Co-extraction of RNA and DNA from animal tissue
Dominik Buchner
Abstract
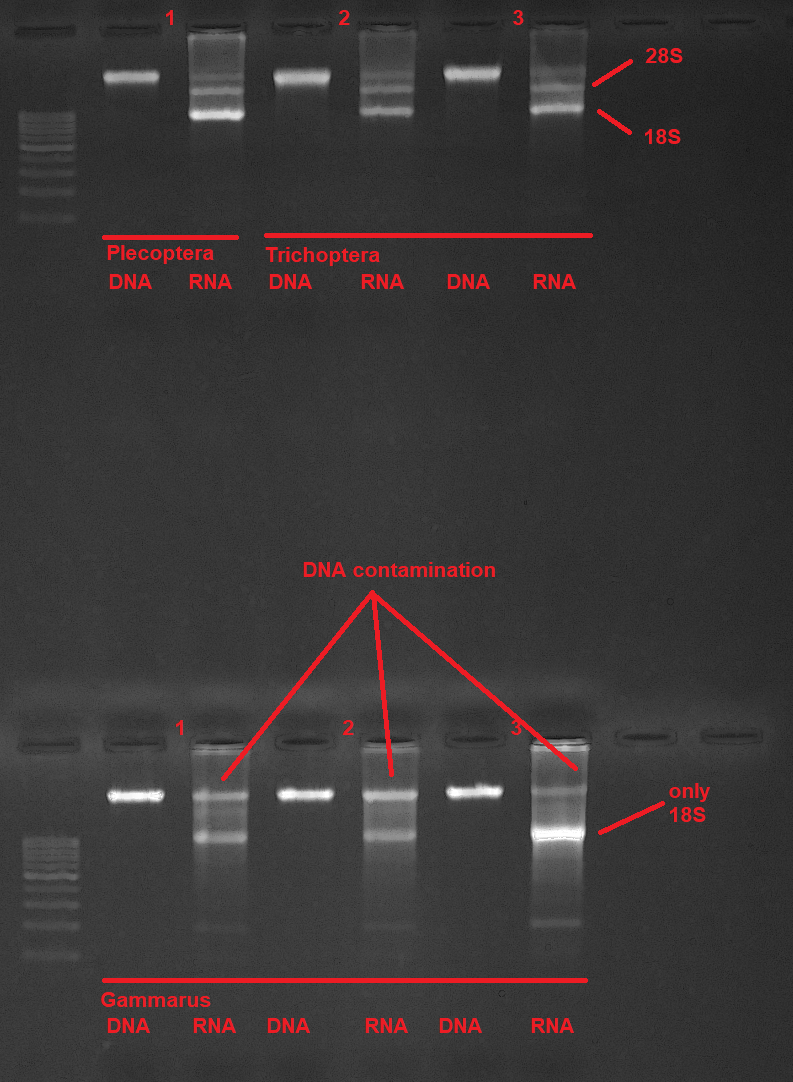
This protocol describes how to co-extract RNA and DNA from animal tissue samples. Samples are homogenized and simultaneously lyzed by bead-beating. Cell debris is pelleted by centrifugation, the DNA is then subsequently bound to a silica column, while the RNA passes the membrane. The RNA in the flow-through is then precipitated with 70% ethanol and bound to a second silica column. Both, DNA and RNA are washed with different wash buffers to remove remaining proteins and other contaminants and finally eluted in separate tubes. If the user is just interested in the RNA, the DNA spin-column can just be discarded.
Before start
Make sure all buffers are prepared before starting.
Steps
Sample preparation and lysis
For each sample prepare one 2 mL screwcap tube pre-filled with approximately 400mg of 2 mm zirconia beads and 0.1 mm glass beads.
Add up to 30mg of animal tissue to the prepared tube.
Add 1000µL to the sample tube.
Immediately bead beat for 0h 5m 0s at maximum speed.
Lysate clearing
``
DNA binding
Transfer 700µL of the cleared lysate from step 5the to a silica spin column to bind the DNA in the lysate. Keep the flow-through. Mark the spin column as the DNA column.
RNA precipitation and binding
Add 700µL to the flow-through from step 6 to adjust the binding conditions for RNA to bind to the silica column.
Vortex the samples to mix the lysate with the ethanol. Do not centrifuge.
Load the mixture on a second spin column. Mark this column as the RNA spin column.
11000x g and discard the flow-through.
Washing steps
Add 700µL to the RNA spin column ,11000x g and discard the flow-through.
Add 500µL to the RNA spin column , add 500µL to the DNA spin column , 11000x g and discard the flow-through.
Add 500µL to the RNA spin column , add 500µL to the DNA spin column , 11000x g and discard the flow-through.
Column drying and elution
11.000x g to dry the silica membrane of the spin columns. Transfer the spin column to a fresh 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube.
Add 100µL directly to the silica membrane. Incubate the column for 0h 3m 0s at Room temperature
11.000x g , store the eluted RNA at -80°C and the eluted DNA at -20°C