XTT Assay for Detection of Bacterial Metabolic Activity in water-based Polyester Polyurethane
Nallely Magaña-Montiel, Luis F Muriel-Millán, Liliana Pardo-López
Abstract
In microbial biodegradation assays, the detection of bacterial growth in water-based plastic dispersions can be difficult to measure using traditional methods because of the turbidity of culture media and the formation of flocculi. Here, we present a protocol for the detection of bacterial growth in Impranil®DLN, a polyester polyurethane (PU) water-based dispersion. By measuring bacterial metabolic activity, as an indicator of cell viability with the water-soluble 2, 3-bis [2-methyloxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl]-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide (XTT) salt. Viable growing cells, i.e., those cells that can utilize PU as a carbon source, will reduce the yellow-colored XTT to a water-soluble orange formazan by the action of dehydrogenase enzymes of the respiratory chain. For the standardization of the protocol, we used Pseudomonas putida KT2440 and Escherichia coli BL21 strains as positive and negative controls, respectively. We determined the metabolic activity of the strains grown with citrate or both citrate and impranil as carbon sources. P. putida KT2440 showed higher XTT-detected metabolic activity in the presence of PU than when it was grown only with citrate, indicating that the strain also used PU as a carbon source. In contrast, the negative control did not show differences in metabolic activity between the growth conditions. Our protocol can be adapted to different bacterial strains and culture media.
Before start
Washing glassware All glassware should be washed twice using 2 mL of methanol-chloroform mixture (1:1) and allowed to dry in a fume hood.
Steps
Preparation of bacterial strains
Scrape some of the frozen surface of the glycerol stock using a sterile loop and streak the bacteria onto a Luria-Bertani (LB) agar plate.
Incubate the culture at 30°C during 24h 0m 0s
Take one isolated colony and inoculate it into 5mLLB broth.
Incubate at 30°C with shaking at 180rpm.
Measure the optical density (OD) at 600 nm of cultures using a spectrophotometer.
Inoculate 250-mL flasks containing 50mL of Basal Medium standardize supplemented with Instant Ocean Sea Salt (0.06 g•L-1) (BM), peptone (10 g•L-1) and yeast extract (5 g•L-1) (BM-PY broth) with an aliquot of the previous culture to obtain an OD600 of approximately 0.1.
Incubate the new culture at 180rpm for the time needed to reach the exponential growth phase: approximately 4h 0m 0s (see the note below).
Collect the cells by centrifugation at6000rpm,4°Cand discard the supernatant.
Wash twice the cellular pellet by suspension in 20mL of sterile 10mM MgSO4followed by centrifugation at 6000rpm,4°C to remove all traces of the old culture medium.
Resuspend the cells in5mLof fresh sterile 10mM MgSO4and reserve to be used as inoculum for the next steps. Keep the washed cells on ice to facilitate their handling and preparation.
Culture media preparation
The strains' ability to grow using the commercial PU coating Impranil®DLN as a carbon source is evaluated in Basal Medium, which is always supplemented with Instant Ocean Sea Salt (0.06 g•L-1).
XTT solution
Prepare a solution of
BM-citrate solution
Prepare a solution of 20 mM sodium citrate in BM.
BM-citrate-Impranil solution
Prepare a BM-citrate solution added with Impranil®DLN (1 mg•mL-1)
XTT experiment for detection of bacterial growth
XTT experiment standardization
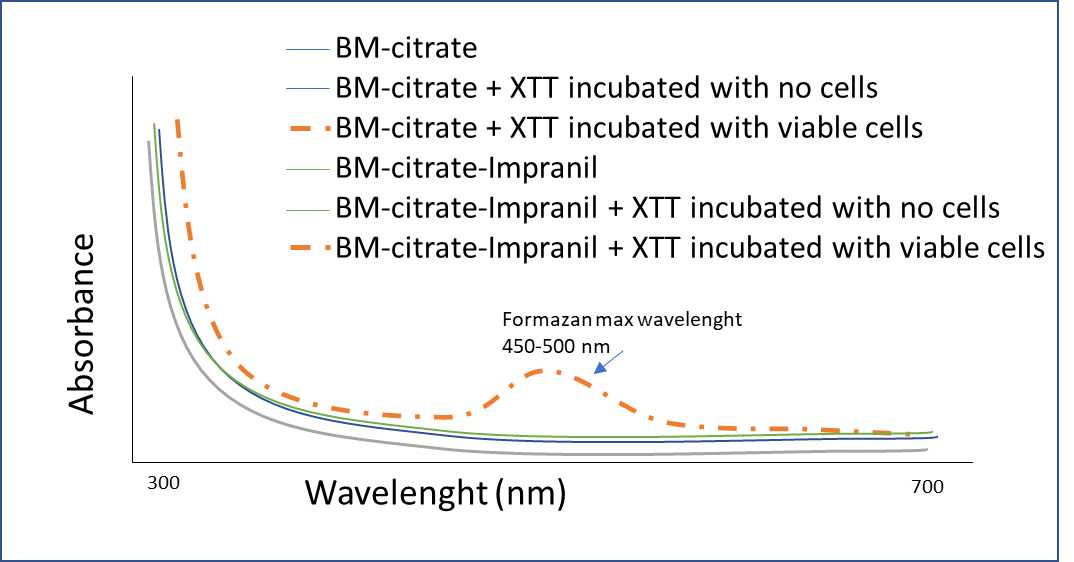
Add 150µL of the BM solution and 50µL of the XTT solution into a 96-well microplate and measure the UV-Vis spectrum in a range of 300 to 700 nm with a microplate spectrophotometer. Also, obtain the spectrum of BM-citrate and BM-citrate-Impranil in the same UV-Vis range. Perform in triplicate.
To obtain the maximum absorbance range of XTT with viable cells:
Prepare Pseudomonas putida KT2440 (positive control) cultures in BM-citrate, BM-citrate-Impranil, and BM without any carbon source (biotic control), by inoculating 20mLof each medium on 50-mL flasks up to obtain an OD600 approximately of 0.3 (~1x 108 cells) in triplicate.
To obtain the maximum absorbance range, add 150µLof each culture medium of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 and50µLof the XTT solution into a 96-well microplate and measure UV-Vis spectrum in a range of 300 to 700 nm with a microplate spectrophotometer, immediately after the addition of XTT and again after 1-3 hours of incubation at 180rpm in dark.
Detection of Bacterial Growth in Polyester Polyurethane
To evaluate microbial growth, measure the absorbance of each treatment every hour with an automated microplate spectrophotometer at Absmax (range of 450nm - 500nm) with a reference wavelength of 630nm immediately after the addition of XTT and again every hour.
Culture media:
| A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abiotic control | Pos. control | Neg. control | Test microorganism | |
| BM | x | x | x | x |
| BM-citrate | x | x | x | x |
| BM-citrate-Impranil | x | x | x | x |
"x" indicates that must be included.
Add 150µL of the different cultures into a 96-well microplate containing 50µL of XTT in each well.
We tested the metabolic activity of P. putida KT2440 (Franklin et al. 1981) and E. coli BL21 as positive and negative controls, respectively.
Immediately after XTT addition, incubate the plate24h 0m 0s at 30.°C
To evaluate microbial growth, measure absorbance every hour with an automated microplate spectrophotometer reader EPOCH2 (BioTek Instruments Inc.) both at 470nm and 630nm (reference wavelength for background subtraction).