Preparation of fibrils and Quality control
The Michael J Fox Foundation Pff Standardization Consortium
Abstract
This is a consensus protocol developed through discussions with Laura Volpicelli-Daley, Caryl Sortwell, Kelvin Luk, Lindsey Gottler, and Virginia Lee. This protocol is intended for research purposes only, using specially-formulated monomeric alpha-synuclein protein available for purchase at Proteos, Inc as the result of efforts by The Michael J. Fox Foundation (MJFF). Each batch of the “Alpha-Synuclein Monomer Protein for Making Pre- Formed Fibrils” has undergone internal purification and quality control at Proteos in addition to external validation to confirm successful generation of pathogenic aSyn PFFs. See Reference section for methods and results from application of alpha-synuclein pre-formed fibrils (aSyn PFFs) in primary neuron cultures in vitro or in mice in vivo. This protocol is referenced in the Polinski et al 2018 paper entitled "Best Practices for Generating and Using Alpha-Synuclein Pre-Formed Fibrils to Model Parkinson's Disease in Rodents" (doi: 10.3233/JPD-171248).
Attachments
Steps
Step 1. Preparation of fibrils. (Timing ~30 min; 7 days for fibril formation)
Thaw aliquot of “Alpha-Synuclein Monomer Protein for Making PreFormed Fibrils” or other recombinant aSyn monomer -80On ice.
Centrifuge at 4°C for 0h 10m 0s in benchtop centrifuge at highest speed (12000x g,0h 0m 0s-15000x g,0h 0m 0s).
Retain only the supernatant with a pipette, avoiding any aSyn that may have pelleted. Determine the protein concentration of the sample.
METHOD 1 (most recommended) : Measure protein by A280 on a nanodrop device. Use Beer’s law to measure concentration (ε for synuclein = voo5960 M−1 cm−1 for human synuclein and 7450 M−1 cm−1 for mouse synuclein).
METHOD 2 (less recommended) : Perform BCA protein assay on this material to determine final protein concentration. We recommend performing the assay at 3 dilutions of protein (in triplicate for each dilution) to obtain accurate measurements.
Assemble the pre-formed fibrils (PFFs) in 1.5mL microcentrifuge tubes by diluting the monomeric protein into PBS for a final concentration of 5mg/mL.
Vortex tubes at high speed for 0h 0m 3s to mix contents.
Place microcentrifuge lid lock on lid of tube to prevent opening of lid. Label and date tube.
Place in orbital shaker (e.g. Eppendorf Thermomixer R) at 37°C.
Shake for 168h 0m 0s at 1000rpm,0h 0m 0s. Solution should turn turbid during this period.
Pipet 25µL aliquots in small tubes using gel loading pipet tips.
Freeze aliquots on dry ice and store at -80°C or store aliquots at -80Room temperature.
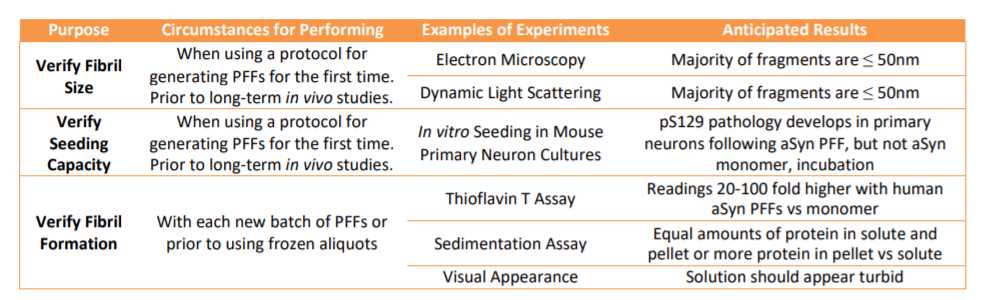
Step 2. Quality control to verify fibril formation
Thaw an aliquot at -80Room temperature and perform Thioflavin T assay toconfirm presence of amyloid fibrils:
Dilute 1millimolar (mM) Thioflavin T stock in PBS to 25micromolar (µM) final concentration (1:40 dilution).
Pipet 95µL of the 25micromolar (µM) Thioflavin T per well of 384 well plate.
Pipet PFFs up and down to mix, add 2.5µL to wells with Thioflavin T.
For controls, include 2.5µL PBS alone and 2.5µL monomeric aSyn.
Incubate at -80Room temperature for 0h 2m 0s to 1h 0m 0s.
Read plate (excitation 450nm, emission 50nm).
- The presence of fibrils can also be assessed by sedimentation.
Dilute 2µL of 5mg/mL PFFs in 20µL PBS.
Spin in ultracentrifuge (e.g. TLA-100) at 100000x g,0h 0m 0s for 0h 30m 0s at 25°C.
Remove supernatant, dilute in 5X Laemlli buffer.
Add 20µL PBS to pellet, pipet up and down several times until resuspended, dilute in 5X Laemlli buffer.
Boil samples at 95°C for 0h 5m 0s.
Run equal volumes of supernatant and pellet fractions on 15% polyacrylamide gel.
Stain with coomassie brilliant blue to visualize bands.
Keep records of results of Thioflavin T and sedimentation assay to make batch to batch comparisons.