A nanobody-based strategy for rapid and scalable purification of human protein complexes
Taylor Anthony Stevens, Giovani Pinton Tomaleri, Masami Hazu, Sophia Wei, Vy N. Nguyen, Charlene DeKalb, Rebecca M. Voorhees, Tino Pleiner

























Extended
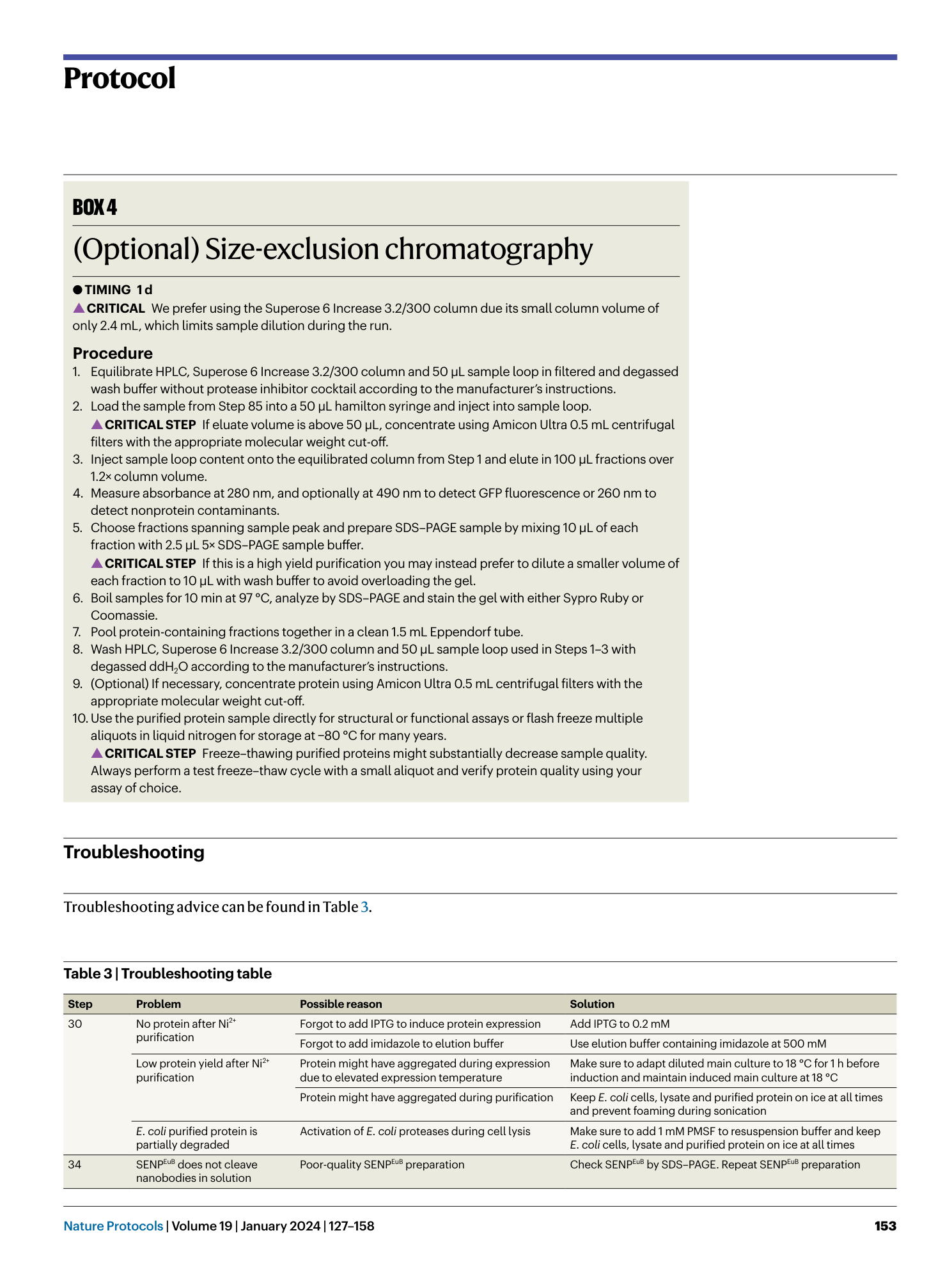
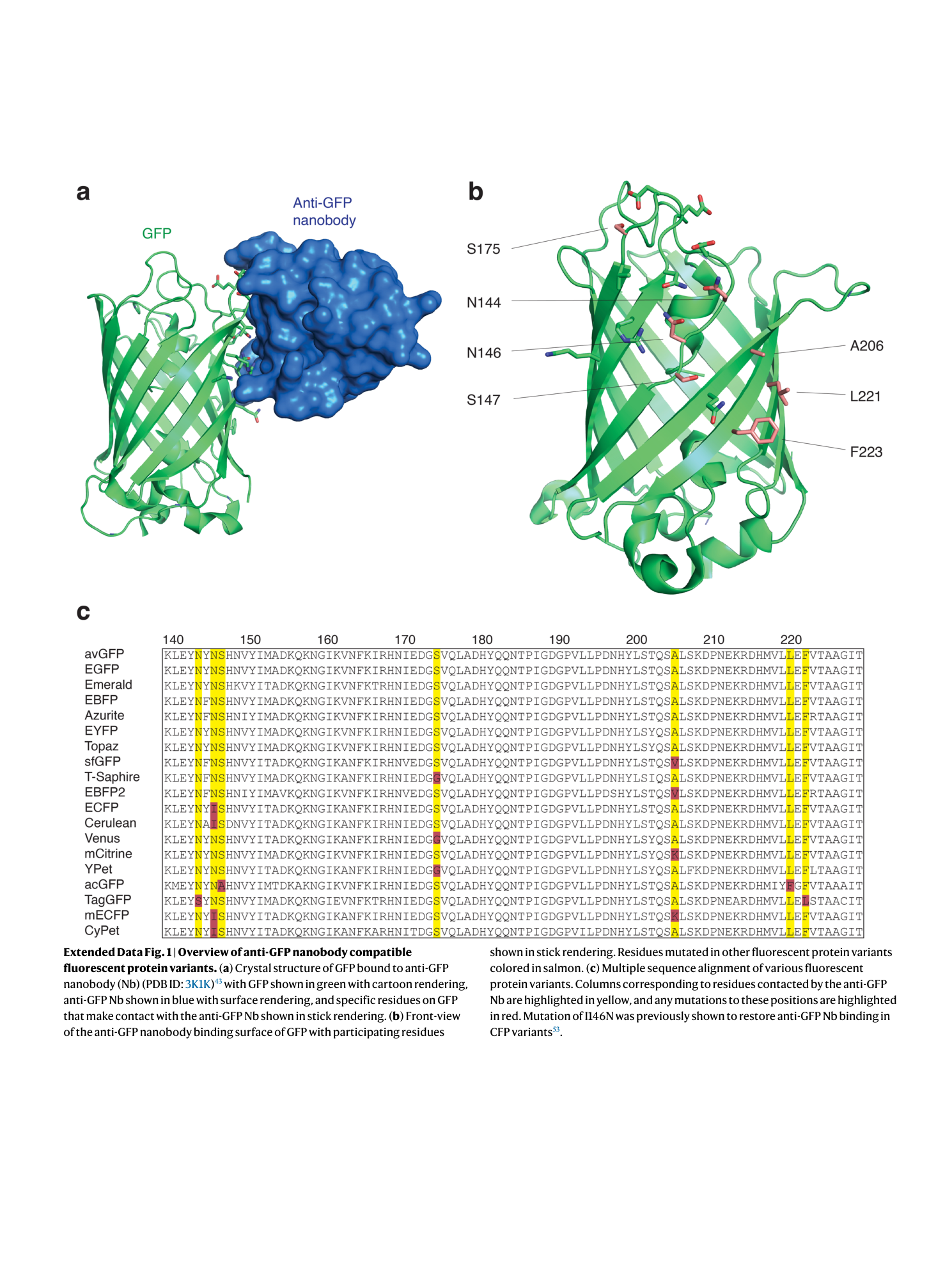
Extended Data Fig. 1 Overview of anti-GFP nanobody compatible fluorescent protein variants.
( a ) Crystal structure of GFP bound to anti-GFP nanobody (Nb) (PDB ID: 3K1K ) 43 with GFP shown in green with cartoon rendering, anti-GFP Nb shown in blue with surface rendering, and specific residues on GFP that make contact with the anti-GFP Nb shown in stick rendering. ( b ) Front-view of the anti-GFP nanobody binding surface of GFP with participating residues shown in stick rendering. Residues mutated in other fluorescent protein variants colored in salmon. ( c ) Multiple sequence alignment of various fluorescent protein variants. Columns corresponding to residues contacted by the anti-GFP Nb are highlighted in yellow, and any mutations to these positions are highlighted in red. Mutation of I146N was previously shown to restore anti-GFP Nb binding in CFP variants 53 .
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Tables 1–3, Fig. 1 and Data 1.
Reporting Summary
Supplementary Data 2
E. coli protein expression data sheet.

