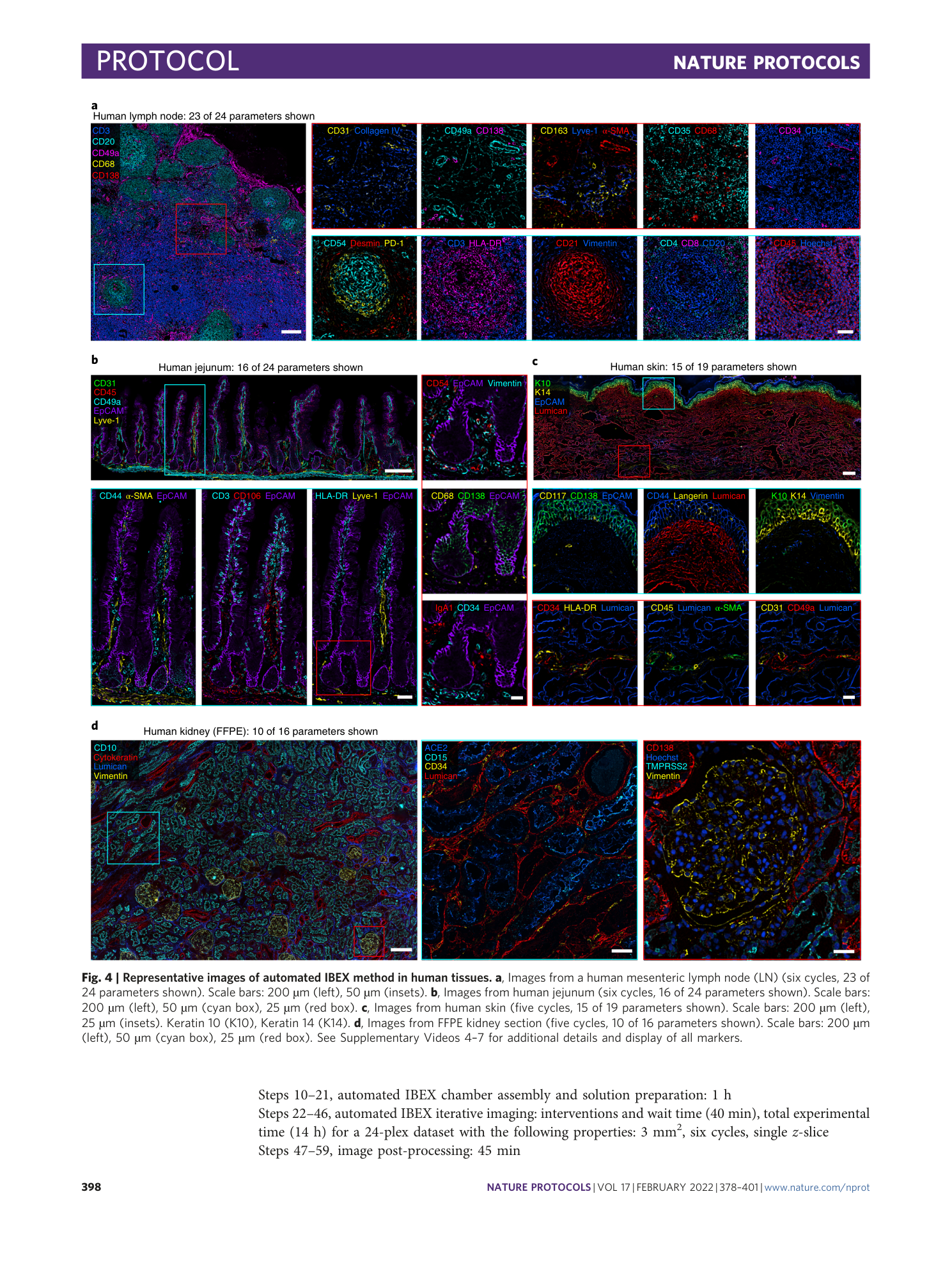
High dimensional imaging of human lymph node using automated IBEX method. THUNDER widefield images of human mesenteric lymph node from a 6 cycle 24 parameter IBEX experiment with Hoechst serving as a fiducial.
Supplementary Video 5
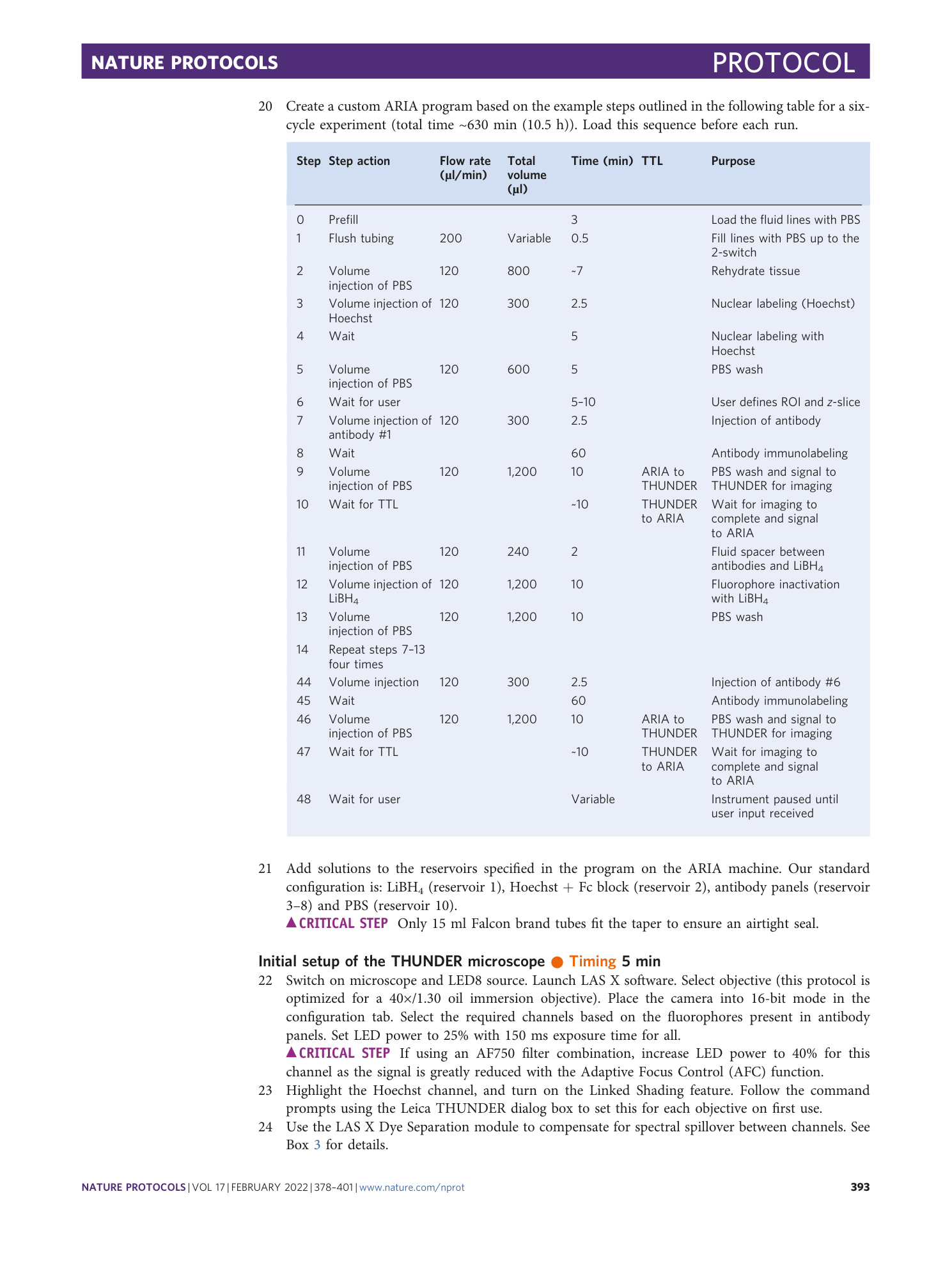
High dimensional imaging of human jejunum using automated IBEX method. THUNDER widefield images of human jejunum from a 6 cycle 24 parameter IBEX experiment with Hoechst serving as a fiducial.
Supplementary Video 6
High dimensional imaging of human skin using automated IBEX method. THUNDER widefield images of human skin from a 5 cycle 19 parameter IBEX experiment with Hoechst serving as a fiducial.
Supplementary Video 7
High dimensional imaging of human kidney (FFPE) using automated IBEX method. THUNDER widefield images of human FFPE kidney sections from a 5 cycle 16 parameter IBEX experiment with Hoechst serving as a fiducial.

