Efficient Depletion of Fission Yeast Condensin by Combined Transcriptional Repression and Auxin-Induced Degradation
Yasutaka Kakui, Frank Uhlmann
Condensin
SMC complex
Chromosome condensation
Auxin-inducible degron
Transcriptional repression
Fission yeast
Abstract
Structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) complexes play pivotal roles in controlling chromatin organization. Condensin is an essential SMC complex that compacts chromatin to form condensed chromosomes in mitosis. Complete condensin inactivation is necessary to reveal how condensin converts interphase chromatin into mitotic chromosomes. Here, we have developed a condensin depletion system in fission yeast that combines transcriptional repression with auxin-inducible protein degradation. This achieves efficient condensin depletion without need for a temperature shift. Our system is useful when studying how condensin contributes to chromosome architecture and is applicable to the study of other SMC complexes.
Steps
Depletion of the Condensin SMC2/Cut14 Subunit
Culture cells in PGM at 25°C until OD595 reaches 0.2–0.4 (4–8 × 106 cells/mL).
Add 1/2000 culture volume of thiamine solution.

Add 1/1000 culture volume IAA stock solution to the culture.
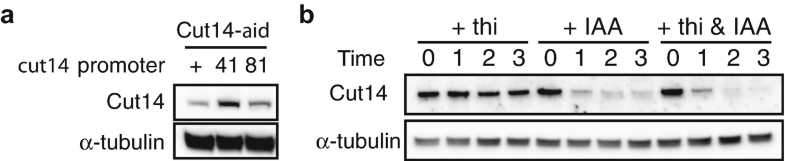
Incubate for 3h 0m 0s at 25°C.
Collect cells.
Confirmation of Condensin Depletion by Western Blotting
Harvest 2.5 OD595 units of cells (5 × 107 cells) in 15 mL tubes.
Centrifuge at 3000rpm,4°C.
Discard the supernatant.
Suspend cells in 1mL.
Transfer cells to screw cap 2 mL tube. As required, samples can be stored 25On ice at this stage.
Centrifuge 13000rpm,4°C.
Discard supernatant.
Suspend cells in 1mL.
Centrifuge 13000rpm,4°C.
Discard supernatant. Remove all the liquid carefully.
Suspend cells in 100µL.
Boil at 95°C for 0h 2m 0s.
Add 200µL to the screw cap 2 mL tubes.
Boil at 95°C for 0h 2m 0s.
Break cells using a Multibead shocker (6.0 m/s for 0h 0m 40s, or until cells are broken).
Boil at 95°C for 0h 2m 0s.
Puncture the bottom of the screw cap tubes using a 23 G needle.
Place the screw cap tube onto a 1.5 mL tube (Fig. 2a).

Place both tubes into a 50 mL tube (Fig. 2b).

Centrifuge 50 mL tubes (from previous step) at 1000rpm.
Discard screw cap tubes, recover the 1.5 mL tubes that contain the protein extract.
Boil at 95°C for 0h 2m 0s.
Spin at 10000rpm to remove cell debris.
Load 5µL–10µL for analysis by SDS-PAGE.
Transfer proteins to a nitrocellulose membrane.
Blocking: Incubate the membrane with 5% skim milk in PBST at 25Room temperature for 0h 30m 0s.
Incubate the membrane with Primary antibody.
Wash the membrane with PBST at 25Room temperature for 0h 5m 0s. (1/4)
Wash the membrane with PBST at 25Room temperature for 0h 5m 0s. (2/4)
Wash the membrane with PBST at 25Room temperature for 0h 5m 0s. (3/4)
Wash the membrane with PBST at 25Room temperature for 0h 5m 0s. (3/4)
Incubate the membrane with Secondary antibody.
Wash the membrane with PBST at 25Room temperature for 0h 5m 0s. (1/3)
Wash the membrane with PBST at 25Room temperature for 0h 5m 0s. (2/3)
Wash the membrane with PBST at 25Room temperature for 0h 5m 0s. (3/3)
Detection of the protein. Follow the manufacturer’s instruction for using the ECL reagents.
Open image in new window.

