Protocol for Use with Standard Insert Libraries (370-420 bp) (NEB#E7120)
New England Biolabs
Abstract
This protocol details how to construct DNA libraries from start to finish using NEBNext reagents.
The corresponding NEB manual is here: https://www.neb.com/-/media/nebus/files/manuals/manuale7120.pdf and this protocol relates to section 1.
Overview

The Enzymatic Methyl-seq kit (EM-seq) for Illumina contains all the components needed to make libraries that are enzymatically modified to detect 5-methylcytosines (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosines (5hmC).
Figure 1 is an overview of the EM-seq workflow. Firstly, a library is made by ligating EM-seq adaptor to sheared end repaired/dA-tailed genomic DNA. This is followed by two sets of enzymatic conversion steps to differentiate cytosines from 5mC and 5hmC. Finally, libraries are PCR amplified before sequencing.
Figure 2. Overview of Sodium Bisulfite Conversion and EM-seq.

Figure 2 shows a comparison of the sodium bisulfite and EM-seq methods. Sodium bisulfite treatment of DNA results in the deamination of cytosines into uracils, however the modified forms of cytosine (5mC and 5hmC) are not deaminated. Therefore, the preference of bisulfite to chemically deaminate cytosines enables the methylation status of cytosines to be determined. When bisulfite treated DNA is PCR amplified, uracils are replaced by thymines and the 5mC/5hmC are replaced by cytosines. Once sequenced, unmethylated cytosines are represented by thymines and 5mC and 5hmC are represented by cytosines. By comparing sequences to non-converted genomes the appropriate methylation status can be assessed.
Enzymatic Methyl-seq is a two step enzymatic conversion process to detect modified cytosines. The first step uses TET2 and an oxidation enhancer to protect modified cytosines from downstream deamination. TET2 enzymatically oxidizes 5mC and 5hmC through a cascade reaction into 5-carboxycytosine [5-methylcytosine (5mC) -> 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) -> 5-formylcytosine (5fC) -> 5-carboxycytosine (5caC)]. This protects 5mC and 5hmC from deamination. 5hmC can also be protected from deamination by glucosylation to form 5ghmc using the oxidation enhancer. The second enzymatic step uses APOBEC to deaminate C but does not convert 5caC and 5ghmC. The resulting converted sequence can be analyzed like bisulfite-treated DNA. Typical aligners used to analyze data include but are not limited to Bismark and BWAMeth.
The workflow described in the NEBNext Enzymatic Methyl-seq Kit is user-friendly and enables methylation detection from inputs ranging between 10 ng–200 ng. EM-seq converted DNA is more intact than bisulfite-converted DNA, resulting in libraries with longer sequencing reads, reduced GC bias and more even genome coverage.
Please note that the bead volumes provided are sufficient for building standard size libraries described in Section 1, Protocol for use with Standard Size Libraries (370–420 bp). If following the Section 2 Protocol, for use with Large Size Libraries (470–520 bp), users need to supply additional beads due to the increased volumes needed for cleanups. We recommend using SPRIselect® Reagent Kit (Beckman Coulter, Inc. #B23317) or AMPure® XP Beads (Beckman Coulter, Inc. #A63881). If you are combining leftover beads from E7120 with the above products, we recommend combing with SPRIselect® Reagent Kit (Beckman Coulter, Inc. #B23317).
Each kit component must pass rigorous quality control standards, and for each new lot the entire set of reagents is functionally validated together by construction of indexed libraries and sequenced on an Illumina sequencing platform.
For larger volume requirements, customized and bulk packaging is available by purchasing through the OEM & Custom Solutions
department at NEB. Please contact custom@neb.com for further information.
Before start
Safe Stopping Point: This is a point where you can safely stop the protocol and store the samples prior to proceeding to the next step in the protocol.
Caution: This signifies a step in the protocol that has two paths leading to the same end point.
(Color): Colors in parenthesis indicate the cap color of the reagent to be added.
Starting Material: 10 ng–200 ng DNA
Steps
DNA Preparation
DNA and Control DNA
Combine genomic DNA (10–200 ng) with control DNAs specified below. Genomic DNA can be in any of the following buffers:
10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 1X TE (10mM Tris pH 8.0, 1mM EDTA), or low TE (10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 0.1 mM EDTA).
| A | B |
|---|---|
| COMPONENT | VOLUME |
| gDNA | 48 µl |
| (lilac) Control DNA Unmethylated Lambda (see Table 1.1) | 1 µl |
| (lilac) Control DNA CpG methylated pUC19 (see Table 1.1) | 1 µl |
| Total Volume | 50 µl |
The following table is a guide for the amount of (lilac) Control DNA CpG methylated pUC19 and (lilac) Control DNA Unmethylated Lambda DNA to be added to samples prior to EM-seq library construction. Expected read numbers along with read length should be considered to ensure that enough controls are included for the users individual sequencing goals.
Table 1.1 Dilutions of control DNAs for a range of genomic DNA inputs. These are suitable for shallow/pre-sequencing (approx. 2 – 4 million paired reads) on a MiSeq prior to deep sequencing (approx. 100-150 million paired reads) on NovaSeq, HiSeq or NextSeq.
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| DILUTION OF (LILAC) LAMBDA CONTROL AND (LILAC) pUC19 CONTROL | ||
| DNA Input Amount | Pre-sequencing 2-4 Milliion Paired Reads | Deep Sequencing 100-150 Million Paired Reads |
| 10 ng | 1:20 | 1:100 |
| 200 ng | No Dilution | 1:50 |
Regardless of sequencing depth, a minimum of 5,000 paired end reads with a read length of 76 bases, for unmethylated Lambda DNA, and 500 paired end reads with a read length of 76 bases, for CpG methylated pUC19, are needed to give enough coverage for accurate conversion estimates.
Different applications may require different sequencing depths and therefore different strategies should be employed when deciding how much control DNA should be added. For example, some libraries may only need 2 million paired end reads whereas other may require 50 million paired end reads or even 300 million paired end reads.
Additional considerations, regarding the amount of controls added, should be taken into account. For example, pre-sequencing libraries to a depth of 2-4 million paired end reads using the recommended dilution for the controls (Table 1.1), followed by deeper sequencing of these same libraries to a higher depth of 100 – 150 million paired reads per library would result in excess reads associated with the controls. This strategy is recommended users who choose to check library conversion prior to deeper
sequencing. Users who dilute controls based on pre-sequencing guidelines will have excess control reads, thus ensuring a higher confidence in library conversion.
Shearing DNA
The combined 50 µl genomic DNA and control DNAs are fragmented to an average fragment size of ~300 bp (370–420 bp final Illumina library). Fragmentation can be done using a preferred fragmentation device such as a Covaris instrument. Enzymatic fragmentation is not recommended as this may result in the removal of methylation marks.
Transfer the 50 µl of sheared DNA to a new PCR tube for End Prep.
Note: DNA does not need to be cleaned up or size selected before End Prep
End Prep of Sheared DNA
On ice, mix the following components in a sterile nuclease-free PCR tube:
| A | B |
|---|---|
| COMPONENT | VOLUME |
| Sheared DNA (Step 2) | 50 µl |
| (green) NEBNext Ultra II End Prep Reaction Buffer | 7 µl |
| (green) NEBNext Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix | 3 µl |
| Total Volume | 60 µl |
Note: NEBNext Ultra II End Prep Reaction Buffer and Enzyme Mix can be pre-mixed ahead of time as a master mix.
Set a 100µL or 200µL pipette to 50µL and then pipette the entire volume up and down at least 10 times to mix thoroughly.
Perform a quick spin to collect all liquid from the sides of the tube.
Note: It is important to mix well. The presence of a small amount of bubbles will not interfere with the performance.
Place in a thermal cycler with the heated lid set to ≥ 75°C or on, and run the following program:
0h 30m 0s at 20°C
0h 30m 0s at 65°C
Hold at 4°C
Ligation of EM-seq Adaptor
On ice, add the following components directly to the End Prep reaction mixture and mix well:
| A | B |
|---|---|
| COMPONENT | VOLUME |
| End Prep reaction mixture (Step 5) | 60 µl |
| (red) NEBNext EM-seq Adaptor | 2.5 µl |
| (red) NEBNext Ligation Enhancer | 1 µl |
| (red) NEBNext Ultra II Ligation Master Mix | 30 µl |
| Total Volume | 93.5 µl |
Note: Ligation Enhancer and Ligation Master Mix can be mixed ahead of time and is stable for at least 8 hours at . We do not recommend adding adaptor to a premix in the adaptor ligation step. Premix adaptor and sample and then add the other ligation reagents. 4°C. We do not recommend adding adaptor to a premix in the adaptor ligation step. Premix adaptor and sample and then add the other ligation reagents.
Set a 100µL or 200µL pipette to 80µL and then pipette the entire volume up and down at least 10 times to mix thoroughly. Perform a quick spin to collect all liquid from the sides of the tube.
CAUTION: The Ligation Master Mix is viscous. Care should be taken to ensure adequate mixing of the ligation reaction, as incomplete mixing will result in reduced ligation efficiency. The presence of a small amount of bubbles will not interfere with performance.
Place in a thermal cycler, and run the following program with the heated lid off:
15 minutes at 20°C
Hold at 4°C
Safe Stopping Point: Samples can be stored overnight at -20°C.
Clean-Up of Adaptor Ligated DNA
Vortex Sample Purification Beads to resuspend.
Add 110 µl (~1.1X) of resuspended NEBNext Sample Purification Beads to each sample. Mix well by pipetting up and down at least 10 times. Be careful to expel all of the liquid out of the tip during the last mix.
Incubate samples on bench top for at least 0h 5m 0s at Room temperature.
Place the tubes against an appropriate magnetic stand to separate the beads from the supernatant.
After 0h 5m 0s (or when the solution is clear), carefully remove and discard the supernatant.
Be careful not to disturb the beads that contain DNA targets.
CAUTION: DO NOT discard the beads.
Add 200µL to the tubes while in the magnetic stand. Incubate at Room temperature for 0h 0m 30s and then carefully removing and discard the supernatant. Be careful not to disturb the beads that contain DNA targets.
Repeat the ethanol wash once for a total of two washes. Be sure to remove all visible liquid after the second wash using a p10 pipette tip.
Air dry the beads for up to 2 minutes while the tubes are on the magnetic stand with the lid open.
CAUTION: Do not over-dry the beads. This may result in lower recovery of DNA target. Elute the samples when the beads are still dark brown and glossy looking, but when all visible liquid has evaporated. When the beads turn lighter brown and start to crack they are too dry.
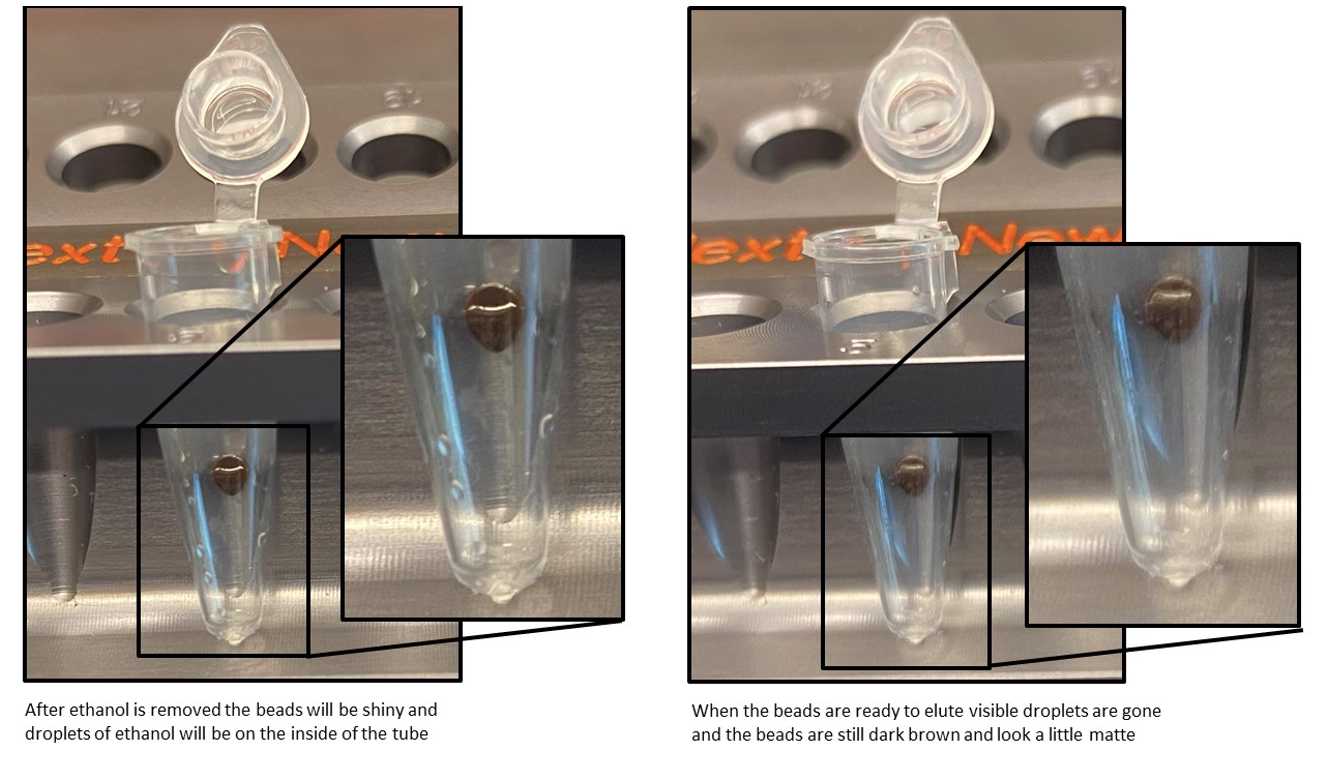

Remove the tubes from the magnetic stand. Elute the DNA target from the beads by adding 29µL (white).
Mix well by pipetting up and down 10 times. Incubate for at least 0h 1m 0s at Room temperature. If necessary, quickly spin the sample to collect the liquid from the sides of the tube before placing back on the magnetic stand.
Place the tube on the magnetic stand. After 0h 3m 0s, or whenever the solution is clear, transfer 28µL to a new PCR tube.
Oxidation of 5-Methylcytosines and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines
Prepare TET2 Buffer . Use option A if you have E7120S/ E7120G (24 Reactions/G size) and option B if you have E7120L (96 reactions).
Option A: E7120S/E7120G
Add 100µL to one tube of TET2 Reaction Buffer Supplement and mix well. Write date on tube.
Option B: E7120L
Add 400µL to one tube of TET2 Reaction Buffer Supplement and mix well. Write date on tube.
The reconstituted buffer should be stored at and discarded after 4 months. -20°C and discarded after 4 months.
On ice, add the following components directly to the EM-seq adaptor ligated DNA.
| A | B |
|---|---|
| COMPONENT | VOLUME |
| EM-seq adaptor ligated DNA (Step 19) | 28 µl |
| (yellow) TET2 Reaction Buffer (TET2 Reaction Buffer plus reconstituted TET2 Reaction Buffer Supplement) | 10 µl |
| (yellow) Oxidation Supplement | 1 µl |
| (yellow) DTT | 1 µl |
| (yellow) Oxidation Enhancer | 1 µl |
| (yellow) TET2 | 4 µl |
| Total Volume | 45 µl |
Mix thoroughly by vortexing, centrifuge briefly. For multiple reactions, a master mix of the above reaction components can be prepared before addition to the sample DNA. 5mC/5hmC oxidation is initiated by the addition of the Fe(II) solution to the reaction in the next step.
Dilute the 500 mM (yellow) Fe(II) Solution by adding 1µL to 1249µL.
Combine Diluted (yellow) Fe(II) Solution and Reaction DNA Oxidation Enzymes as described below.
| A | B |
|---|---|
| COMPONENT | VOLUME |
| Reaction Mixture (Step 23) | 45 μl |
| Diluted Fe(II) Solution (from step 24) | 5 μl |
| Total Volume | 50 μl |
Mix thoroughly by vortexing or by pipetting up and down at least 10 times, centrifuge briefly.
Place in a thermal cycler, and run the following program with the heated lid set to ≥ 45°C or on:
1 hour at 37°C
Hold at 4°C
Transfer the samples to ice and add 1µL (yellow).
| A | B |
|---|---|
| COMPONENT | VOLUME |
| Oxidized DNA (Step 25) | 50 µl |
| (yellow) Stop Reagent | 1 µl |
| Total Volume | 51 µl |
Mix thoroughly by vortexing or by pipetting up and down at least 10 times and centrifuge briefly.
Place in a thermal cycler, and run the following program with the heated lid set to ≥45°C or on:
30 minutes at 37°C
Hold at 4°C
Clean-Up of TET2 Converted DNA
Vortex Sample Purification Beads to resuspend.
Add 90 µl (1.8X) of resuspended NEBNext Sample Purification Beads to each sample. Mix well by pipetting up and down at least 10 times. Be careful to expel all of the liquid out of the tip during the last mix.
Incubate samples on bench top for at least 0h 5m 0s at Room temperature.
Place the tubes against an appropriate magnetic stand to separate the beads from the supernatant.
After 0h 5m 0s (or when the solution is clear) carefully remove and discard the supernatant. Be careful not to disturb the beads that contain DNA targets.
CAUTION: DO NOT discard the beads.
Add 200µL to the tubes while in the magnetic stand. Incubate at Room temperature for 0h 0m 30s , then carefully remove and discard the supernatant. Be careful not to disturb the beads that contain DNA targets.
Repeat the wash once for a total of two washes. Be sure to remove all visible liquid after the second wash using a p10 pipette tip.
Air dry the beads for up to 2 minutes while the tubes are on the magnetic stand with the lid open.
CAUTION: Do not over-dry the beads. This may result in lower recovery of DNA target. Elute the samples when the beads are still dark brown and glossy looking, but when all visible liquid has evaporated. When the beads turn lighter brown and start to crack they are too dry.
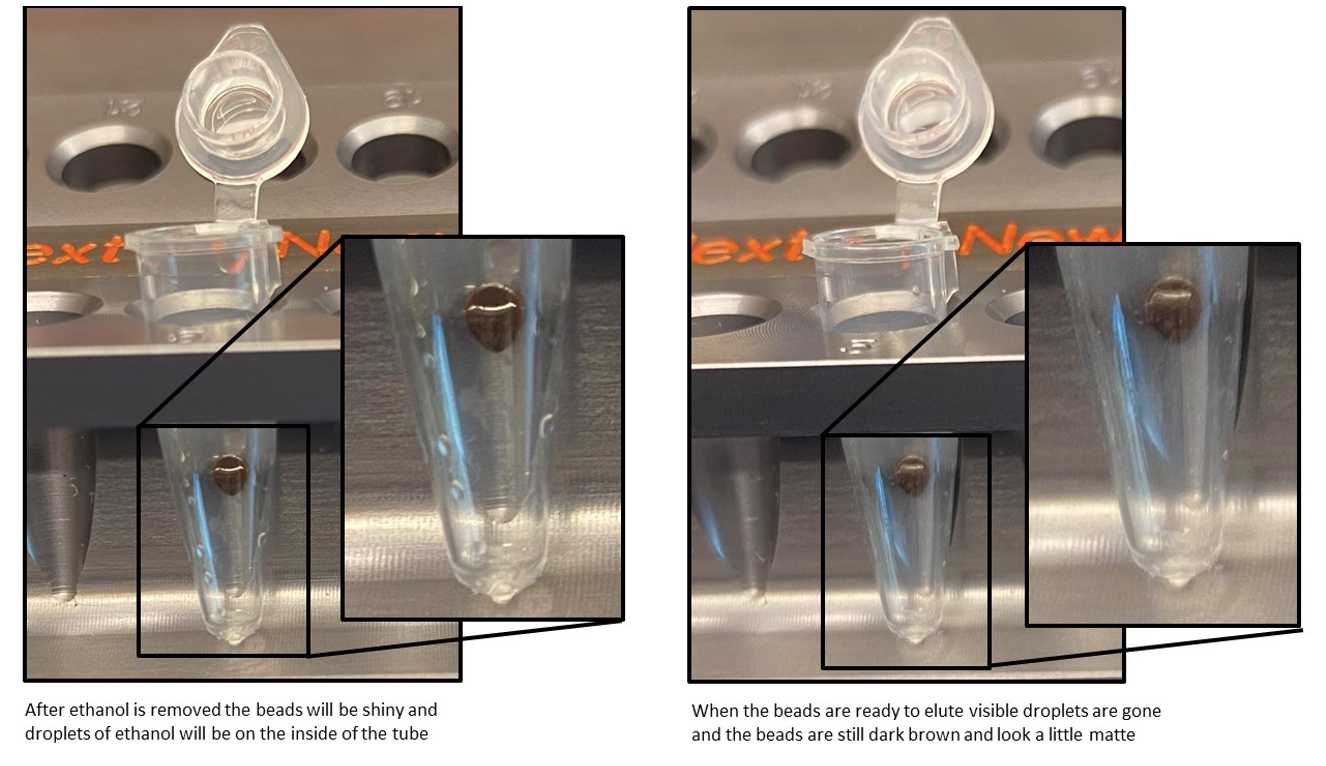

Remove the tubes from the magnetic stand. Elute the DNA target from the beads by adding 17µL.
Mix well by pipetting up and down 10 times. Incubate for at least 0h 1m 0s at Room temperature. If necessary, quickly spin the sample to collect the liquid from the sides of the tube before placing back on the magnetic stand.
Place the tube on the magnetic stand. After 0h 3m 0s (or whenever the solution is clear), transfer 16µL to a new PCR tube.
Denaturation of DNA
Use Option A for denaturing using Formamide and Option B for denaturing using 0.1 N Sodium hydroxide.
Option A: Formamide (Recommended)
Pre-heat thermal cycler to 85°C with the heated lid set to ≥ 105°C or on.
Add 4µL to the 16µL(Step 39). Vortex to mix or by pipetting up and down at least 10 times, centrifuge briefly.
Incubate at 85°C for 0h 10m 0s in the pre-heated thermal cycler.
Immediately place 85On ice and allow the sample to fully cool (~2 minutes) before proceeding to Deamination of Cytosines.
Option B: Sodium Hydroxide (Optional, see FAQ at NEB.com about preparing NaOH)
Prepare freshly diluted 0.1 N NaOH.
Pre-heat thermal cycler to 50°C with the heated lid set to ≥ 105°C or on.
Add 4µL to the 16µL (Step 39). Vortex to mix or by pipetting up and down at least 10 times, centrifuge briefly.
Incubate at 50°C for 0h 10m 0s in the pre-heated thermal cycler.
Immediately place 60On ice and allow the sample to fully cool (~2 minutes) before proceeding to Deamination of Cytosines.
Deamination of Cytosines
On ice, add the following components to the denatured DNA.
| A | B |
|---|---|
| COMPONENT | VOLUME |
| Denatured DNA (Step 43 or 48) | 20 µl |
| Nuclease-free water | 68 µl |
| (orange) APOBEC Reaction Buffer | 10 µl |
| (orange) BSA | 1 µl |
| (orange) APOBEC | 1 µl |
| Total Volume | 100 µl |
Mix thoroughly by vortexing or by pipetting up and down at least 10 times, centrifuge briefly.
Place in a thermal cycler, and run the following program wiht the heated lid set to ≥ 45°Cor on.
3h 0m 0sat 37°C
Hold at 4°C
Clean up of Deaminated DNA
Vortex Sample Purification Beads to resuspend.
Add 100 µl (1.0X) of resuspended NEBNext Sample Purification Beads to each sample. Mix well by pipetting up and down at least 10 times. Be careful to expel all of the liquid out of the tip during the last mix.
Incubate sample on bench top for at least 0h 5m 0s at Room temperature.
Place the tubes against an appropriate magnetic stand to separate the beads from the supernatant.
After 0h 5m 0s (or when the solution is clear), carefully remove and discard the supernatant. Be careful not to disturb the beads that contain DNA targets.
Add 200µL to the tubes while in the magnetic stand. Incubate at Room temperature for 0h 0m 30s , then carefully remove and discard the supernatant. Be careful not to disturb the beads that contain DNA targets.
Repeat the wash once for a total of two washes. Be sure to remove all visible liquid after the second wash using a p10 pipette tip.
Air dry the beads for up to 0h 1m 30s while the tubes are on the magnetic stand with the lid open.
CAUTION: Do not over-dry the beads. This may result in lower recovery of DNA target. Elute the samples when the beads are still dark brown and glossy looking, but when all visible liquid has evaporated. When the beads turn lighter brown and start to crack they are too dry.
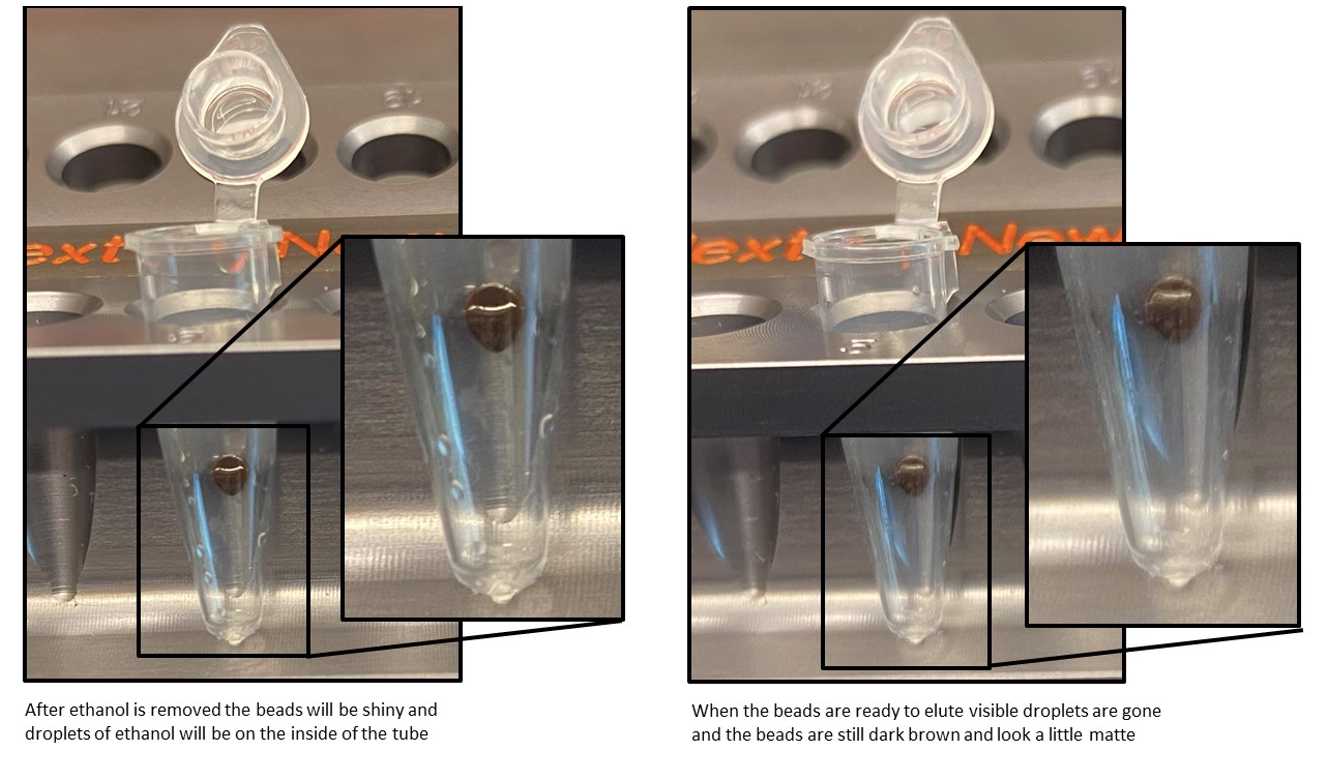

Remove the tubes from the magnetic stand. Elute the DNA target from the beads by adding 21µL.
Mix well by pipetting up and down 10 times. Incubate for at least 0h 1m 0s at Room temperature. If necessary, quickly spin the sample to collect the liquid from the sides of the tube before placing back on the magnetic stand.
Place the tube on the magnetic stand. After 0h 3m 0s (or whenever the solution is clear), transfer 20µL to a new PCR tube.
PCR Amplification
On ice, add the following components to the deaminated DNA:
| A | B |
|---|---|
| COMPONENT | VOLUME |
| Deaminated DNA (Step 62) | 20 µl |
| EM-seq Index Primer*, ** | 5 µl |
| (blue) NEBNext Q5U Master Mix | 25 µl |
| Total Volume | 50 µl |
*Refer to Section 3 in the manual at NEB.com for barcode pooling guidelines.
**EM-seq primers are supplied in tubes in NEB #E7120S or as a 96 Unique Dual Index Primers Pairs Plate in NEB #E7120L.
Mix thoroughly by vortexing or by pipetting up and down at least 10 times, centrifuge briefly.
DenPlace the tube in a thermal cycler with the heated lid set to 105°C and perform PCR amplification using the following cycling conditions:
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| CYCLE STEP | TEMP | TIME | CYCLES |
| Initial Denaturation | 98°C | 30 seconds | 1 |
| Denaturation | 98°C | 10 seconds | 4-8* |
| Annealing | 62°C | 30 seconds | |
| Extension | 65°C | 60 seconds | |
| Final Extension | 65°C | 5 minutes | 1 |
| Hold | 4°C | ∞ | - |
*Cycle Recommendations:
- 10 ng DNA input: 8 cycles
- 50 ng DNA input: 5-6 cycles
- 200 ng DNA input: 4 cycles Safe Stopping Point: Samples can be stored overnight at either 4°C in the thermal cycler or at -20°C in the freezer.
Clean-Up of Amplified Libraries
Vortex Sample Purification Beads to resuspend.
Add 45 µl (0.9X) of resuspended NEBNext Sample Purification Beads to each sample. Mix well by pipetting up and down at least 10 times. Be careful to expel all of the liquid out of the tip during the last mix.
Incubate samples on bench top for at least 0h 5m 0s at Room temperature.
Place the tubes against an appropriate magnetic stand to separate the beads from the supernatant.
After 0h 5m 0s (or when the solution is clear), carefully remove and discard the supernatant. Be careful not to disturb the beads that contain DNA targets.
Add 200µL to the tubes while in the magnetic stand. Incubate at Room temperature for 0h 0m 30s , then carefully remove and discard the supernatant. Be careful not to disturb the beads that contain DNA targets.
Repeat the wash once for a total of two washes. Be sure to remove all visible liquid after the second wash using a p10 pipette tip.
Air dry the beads for up to 0h 2m 0s while the tubes are on the magnetic stand with the lid open. CAUTION: Do not over-dry the beads. This may result in lower recovery of DNA target. Elute the samples when the beads are still dark brown and glossy looking, but when all visible liquid has evaporated. When the beads turn lighter brown and start to crack they are too dry.
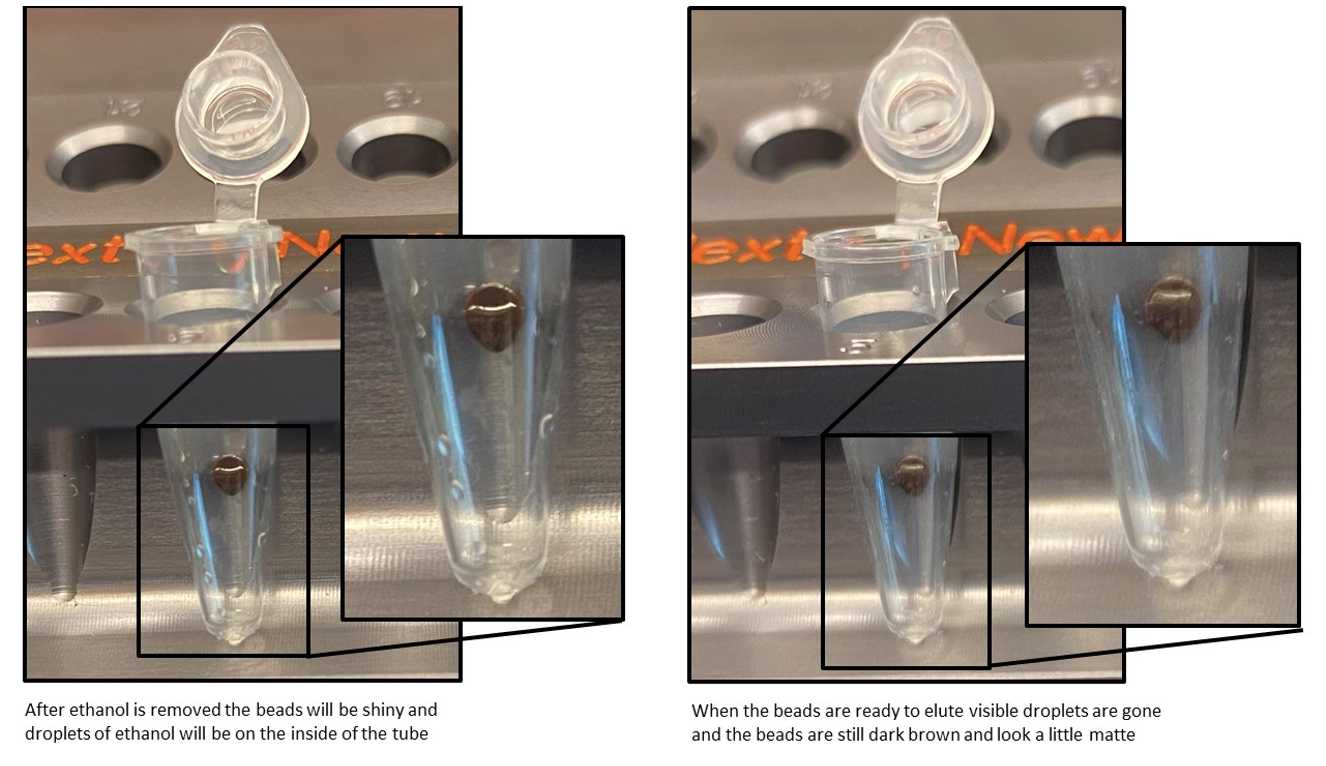

Remove the tubes from the magnetic stand. Elute the DNA target from the beads by adding 21µL For long terms storage use, 21 µl of 1XTE (10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0), Low TE (10 mM Tris, 0.2 mM EDTA, pH 8.0) or 0.1XTE (1 mM Tris, 0.1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0).
Mix well by pipetting up and down 10 times. Incubate for at least 0h 1m 0s at Room temperature. If necessary, quickly spin the sample to collect the liquid from the sides of the tube before placing back on the magnetic stand.
Place the tube on the magnetic stand. After 0h 3m 0s (or whenever the solution is clear), transfer 20µL to a new PCR tube.